![[Oxford Nanopore Technologies]](https://github.com/ONT_logo.png)
Remora models predict methylation/modified base status separated from basecalling. The Remora repository is focused on the preparation of modified base training data and training modified base models. Some functionality for running Remora models and investigation of raw signal is also provided. For production modified base calling use Dorado. For recommended modified base downstream processing use modkit. For more advanced modified base data preparation from "randomers" see the Betta release community note and reach out to customer support to inquire about access (customer.support@nanoporetech.com).
Install from pypi:
pip install ont-remora
Install from github source for development:
git clone git@github.com:nanoporetech/remora.git pip install -e remora/[tests]
It is recommended that Remora be installed in a virtual environment.
For example python3 -m venv venv; source venv/bin/activate.
For GPU optimization using torch, ensure that a version of torch compatible with the system GPU/CUDA drivers is installed. Note that Remora does not attempt to resolve the correct version of torch. See the torch installation page for compatible drivers and installation instructions.
As an example to install Remora with CUDA 11.8 drivers the following command can be used:
pip install torch --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118 pip install ont-remora
See help for any Remora sub-command with the -h flag.
Remora models predict modified bases anchored to canonical basecalls or reference sequence from a nanopore read.
The Remora training/prediction input unit (referred to as a chunk) consists of:
- Section of normalized signal
- Canonical bases attributed to the section of signal
- Mapping between these two
Chunks have a fixed signal length defined at data preparation/model training time. These values are saved with the Remora model to extract chunks in the same manner at inference. A fixed position within the chunk is defined as the "focus position" around which the fixed signal chunk is extracted. By default, this position is the center of the "focus base" being interrogated by the model.
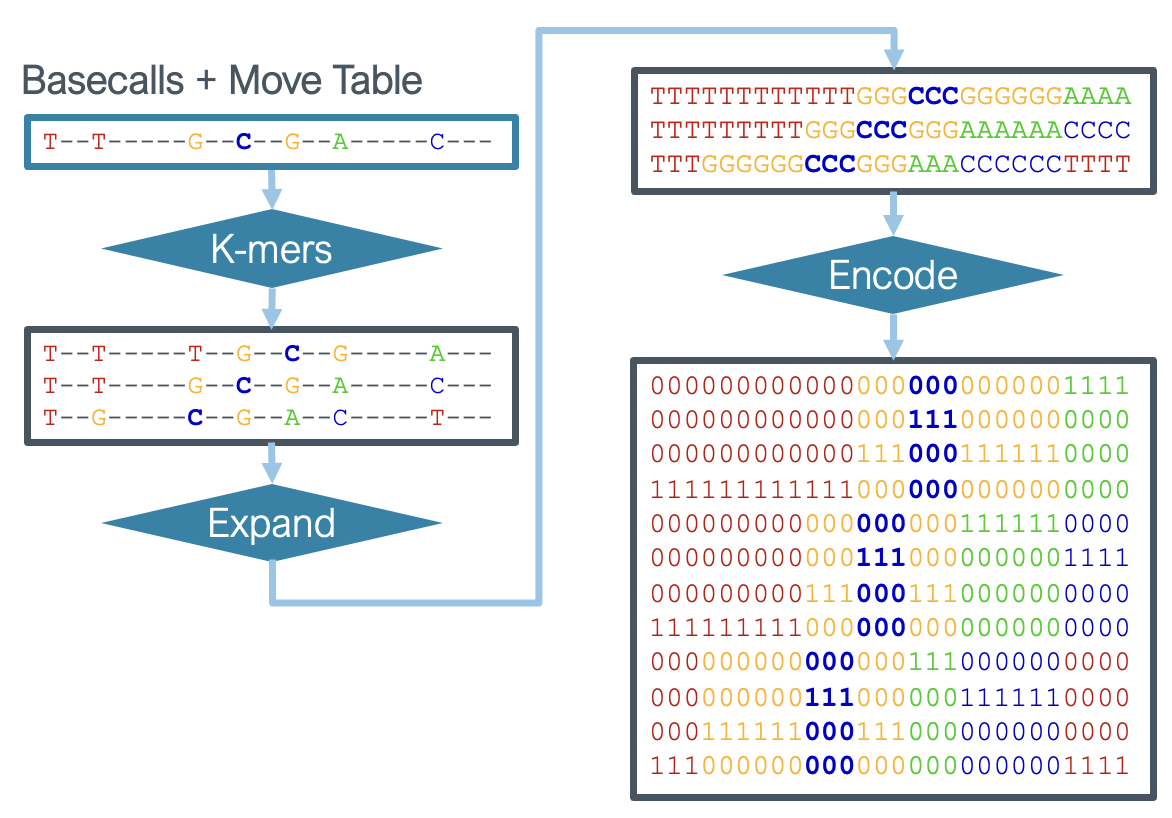
The canonical bases and mapping to signal (a.k.a. "move table") are combined for input into the neural network in several steps.
