JWT Middleware for Gin Framework
This is a middleware for Gin framework.
It uses jwt-go to provide a jwt authentication middleware. It provides additional handler functions to provide the login api that will generate the token and an additional refresh handler that can be used to refresh tokens.
Usage
Download and install it:
$ go get github.com/appleboy/gin-jwt/v2Import it in your code:
import "github.com/appleboy/gin-jwt/v2"Example
Please see the example file and you can use ExtractClaims to fetch user data.
package main
import (
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
"github.com/appleboy/gin-jwt/v2"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
type login struct {
Username string `form:"username" json:"username" binding:"required"`
Password string `form:"password" json:"password" binding:"required"`
}
var identityKey = "id"
func helloHandler(c *gin.Context) {
claims := jwt.ExtractClaims(c)
user, _ := c.Get(identityKey)
c.JSON(200, gin.H{
"userID": claims["id"],
"userName": user.(*User).UserName,
"text": "Hello World.",
})
}
// User demo
type User struct {
UserName string
FirstName string
LastName string
}
func main() {
port := os.Getenv("PORT")
r := gin.New()
r.Use(gin.Logger())
r.Use(gin.Recovery())
if port == "" {
port = "8000"
}
// the jwt middleware
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.GinJWTMiddleware{
Realm: "test zone",
Key: []byte("secret key"),
Timeout: time.Hour,
MaxRefresh: time.Hour,
IdentityKey: identityKey,
PayloadFunc: func(data interface{}) jwt.MapClaims {
if v, ok := data.(*User); ok {
return jwt.MapClaims{
identityKey: v.UserName,
}
}
return jwt.MapClaims{}
},
IdentityHandler: func(c *gin.Context) interface{} {
claims := jwt.ExtractClaims(c)
return &User{
UserName: claims["id"].(string),
}
},
Authenticator: func(c *gin.Context) (interface{}, error) {
var loginVals login
if err := c.ShouldBind(&loginVals); err != nil {
return "", jwt.ErrMissingLoginValues
}
userID := loginVals.Username
password := loginVals.Password
if (userID == "admin" && password == "admin") || (userID == "test" && password == "test") {
return &User{
UserName: userID,
LastName: "Bo-Yi",
FirstName: "Wu",
}, nil
}
return nil, jwt.ErrFailedAuthentication
},
Authorizator: func(data interface{}, c *gin.Context) bool {
if v, ok := data.(*User); ok && v.UserName == "admin" {
return true
}
return false
},
Unauthorized: func(c *gin.Context, code int, message string) {
c.JSON(code, gin.H{
"code": code,
"message": message,
})
},
// TokenLookup is a string in the form of "<source>:<name>" that is used
// to extract token from the request.
// Optional. Default value "header:Authorization".
// Possible values:
// - "header:<name>"
// - "query:<name>"
// - "cookie:<name>"
// - "param:<name>"
TokenLookup: "header: Authorization, query: token, cookie: jwt",
// TokenLookup: "query:token",
// TokenLookup: "cookie:token",
// TokenHeadName is a string in the header. Default value is "Bearer"
TokenHeadName: "Bearer",
// TimeFunc provides the current time. You can override it to use another time value. This is useful for testing or if your server uses a different time zone than your tokens.
TimeFunc: time.Now,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("JWT Error:" + err.Error())
}
r.POST("/login", authMiddleware.LoginHandler)
r.NoRoute(authMiddleware.MiddlewareFunc(), func(c *gin.Context) {
claims := jwt.ExtractClaims(c)
log.Printf("NoRoute claims: %#v\n", claims)
c.JSON(404, gin.H{"code": "PAGE_NOT_FOUND", "message": "Page not found"})
})
auth := r.Group("/auth")
// Refresh time can be longer than token timeout
auth.GET("/refresh_token", authMiddleware.RefreshHandler)
auth.Use(authMiddleware.MiddlewareFunc())
{
auth.GET("/hello", helloHandler)
}
if err := http.ListenAndServe(":"+port, r); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}Demo
Please run example/server.go file and listen 8000 port.
$ go run example/server.goDownload and install httpie CLI HTTP client.
