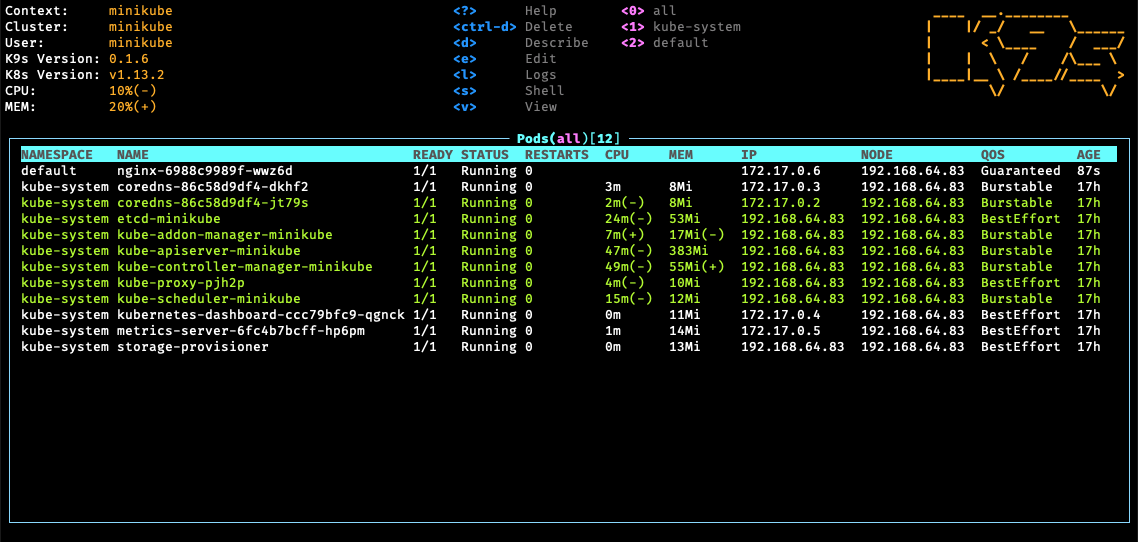
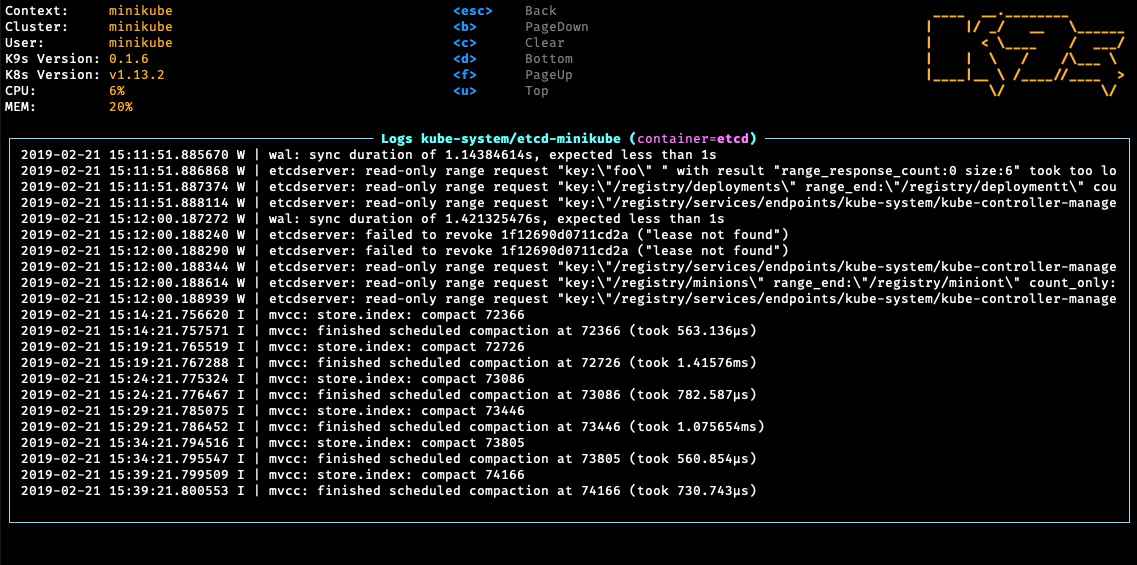
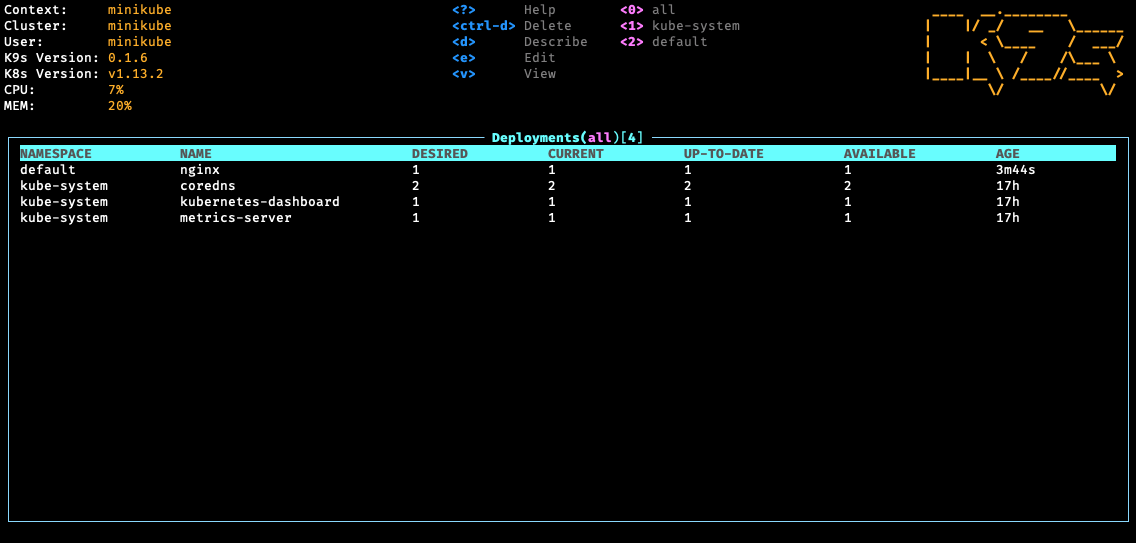
K9s provides a curses based terminal UI to interact with your Kubernetes clusters. The aim of this project is to make it easier to navigate, observe and manage your applications in the wild. K9s continually watches Kubernetes for changes and offers subsequent commands to interact with observed Kubernetes resources.
K9s is available on Linux, OSX and Windows platforms.
-
Binaries for Linux, Windows and Mac are available as tarballs in the release page.
-
Via Homebrew or LinuxBrew for OSX and Linux
brew install derailed/k9s/k9s
-
Via MacPorts
sudo port install k9s
-
Archlinux (AUR)
K9s is available in the Arch User Repository under the name k9s-bin, you can install it with your favorite AUR helper like so:
yay -S k9s-bin
-
Building from source K9s was built using go 1.13 or above. In order to build K9 from source you must:
-
Clone the repo
-
Add the following command in your go.mod file
replace ( github.com/derailed/k9s => MY_K9S_CLONED_GIT_REPO ) -
Build and run the executable
go run main.go
-
-
K9s uses 256 colors terminal mode. On `Nix system make sure TERM is set accordingly.
export TERM=xterm-256color
# List all available CLI options
k9s help
# To get info about K9s runtime (logs, configs, etc..)
k9s info
# To run K9s in a given namespace
k9s -n mycoolns
# Start K9s in an existing KubeConfig context
k9s --context coolCtxK9s uses aliases to navigate most K8s resources.
| Command | Result | Example |
|---|---|---|
:alias<ENTER> |
View a Kubernetes resource aliases | :po<ENTER> |
? |
Show keyboard shortcuts and help | |
Ctrl-a |
Show all available resource alias | select+<ENTER> to view |
/filterENTER |
Filter out a resource view given a filter | /bumblebeetuna |
/-l label-selectorENTER |