First each base is expanded to the k-mer surrounding that base (as defined by the --kmer-context-bases hyper-parameter).
Then each k-mer is expanded according to the move table.
Finally each k-mer is one-hot encoded for input into the neural network.
This procedure is depicted in the figure below.
Remora data preparation begins from a POD5 file containing signal data and a BAM file containing basecalls from the POD5 file.
Note that the BAM file must contain the move table (--emit-moves in Dorado) and the MD tag (default in Dorado with mapping and --MD argument for minimap2).
If using minimap2 for alignment use samtools fastq -T "*" [in.bam] | minimap2 -y -ax lr:hq [ref.fa] - | samtools view -b -o [out.bam] in order to transfer the move table tags through the alignment step since minimap2 does not support SAM/BAM input.
The following example generates training data from canonical (PCR) and modified (M.SssI treatment) samples in the same fashion as the released 5mC CG-context models.
Example reads can be found in the Remora repository (see test/data/ directory).
K-mer tables for applicable conditions can be found in the kmer_models repository.
remora \
dataset prepare \
can_reads.pod5 \
can_mappings.bam \
--output-path can_chunks \
--refine-kmer-level-table levels.txt \
--refine-rough-rescale \
--motif CG 0 \
--mod-base-control
remora \
dataset prepare \
mod_reads.pod5 \
mod_mappings.bam \
--output-path mod_chunks \
--refine-kmer-level-table levels.txt \
--refine-rough-rescale \
--motif CG 0 \
--mod-base m 5mCThe above commands each produce a core Remora dataset stored in the directory defined by --output-path.
Core datasets contain memory mapped numpy files for each core array (chunk data) and a JSON format metadata config file.
These memory mapped files allow efficient access to very large datasets.
Before Remora, 3.0 datasets were stored as numpy array dictionaries.
Updating datasets can be accomplished with the scripts/update_dataset.py script included in the repository.
Core datasets (or other composed datasets) can be composed to produce a new dataset.
The remora dataset make_config command creates these config files specifying the composition of the new dataset.
When reading batches from these combined datasets, the default behavior will be to draw chunks randomly from the entire set of chunks.
This setting is useful for multiple flowcells of the same condition.
The --dataset-weights argument produces a config which generates batches with a fixed proportion of chunks from each input dataset.
This setting is useful when combining different data types, for example control and modified datasets.
The remora dataset merge command is supplied to merge datasets, copying the data into a new core Remora dataset.
This may increase efficiency of data access for datasets composed of many core datasets, but only supports the default behavior from the make_config command (sampling over all chunks).
The remora dataset copy command is provided in order to move datasets to a new location.
This can be useful when handling config datasets composed of many core datasets.
Copying a dataset is especially useful to achieve higher training speeds when core datasets are stored on a network file system (NFS).
Composed dataset config files can also be specified manually.
Config files are JSON format files containing a single list.
Each element in the list represents one dataset.
Datasets must specify the path to the core dataset (or another config) and the weight of this sub-dataset.
Optionally the dataset hash and a filter file may be included for each dataest.
These values may be specified via a list (ordered: path, weight, hash, filter), or via a dictionary (keys: path, weight, hash, filter).
The make_config output config file will contain the dataset hash to ensure the contents of a dataset are unchanged whe reading.
See the remora dataset make_filter command for more details on filters.
Metadata attributes from each core dataset are checked for compatibility and merged where applicable. Chunk raw data are loaded from each core dataset at specified proportions to construct batches at loading time. In a break from Remora <3.0, datasets allow "infinite iteration", where each core dataset is drawn from indefinitely and independently to supply training chunks. For validation from a fixed set of chunks, finite iteration is also supported.
To generate a dataset config from the datasets created above one can use the following command.
remora \
dataset make_config \
train_dataset.jsn \
can_chunks \
mod_chunks \
--dataset-weights 1 1 \
--log-filename train_dataset.logModels are trained with the remora model train command.
For example a model can be trained with the following command.
remora \
model train \
train_dataset.jsn \
--model remora/models/ConvLSTM_w_ref.py \
--device 0 \
--chunk-context 50 50 \
--output-path train_resultsThis command will produce a "best" model in torchscript format for use in Bonito, remora infer, or remora validate commands.
Models can be exported for use in Dorado with the remora model export train_results/model_best.pt train_results_dorado_model command.
