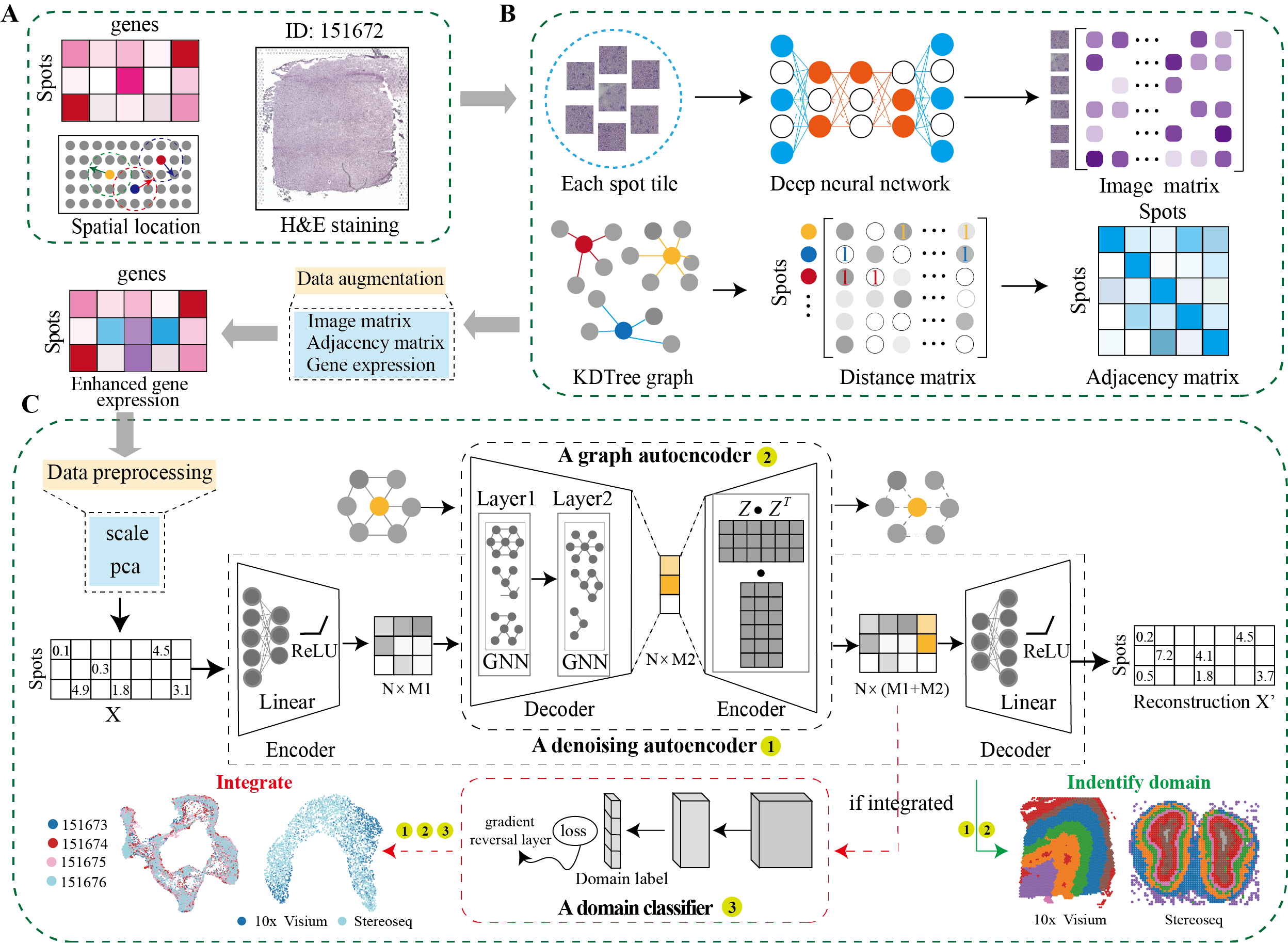
DeepST first uses H&E staining to extract tissue morphology information through a pre-trained deep learning model, and normalizes each spot’s gene expression according to the similarity of adjacent spots. DeepST further learns a spatial adjacency matrix on spatial location for the construction of graph convolutional network. DeepST uses a graph neural network autoencoder and a denoising autoencoder to jointly generate a latent representation of augmented ST data, while domain adversarial neural networks (DAN) are used to integrate ST data from multi-batches or different technologies. The output of DeepST can be applied to identify spatial domains, batch effect correction and downstream analysis.
We created the python package called DeepST that uses scanpy to streamline the integration of spatial transcriptomics datasets and
evaluate the results. DeepST is implemented in the open-source python using PyTorch and PyG libraries.
git clone https://github.com/spatial-Transcriptomics/DeepST.git
cd DeepST(Recommended) Using python virtual environment with conda
wget https://github.com/JiangBioLab/DeepST/archive/refs/heads/main.zip
unzip main.zip
cd /home/.../DeepST-main ### your own path
conda create -n deepst_env python=3.9
conda activate deepst_env
## step1 Installing PyTorch’s CUDA support or CPU support on Linux
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu116 #### GPU
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu #### CPU
## step2 Installing PyG package. If unsuccessful, refer to the "Install PyG package".
pip install pyg_lib torch_scatter torch_sparse torch_cluster torch_spline_conv torch_geometric -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.13.0+cu116.html #### GPU
pip install pyg_lib torch_scatter torch_sparse torch_cluster torch_spline_conv torch_geometric -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.13.0+cpu.html ### CPU
## step3 Download other dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt1. Install PyTorch package
-
Installation via Anaconda.
conda install pytorch torchvision torchaudio cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch-
Installation via Pip Wheels
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio2. Install PyG package
- Installation via Anaconda.
