This project is a kind of Micro CPU architecture did during Digital Systems discipline in Logisim ITA, consisting in a very simple architecture to do basic arithmetic operations as it's loaded by a specific memory file (whereas some samples were provided in this repository files). It was made for educational pourposes at ICMC-USP to understand precisely some of the basic concepts about computer architecture, such as flip-flops, registers, counter and how a ROM memory works in practice.
The entire project was made by Natan Sanches, Marcos Almeida Patrício Nogueira and João Guilherme Jarochinski Marinho for Digital Systems class.
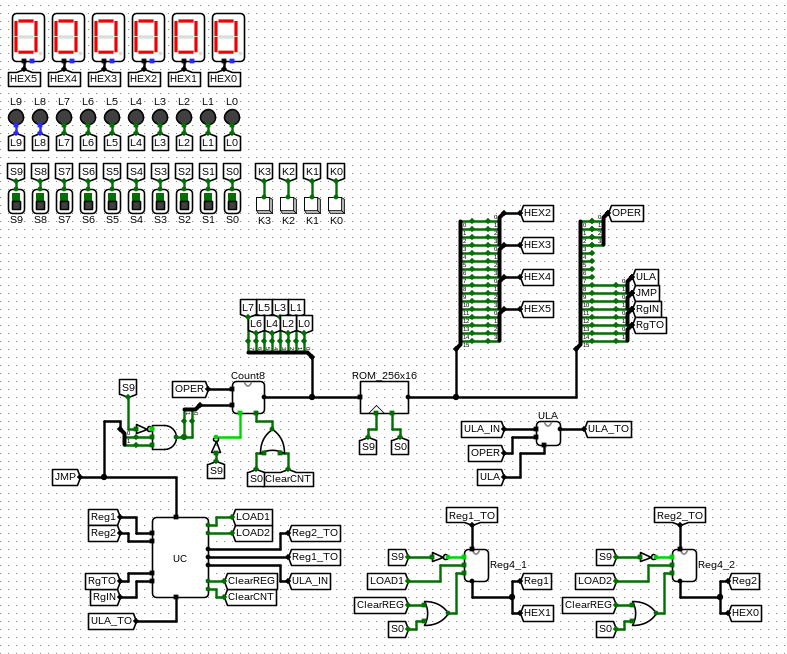
The arithmetic logic unit was built to operate with 4 bits size numbers, where the circuit's entire logic is based from a sequence of 16 bits inside its memory file. It's interesting that the counter (which controls the memory addresses accesses sequentially) was made with an extension to jump to a specific memory address when a particular command is given, giving us more manipulation power over the memory file.
The main circuit file can be found in this repository and can be loaded in Logisim ITA without further problems.
We can also point it's usage:
- S0 dip switch controls the circuit's clock;
- S9 dip switch controls the circuit's Master Clear command;
- HEX5-HEX2 displays show which address is being acessed at that time;
- HEX1 display shows what's inside of the first register;
- HEX0 display shows what's inside of the second register;
- L7-L0 LEDs show the current count by the counter.
One of the memory files shall be loaded inside ROM_256x16 subcircuit (since it's just the default Logisim's ROM memory forwarded by a register, as we need it to sync with the entire circuit). After that, the circuit should be ready to work and should do some arithmetic operations (such as adding and subtracting some numbers) inside both registers. The numerical values were defined inside each memory file, so they can't be modified by the user.