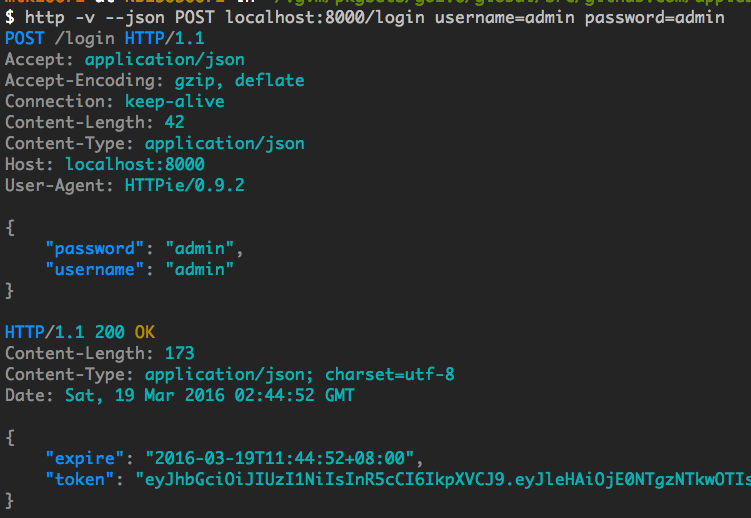
Login API:
$ http -v --json POST localhost:8000/login username=admin password=adminOutput screenshot
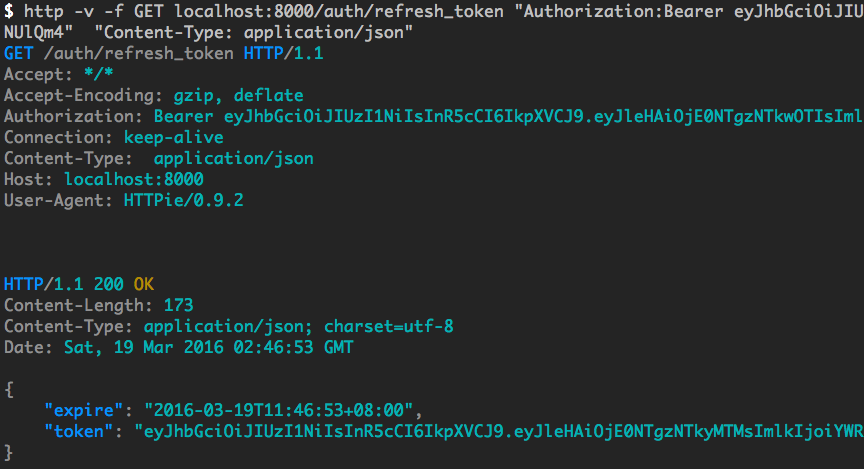
Refresh token API:
$ http -v -f GET localhost:8000/auth/refresh_token "Authorization:Bearer xxxxxxxxx" "Content-Type: application/json"Output screenshot
Hello world
Please login as admin and password as admin
$ http -f GET localhost:8000/auth/hello "Authorization:Bearer xxxxxxxxx" "Content-Type: application/json"Response message 200 OK:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 24
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Date: Sat, 19 Mar 2016 03:02:57 GMT
{
"text": "Hello World.",
"userID": "admin"
}
Authorization
Please login as test and password as test
$ http -f GET localhost:8000/auth/hello "Authorization:Bearer xxxxxxxxx" "Content-Type: application/json"Response message 403 Forbidden:
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
Content-Length: 62
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Date: Sat, 19 Mar 2016 03:05:40 GMT
Www-Authenticate: JWT realm=test zone
{
"code": 403,
"message": "You don't have permission to access."
}
Cookie Token
Use these options for setting the JWT in a cookie. See the Mozilla documentation for more information on these options.
SendCookie: true,
SecureCookie: false, //non HTTPS dev environments
CookieHTTPOnly: true, // JS can't modify
CookieDomain: "localhost:8080",
CookieName: "token", // default jwt
TokenLookup: "cookie:token",Login Flow
- Authenticator: handles the login logic. On success LoginResponse is called, on failure Unauthorized is called.
- LoginResponse: optional, allows setting a custom response such as a redirect.
JWT Flow
- PayloadFunc: maps the claims in the JWT.
- IdentityHandler: extracts identity from claims.
- Authorizator: receives identity and handles authorization logic.
- Unauthorized: handles unauthorized logic.