DLRover makes the distributed training of large AI models easy, stable, fast and green. It can automatically train the Deep Learning model on the distributed cluster. It helps model developers to focus on model arichtecture, without taking care of any engineering stuff, say, hardware acceleration, distributed running, etc. Now, it provides automated operation and maintenance for deep learning training jobs on K8s/Ray. Major features as
- Fault-Tolerance, single node failover without restarting the entire job.
- Auto-Scaling, Automatically scale up/down resources at both node level and CPU/memory level.
- Dynamic data sharding, dynamic dispatch training data to each worker instead of dividing equally, faster worker more data.
- Automatic Resource Optimization, Automatically optimize the job resource to improve the training performance and resources utilization.
- [2023/11] ATorch supporting efficient and easy-to-use model training is released.
- [2023/10] AGD: an Auto-switchable Optimizer using Stepwise Gradient Difference as Preconditioning Matrix, NeurIPS 2023.
- [2023/09] Weighted Sharpness-Aware Minimization (WSAM) has been accepted by KDD'23.
- [2023/08] DLRover improves the stability of pre-trained model training over thousands of GPUs.
- [2023/04] DLRover auto-scales nodes of a DeepRec distributed training job.
DLRover can restore the training when the process fails without stopping the training job. The actions to restore training in DLRover are:
- Diagnose the failure reason.
- Restart the process not the node due to software errors.
- Restart the failed nodes due to hardward errors.
For detail, we can see experiments of fault-tolerance and elasticity.
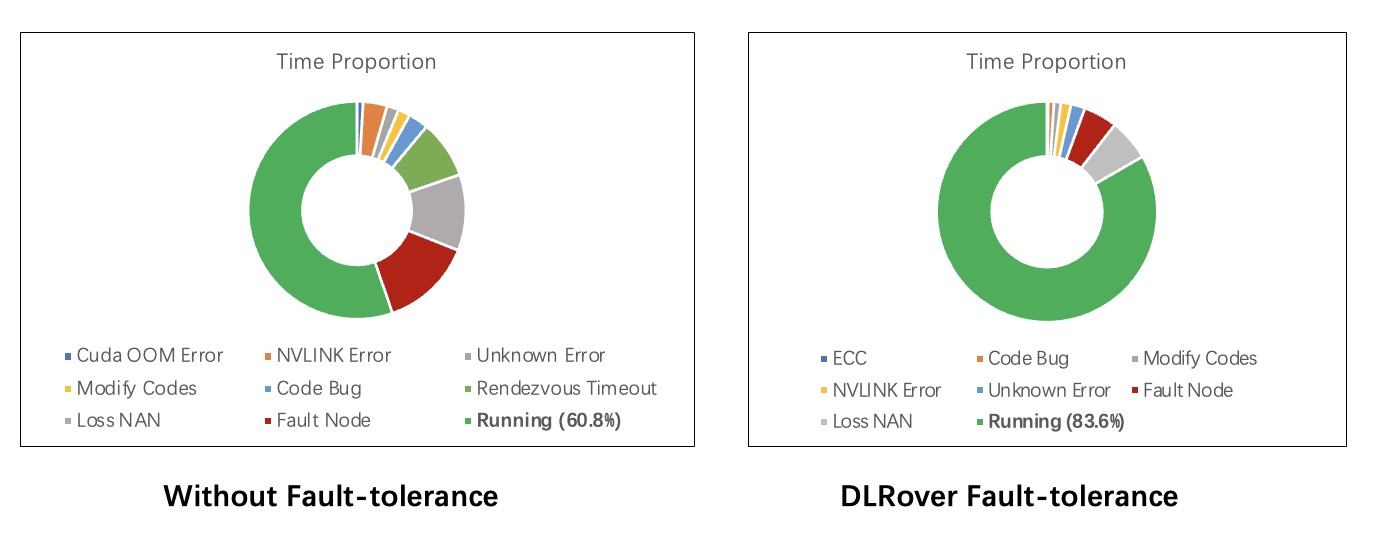
DLRover supports fault tolerance of the process failure and the node failure to restore trainig. Compared with restarting a new job, DLRover can reduce the overhead to schedule all Pods, pull image and install packages on all nodes.
