Turbo Logger is a library for instrumenting your web apps to log messages to a server. What can you do with that?
- Analyze user actions (sign in, sign out, button clicks, page navigations, etc.)
- Monitor API calls and response times
- Diagnose uncaught exceptions
Turbo Logger itself is a TypeScript library that is agnostic of the front-end framework. We have given an example of integrating it with React.
- 5 log levels: trace, debug, info, warn, error
- Typesafe data structures using TypeScript discriminating unions
- Batch uploads for efficient network and server usage
- Integrations:
- react-router: to log page views
- react-error-boundary: to log uncaught errors in the React component tree. A fallback dialog is provided to alert the user and retry the operation.
- useErrorBoundary API: to catch errors for event handlers and asynchronous code, because error boundaries in React do not catch these errors (this hook is provided by React Query )
- clientjs: to provide device fingerprints in the logs
Following Log types are available out of the box:
- ApiCallLog: call to an API
- MessageLog: a general message
- PageViewLog: navigation to a new page
- SignInErrorLog: failed sign-in attempt
- SignInLog: successful sign-in
- SignOutLog: sign out
- UiElementEventLog: event produced by a UI element
- UncaughtErrorLog: uncaught error
For further details, see Log.ts and the Logger API.
[
{
"timestamp": "2022-09-01T22:26:36.265Z",
"level": "info",
"appId": "turbo-logger-demo",
"sessionId": "591c2c8c-cf12-493c-817c-577a670db417",
"environment": "development",
"userId": "unknown",
"fingerprint": {
"browser": "Chrome",
"browserVersion": "104.0.0.0",
"os": "Mac OS",
"osVersion": "10.15.7",
"screenResolution": "2560x1440",
"timezone": "-04",
"language": "en-US"
},
"type": "UiElementEvent",
"event": "blur",
"container": "SignInPage",
"elementType": "input",
"elementId": "password"
},
{
"timestamp": "2022-09-01T22:26:36.382Z",
"level": "info",
"appId": "turbo-logger-demo",
"sessionId": "591c2c8c-cf12-493c-817c-577a670db417",
"environment": "development",
"userId": "demo",
"fingerprint": {
"browser": "Chrome",
"browserVersion": "104.0.0.0",
"os": "Mac OS",
"osVersion": "10.15.7",
"screenResolution": "2560x1440",
"timezone": "-04",
"language": "en-US"
},
"type": "SignIn"
},
{
"timestamp": "2022-09-01T22:26:36.394Z",
"level": "info",
"appId": "turbo-logger-demo",
"sessionId": "591c2c8c-cf12-493c-817c-577a670db417",
"environment": "development",
"userId": "demo",
"fingerprint": {
"browser": "Chrome",
"browserVersion": "104.0.0.0",
"os": "Mac OS",
"osVersion": "10.15.7",
"screenResolution": "2560x1440",
"timezone": "-04",
"language": "en-US"
},
"type": "PageView",
"pathname": "/demo",
"url": "http://localhost:3000/demo"
},
{
"timestamp": "2022-09-01T22:26:36.439Z",
"level": "info",
"appId": "turbo-logger-demo",
"sessionId": "591c2c8c-cf12-493c-817c-577a670db417",
"environment": "development",
"userId": "demo",
"fingerprint": {
"browser": "Chrome",
"browserVersion": "104.0.0.0",
"os": "Mac OS",
"osVersion": "10.15.7",
"screenResolution": "2560x1440",
"timezone": "-04",
"language": "en-US"
},
"type": "ApiCall",
"url": "http://localhost:8000/top-10-movies",
"method": "get",
"startTime": "2022-09-01T22:26:36.394Z",
"endTime": "2022-09-01T22:26:36.438Z",
"durationMillis": 44,
"status": 200,
"statusText": "OK"
}
]Logger is a simple module that collects logs in an internal buffer. To push a log to the buffer, you must call one of the five logging methods:
- Logger.trace()
- Logger.debug()
- Logger.info()
- Logger.warn()
- Logger.error()
You must periodically retrieve the logs collected in the buffer and clear it.
