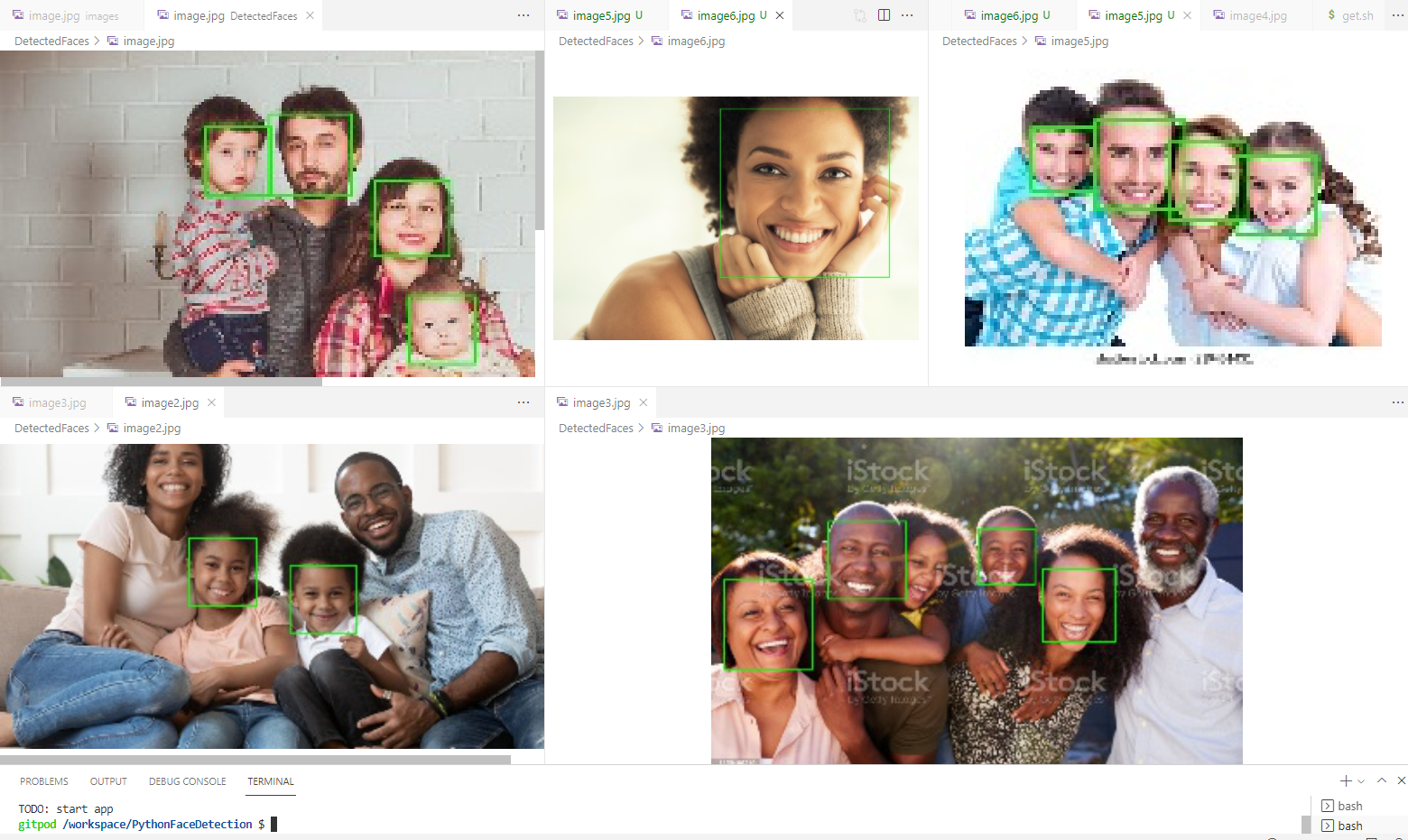
Face detection is a computer vision technology that detects whether a face is present or not in an image. This is different from both facial recognition, which identifies a face (i.e. to unlock your phone) and facial analyses which makes an inferences about a detected face (i.e. this face is happy).
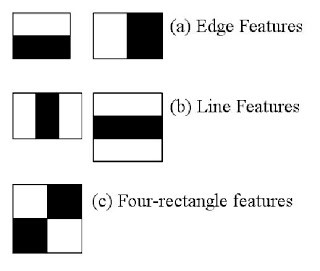
An image is composed of pixels which are in turn made up of bits, the same way sentences are made up of words and words are made up of letters. An image also contains features - pixels, edges, corners, and shapes. Haar-like features are rectangular regions in specific areas of an image.
Haar-like features are the base of the detection algorithm used in this project - the Viola-Jones algorithm. It scans an image looking for visual clues as to whether a face is present or not. The algorithm functions in four main steps :
-
It selects Haar-like features, detecting where lines and edges are in an image that may indicate for example where a nose or a mouth is.
-
It transforms the original image to create an
integral image- a numerical representation of the original image. This helps speed up the process of summing up all the pixels in an image to calculate the Haar-like features. Each pixel's value is the sum of all the pixels above it and to the left. (This reminds me of all the dynamic programming exercises I've done this semester.) -
It runs AdaBoost training, an algorithm that boosts the performance of the base algorithm. In this step, classifiers are created to detect pieces of what might make up a face. Strong classifiers are made up of the very best weak classifiers found in the image.
-
Classifier cascades made up of strong classifiers are used to search subregions of an image. If a weak classifier is not present in a subregion of the image, the algorithm skips the rest of that subregion. For example, if there are no eyes, the face likely doesn't exist here so skip this section. If all the weak classifiers exist here, there is likely a face here and we've found it!
Sources
- Traditional Face Detection With Python course from Real Python
- Miniconda for Anaconda on Gitpod workspace