| Step to restore training | Failure without DLRover | Node failure with DLRover | Process failure with DLRover |
|---|---|---|---|
| Restore action | Restart Job | Restart failed nodes | Restart training process |
| Schedule node, pull image and install packages | All nodes | Only new nodes | No |
| Node health check | No | All nodes execute a simple allgtather task | All nodes execute a allgtather simple task |
| Start training process | Yes | Yes | Yes |
DLRover can recover failed parameter servers and workers to resume training. Compared with manual restarting jobs, DLRover can reduce the overhead to restore the training.
| Step to restore training | Failure without DLRover | PS failure with DLRover | Worker failure with DLRover |
|---|---|---|---|
| Restore action | Restart Job | Restart failed PS | Restart failed workers |
| Schedule node, pull image and install packages | All nodes | Only new PS | Only new workers |
| Start session | all nodes | all nodes | Only new workers |
| Initialize Graph | Yes | Yes | Only new workers |
| Restore checkpoint | Yes | Yes | No |
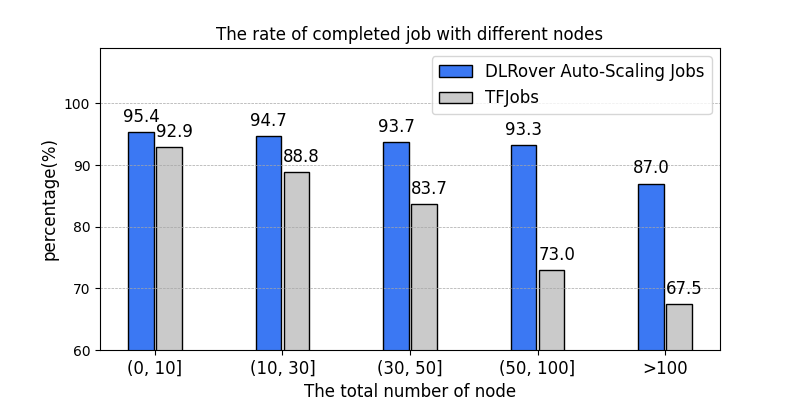
What's more, DLRover also can automatic diagnose the reason of failure. For example, the OOM is the common error due to user's insufficient memory configuration. DLRover can automatically launch a Pod with more memory to recover the OOM node. In AntGroup, DLRover manages hundreds of DL training jobs every day on the customized Kubernetes cluster in AntGroup. Except for the failed job resulting from code errors, the rate of completed jobs raise 89% with tf-operator in KubeFlow to 95%. Other unrecoverable failure reasons of a job are data error, NaN loss of the model, network breakdown, and so on.
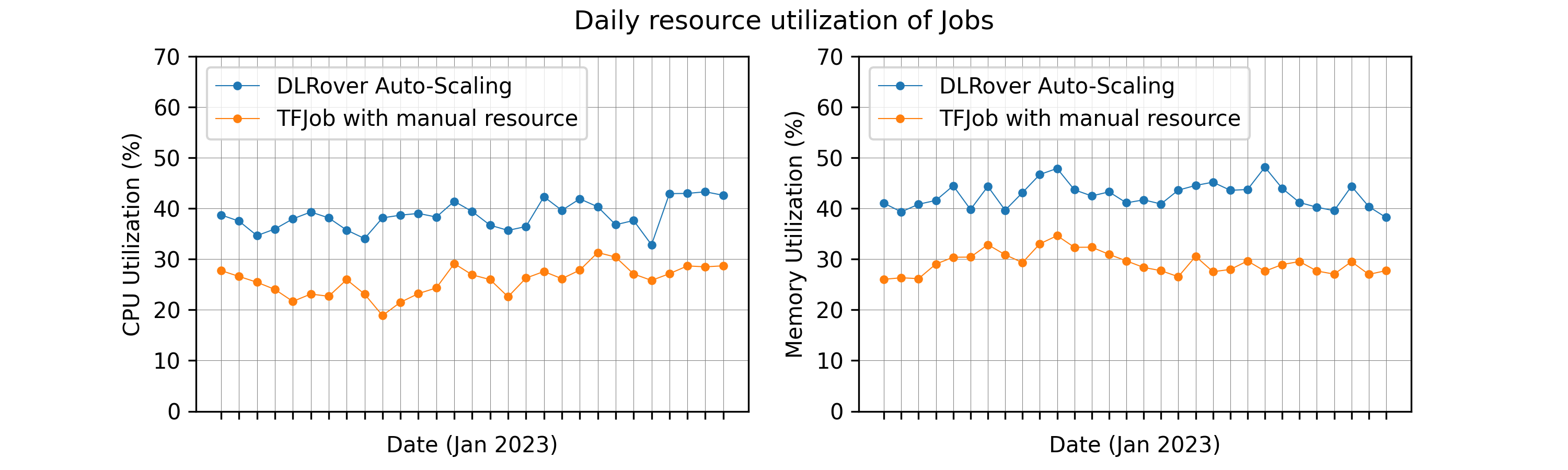
DLRover automatically scales up/down resources (for parameter servers or workers) at the runtime of a training job. By monitoring the workload of nodes and throughput, DLRover can diagnose the bottleneck of the resource configuration. The common bottleneck contains node straggler, the unbalanced workload of PS, insufficient CPU cores of nodes, and the insufficient number of nodes. DLRover can improve the training performance by dynamic resource adjustment.