These two operations are performed using a single call to
Logger.clearLogBuffer(). It is your responsibility to then transmit the
retrieved logs to a server using your favorite API (e.g. fetch, axios or
GraphQL). Here's an example of how to do this using axios:
/** Sends all the buffered logs to the server */
async function flush() {
const logBuffer = Logger.clearLogBuffer();
if (logBuffer.length === 0) {
return;
}
try {
// Transmit the log buffer
const resp = await axiosInstance.post('/', logBuffer);
return resp.data;
} catch (e) {
console.log('Error sending logs');
}
}# Run ci in the root directory to install dependencies
npm ci
# Run a full build to make sure everything is set up correctly
npm run build
# Run the demo app
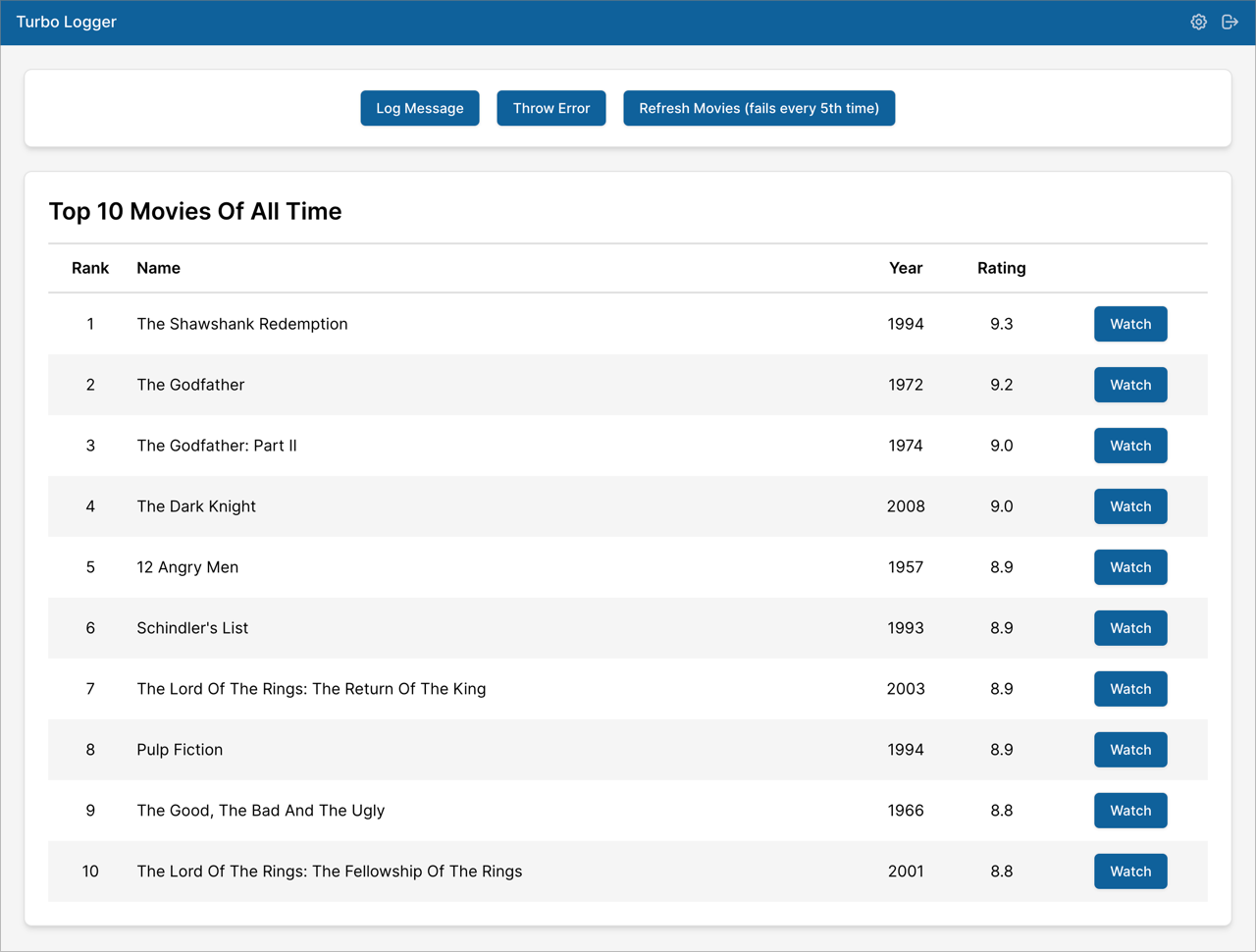
npm run dev- Now point your browser to http://localhost:3000/. You will see the demo app as shown below.
- Open the Chrome debugger
- Try out the suggested operations to see the logs in the chrome debugger.
Note: Do not run
npm installornpm ciin any of the subdirectories. It will break the build. There should be only onepackage-lock.jsonfile in the entire repo (at the root).
npm install @turboutils/logger
Create a LoggerService in your app, similar to the
LoggerService in the
turbo-logger-demo app. The basic function of this service is to flush the logs
periodically to a log server. In this example, we flush the logs every 5
seconds.
Note that the initialization code sets the appId, the sessionId and the
environment. In addition, it sets up axios interceptors to log any API calls
made through axios.
function init() {
Logger.setAppId(appId);
Logger.setSessionId(sessionId);
Logger.setEnvironment(environment);
setupInterceptors(axios);
// Set interval to flush logs
window.setInterval(async () => {
await flush();
}, flushInterval);
}Also note that the LoggerService sets up a separate axiosInstance to
transmits the logs. This avoids any interference between the application API
calls and the logger API calls.
Initialize the LoggerService as soon as your application starts. See example
here.
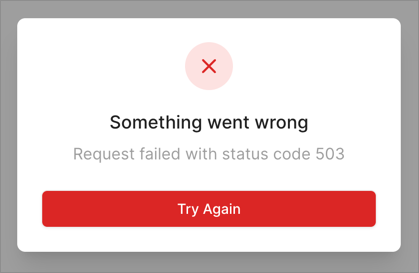
Add an ErrorBoundary at the top of your component tree and use it to show and
log uncaught errors. See an example
here. A sample
ErrorFallbackComponent is provided
here
and looks like this:
If you are using React Query to make API
calls, make sure that you initialize it using the useErrorBoundary option (see
here). This allows React Query to
leverage the ErrorBoundary when an exception happens.
If you use React Router, instrument it to log page
navigations. Use the usePageViewLog hook as shown
here.
Find suitable spots in your application to inject sign in, sign out and unsuccessful sign in logs. See examples here and here.
Capture key user interactions, like button clicks or selection changes. You can see an example here. For a full list of events refer to the Log data structure.