For testing purposes, inference within Remora is provided. For standard model architectures and inference methods, using the exported Dorado model during basecalling is recommended.
remora \
infer from_pod5_and_bam \
can_signal.pod5 \
can_mappings.bam \
--model train_results/model_best.pt \
--out-file can_infer.bam \
--log-filename can_infer.log \
--device 0
remora \
infer from_pod5_and_bam \
mod_signal.pod5 \
mod_mappings.bam \
--model train_results/model_best.pt \
--out-file mod_infer.bam \
--log-filename mod_infer.log \
--device 0The remora validate from_modbams command is deprecated and will be removed in a future version of Remora.
The modkit validate command is now recommended for this purpose.
Reference-anchored inference allows users to make per-read per-site modified base calls against the reference sequence to which a read is mapped.
This is in contrast to standard Remora model inference where calls are made against the basecalls.
This mode can be useful to explore modified bases around which the canonical basecaller does not perform well.
This inference mode is toggled by the --reference-anchored argument to the remora infer from_pod5_and_bam command.
The output BAM file from this command will take each mapped read and replace the basecalls with the mapped reference bases. The move table will be transferred to the mapped reference bases and interpolated over mapping reference deletions in order to make enable extraction of Remora chunks for inference.
Note that this means that the canonical basecalls will show 0 errors over the entire output BAM file. The intended purpose of this output is only to store the modified base status for each read at each applicable base. Any analysis of basecall metrics should not use the output of this command.
See the selection of current released models with remora model list_pretrained.
Pre-trained models are stored remotely and can be downloaded using the remora model download command or will be downloaded on demand when needed.
Models may be run from Bonito. See Bonito documentation to apply Remora models.
More advanced research models may be supplied via Rerio. These files require download from Rerio and then the path to this download must be provided to Remora. Note that older ONNX format models require Remora version < 2.0.
Downloaded or trained models can be inspected with the remora model inspect command to view the metadata attributes of the model.
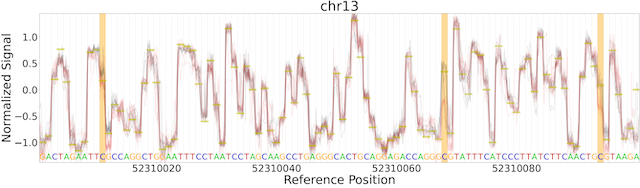
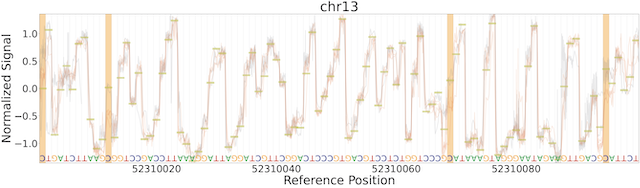
Raw signal plotting is available via the remora analyze plot ref_region command.
The plot ref_region command is useful for gaining intuition into signal attributes and visualize signal shifts around modified bases.
As an example using the test data, the following command produces the plots below.
Note that only a single POD5 file per sample is allowed as input and that the BAM records must contain the mv and MD tags (see the see "Data Preparation" section above for details).
remora \
analyze plot ref_region \
--pod5-and-bam can_reads.pod5 can_mappings.bam \
--pod5-and-bam mod_reads.pod5 mod_mappings.bam \
--ref-regions ref_regions.bed \
--highlight-ranges mod_gt.bed \
--refine-kmer-level-table levels.txt \
--refine-rough-rescale \
--log-filename log.txtThe Remora API to access, manipulate and visualize nanopore reads including signal, basecalls, and reference mapping is described in more detail in the notebooks section of this repository.
This is a research release provided under the terms of the Oxford Nanopore Technologies' Public Licence. Research releases are provided as technology demonstrators to provide early access to features or stimulate Community development of tools. Support for this software will be minimal and is only provided directly by the developers. Feature requests, improvements, and discussions are welcome and can be implemented by forking and pull requests. Much as we would like to rectify every issue, the developers may have limited resource for support of this software. Research releases may be unstable and subject to rapid change by Oxford Nanopore Technologies.
© 2021-2024 Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ltd. Remora is distributed under the terms of the Oxford Nanopore Technologies' Public Licence.
Research releases are provided as technology demonstrators to provide early access to features or stimulate Community development of tools. Support for this software will be minimal and is only provided directly by the developers. Feature requests, improvements, and discussions are welcome and can be implemented by forking and pull requests. However much as we would like to rectify every issue and piece of feedback users may have, the developers may have limited resource for support of this software. Research releases may be unstable and subject to rapid iteration by Oxford Nanopore Technologies.