In order to improve the training througphput, users prefer to configure their jobs with over-provision resources to avoid any potential risk from insufficient resources. This usually ends up in huge resource waste. DLRover Auto-Scaling can allocate resources by the demand of model training to reduce the waste of resources.
Dynamic data sharding splits the dataset into many small shards and each shard only contains a few batches of training samples. The worker will get a shard only when it using up samples of the last one. With the dynaic sharding, DLRover can
- recover the shard if the worker fails before using up samples of the shard.
- mitigate the worker straggler by assigning more shards to the fast worker.
With the data source transparency provided by dynamic data sharding, DLRover can be integrated with offline training which consumes batch data, and also supports online learning with real-time streaming data. (fed with a message queue like RocketMQ/Kafka/Pulsar/..., or executed as a training sink node inside Flink/Spark/Ray/...)
By practice, DLRover is an ideal component to build an end-to-end industrial online learning system,
estimator.md provides a detailed example implemented with tf.estimator.Estimator.
We can use dlrover-run to run the training script which
torchrun or torch.distributed.run can run.
We run DLRover locally like
pip install dlrover[torch]
dlrover-run --standalone --nproc_per_node=$NUM_TRAINERS train_scripts.pyFirstly, the user need to deploy the DLRover elasticjob controller in a kubernetes
cluster by followding the tutorial. Then, we need
to install dlrover[torch] and execute dlrover-run in
the command of the Pod container like the example torch_mnist_job.yaml.
pip install dlrover[torch] && \
dlrover-run --network-check --nnodes=$NODE_NUM --nproc_per_node=$NUM_TRAINERS train_scripts.py--nnodes is the number of nodes and --nproc_per_node is the number of process
on each node. They are the same as the arguments of torchrun.
We can also use dlrover-run in other k8s jobs like kubeflow/PyTorchJob.
We need to set the NODE_RANK and DLROVER_MASTER_ADDR before dlrover-run.
For example, the PyTorchJob has set the RANK, MASTER_ADDR and MASTER_PORT
into environments. We can run dlrover-run like
NODE_RANK=$RANK DLROVER_MASTER_ADDR=$MASTER_ADDR:$MASTER_PORT \
dlrover-run --standalone --network-check --nnodes=$NODE_NUM --nproc_per_node=$NUM_TRAINERS train_script.pyNote:
-
dlrover-runextendstorchrunwhich dynamically configuresMASTER_ADDRandMASTER_PORTfor training processes. We can use the staticMASTER_ADDRandMASTER_PORTof PyTorchJob as the address of DLRover job master. -
The elastic scheduling of DLRover to restore or scale up/down Pods is not enabled without DLRover ElasticJob.
We can use DLRover to train a TensorFlow by the following steps:
- Use TensorFlow estimator to develop the TensorFlow model.
- Define the input of
tf.datasetin a training configuration of DLRover. - Define your reader to read samples from the dataset file.
We can refer to the estimator.md to train a model with DLRover.
- Aysnchronously save the checkpoint to the storage.
- Significantly reduce checkpoint saving/restore time which blocks training.
- Save the checkpoint from the CPU memory even if the training process fails.
- Fine-grained automatic distributed training for GPU Synchronous jobs
- hybrid-parallel mode
- adapted hyper parameters adjustment with dynamic resources
- more strategies for Fine-grained scenarioes
- Full stack solution for Online Deep Learning
- High performance extension library for Tensorflow/Pytorch to speed up training
- ...
Please refer to the DEVELOPMENT
Train a TensorFlow Estimator on Kubernetes
Train a PyTorch Model on Kubernetes