Filter resource view by labels | /-l app=fred |
<Esc> |
Bails out of view/command/filter mode | |
d,v, e, l,... |
Key mapping to describe, view, edit, view logs,... | d (describes a resource) |
:ctx<ENTER> |
To view and switch to another Kubernetes context | :+ctx+<ENTER> |
:ns<ENTER> |
To view and switch to another Kubernetes namespace | :+ns+<ENTER> |
Ctrl-d |
To delete a resource (TAB and ENTER to confirm) | |
Ctrl-k |
To delete a resource (no confirmation dialog) | |
:q, Ctrl-c |
To bail out of K9s |
K9s keeps its configurations in a .k9s directory in your home directory.
NOTE: This is still in flux and will change while in pre-release stage!
# config.yml
k9s:
# Indicates api-server poll intervals.
refreshRate: 2
# Indicates log view maximum buffer size. Default 1k lines.
logBufferSize: 200
# Indicates how many lines of logs to retrieve from the api-server. Default 200 lines.
logRequestSize: 200
# Indicates the current kube context. Defaults to current context
currentContext: minikube
# Indicates the current kube cluster. Defaults to current context cluster
currentCluster: minikube
# Persists per cluster preferences for favorite namespaces and view.
clusters:
cooln:
namespace:
active: coolio
favorites:
- cassandra
- default
view:
active: po
minikube:
namespace:
active: all
favorites:
- all
- kube-system
- default
view:
active: dpIn K9s, you can define your own command aliases (shortnames) to access your resources. In your $HOME/.k9s define a file called alias.yml. A K9s alias defines pairs of alias:gvr. A gvr represents a fully qualified Kubernetes resource identifier. Here is an example of an alias file:
# $HOME/.k9s/alias.yml
alias:
pp: v1/pods
crb: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1/clusterrolebindingsUsing this alias file, you can now type pp/crb to list pods or clusterrolebindings respectively.