You can now install PyG via Anaconda for all major OS/PyTorch/CUDA combinations 🤗 Given that you have PyTorch >= 1.8.0 installed, simply run:
conda install pyg -c pyg -c conda-forge- Installation via Pip Wheels
We have outsourced a lot of functionality of PyG to other packages, which needs to be installed in advance. These packages come with their own CPU and GPU kernel implementations based on the PyTorch C++/CUDA extension interface. We provide pip wheels for these packages for all major OS/PyTorch/CUDA combinations:
pip install pyg -c pyg -c conda-forge1). Ensure that at least PyTorch 1.4.0 is installed:
python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)"
>>> 1.9.02). Find the CUDA version PyTorch was installed with:
python -c "import torch; print(torch.version.cuda)"
>>> 11.13). Install the relevant packages:
pip install torch-scatter -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-${TORCH}+${CUDA}.html
pip install torch-sparse -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-${TORCH}+${CUDA}.html
pip install torch-geometric
#### where ${CUDA} and ${TORCH} should be replaced by the specific CUDA version (cpu, cu92, cu101, cu102, cu110, cu111) and PyTorch version (1.4.0, 1.5.0, 1.6.0, 1.7.0, 1.7.1, 1.8.0, 1.8.1, 1.9.0, 1.9.1), respectively. For example, for PyTorch 1.9.0/1.9.1 and CUDA 11.1, type:
pip install torch-scatter -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.9.0+cu111.html
pip install torch-sparse -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.9.0+cu111.html
pip install torch-geometric
#### For PyTorch 1.8.0/1.8.1 and CUDA 10.2, type:
pip install torch-scatter -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.8.0+cu102.html
pip install torch-sparse -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.8.0+cu102.html
pip install torch-geometric4). Install additional packages (optional): To add additional functionality to PyG, such as k-NN and radius graph generation or SplineConv support, run
pip install torch-cluster -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-${TORCH}+${CUDA}.html
pip install torch-spline-conv -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-${TORCH}+${CUDA}.htmlDeepST is used on spatial transcriptomics (ST) datasets. In essence, you can refer to the following examples:
First, cd /home/.../DeepST-main/deepst
import os
from DeepST import run
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pathlib import Path
data_path = "../data/DLPFC" #### to your path
data_name = '151673' #### project name
save_path = "../Results" #### save path
n_domains = 7 ###### the number of spatial domains.
deepen = run(save_path = save_path,
platform = "Visium",
pca_n_comps = 200,
pre_epochs = 800, #### According to your own hardware, choose the number of training
epochs = 1000, #### According to your own hardware, choose the number of training
Conv_type="GCNConv", #### you can choose GNN types.
)
adata = deepen._get_adata(data_path, data_name)
adata = deepen._get_augment(adata, adjacent_weight = 0.3, neighbour_k = 4,)
graph_dict = deepen._get_graph(adata.obsm["spatial"], distType="BallTree", k=12)
adata = deepen._fit(adata, graph_dict, pretrain = True)
adata = deepen._get_cluster_data(adata, n_domains = n_domains, priori=True) ###### without using prior knowledge, setting priori = False.
######## spatial domains
deepen.plot_domains(adata, data_name)
######## UMAP
deepen.plot_umap(adata, data_name)
...import os
from DeepST import run
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pathlib import Path
data_path = "../data/DLPFC"
data_name_list = ['151673', '151674', '151675', '151676']
save_path = "../Results"
n_domains = 7
deepen = run(save_path = save_path,
pca_n_comps = 200,
pre_epochs = 800, #### According to your own hardware, choose the number of training
epochs = 1000, #### According to your own hardware, choose the number of training
platform = "Visium",
)
adata, graph_dict, domains = deepen._get_multiple_adata(data_path, data_name_list)
adata = deepen._fit(adata, graph_dict, domains, pretrain = True)
adata = deepen._get_cluster_data(adata, n_domains = n_domains, priori=True)
########
######## UMAP
deepen.plot_umap(adata, color=["DeepST_domain", "batch_name"], data_name_list)
...import os
from DeepST import run
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pathlib import Path
data_path = "../Datasets"
data_name = 'Stereoseq'
save_path = "../Results"
n_domains = 8
deepen = run(save_path = save_path,
platform = "stereoseq", ##### varous platforms
pca_n_comps = 200,
pre_epochs = 800,
pre_epochs = 1000,
)
adata, graph_dict, domains = deepen._get_single_adata(data_path, data_name, weights="weights_matrix_nomd") #### Augmentation without using morphological information
adata = deepen._fit(adata, graph_dict, pretrain = False)
adata = deepen._get_cluster_data(adata, n_domains = n_domains, priori=True)
######## spatial domains
deepen.plot_domains(adata, data_name)
######## UMAP
deepen.plot_umap(adata, data_name)
...Tools that are compared include:
| Platform | Tissue | SampleID |
|---|---|---|
| 10x Visium | Human dorsolateral pre-frontal cortex (DLPFC) | 151507, 151508, 151509, 151510, 151669, 151670, 151671, 151672, 151673, 151674, 151675, 151676 |
| 10x Visium | Mouse brain section | Coronal, Sagittal-Anterior, Sagittal-Posterior |
| 10x Visium | Human breast cancer | Invasive Ductal Carcinoma breast, Ductal Carcinoma In Situ & Invasive Carcinoma |
| Stereo-Seq | Mouse olfactory bulb | Olfactory bulb |
| Slide-seq | Mouse hippocampus | Coronal |
| MERFISH | Mouse brain slice | Hypothalamic preoptic region |
Spatial transcriptomics data of other platforms can be downloaded https://www.spatialomics.org/SpatialDB/
Feel free to submit an issue or contact us at xuchang0214@163.com for problems about the packages.