K9s allows you to define your own cluster commands via plugins. K9s will look at $HOME/.k9s/plugin.yml to locate available plugins. A plugin is defined as follows:
# $HOME/.k9s/plugin.yml
plugin:
# Defines a plugin to provide a `Ctrl-L` shorcut to tail the logs while in pod view.
fred:
shortCut: Ctrl-L
description: Pod logs
scopes:
- po
command: /usr/local/bin/kubectl
background: false
args:
- logs
- -f
- $NAME
- -n
- $NAMESPACE
- --context
- $CONTEXTThis defines a plugin for viewing logs on a selected pod using CtrlL mnemonic.
The shortcut option represents the command a user would type to activate the plugin. The command represents adhoc commands the plugin runs upon activation. The scopes defines a collection of resources names/shortnames for which the plugin shortcut will be made available to the user. You can specify all to provide this shortcut for all views.
K9s does provide additional environment variables for you to customize your plugins. Currently, the available environment variables are as follows:
$NAMESPACE-- the selected resource namespace$NAME-- the selected resource name$KUBECONFIG-- the KubeConfig location.$CLUSTERthe active cluster name$CONTEXTthe active context name$USERthe active user$GROUPSthe active groups$COLXthe column at index X for the viewed resource
NOTE: This is an experimental feature! Options and layout may change in future K9s releases as this feature solidifies.
K9s integrates Hey from the brilliant and super talented Jaana Dogan of Google fame. Hey is a CLI tool to benchmark HTTP endpoints similar to AB bench. This preliminary feature currently supports benchmarking port-forwards and services (Read the paint on this is way fresh!).
To setup a port-forward, you will need to navigate to the PodView, select a pod and a container that exposes a given port. Using SHIFT-F a dialog comes up to allow you to specify a local port to forward. Once acknowledged, you can navigate to the PortForward view (alias pf) listing out your active port-forwards. Selecting a port-forward and using CTRL-B will run a benchmark on that HTTP endpoint. To view the results of your benchmark runs, go to the Benchmarks view (alias be). You should now be able to select a benchmark and view the run stats details by pressing <ENTER>. NOTE: Port-forwards only last for the duration of the K9s session and will be terminated upon exit.
Initially, the benchmarks will run with the following defaults:
- Concurrency Level: 1
- Number of Requests: 200
- HTTP Verb: GET
- Path: /
The PortForward view is backed by a new K9s config file namely: $HOME/.k9s/bench-mycluster.yml. Each cluster you connect to will have its own bench config file. Changes to this file should automatically update the PortForward view to indicate how you want to run your benchmarks.
Here is a sample benchmarks.yml configuration. Please keep in mind this file will likely change in subsequent releases!
# This file resides in $HOME/.k9s/bench-mycluster.yml
benchmarks:
# Indicates the default concurrency and number of requests setting if a container or service rule does not match.
defaults:
# One concurrent connection
concurrency: 1
# 500 requests will be sent to an endpoint
requests: 500
containers:
# Containers section allows you to configure your http container's endpoints and benchmarking settings.
# NOTE: the container ID syntax uses namespace/pod_name:container_name
default/nginx:nginx:
# Benchmark a container named nginx using POST HTTP verb using http://localhost:port/bozo URL and headers.
concurrency: 1
requests: 10000
http:
path: /bozo
method: POST
body:
{"fred":"blee"}
header:
Accept:
- text/html
Content-Type:
- application/json
services:
# Similary you can Benchmark an HTTP service exposed either via nodeport, loadbalancer types.
# Service ID is ns/svc-name
default/nginx:
# Hit the service with 5 concurrent sessions
concurrency: 5
# Issues a total of 500 requests
requests: 500
http:
method: GET
# This setting will depend on whether service is nodeport or loadbalancer. Nodeport may require vendor port tuneling setting.
# Set this to a node if nodeport or LB if applicable. IP or dns name.
host: 10.11.13.14
path: /bumblebeetuna
auth:
user: jean-baptiste-emmanuel
password: Zorg!Entering the command mode and typing a resource name or alias, could be cumbersome for navigating thru often used resources. We're introducing hotkeys that allows a user to define their own hotkeys to activate their favorite resource views. In order to enable hotkeys please follow these steps:
-
In your .k9s home directory create a file named
hotkey.yml -
Add the following to your
hotkey.yml. You can use short names or resource name to specify a command ie same as typing it in command mode.hotKey: shift-0: shortCut: Shift-0 description: View pods command: pods shift-1: shortCut: Shift-1 description: View deployments command: dp shift-2: shortCut: Shift-2 description: View services command: service shift-3: shortCut: Shift-3 description: View statefulsets command: sts
Not feeling so hot? Your custom hotkeys list will be listed in the help view.<?>. Also your hotkey file will be automatically reloaded so you can readily use your hotkeys as you define them.
You can choose any keyboard shotcuts that make sense to you, provided they are not part of the standard K9s shortcuts list.
NOTE: This feature/configuration might change in future releases!
On RBAC enabled clusters, you would need to give your users/groups capabilities so that they can use K9s to explore their Kubernetes cluster. K9s needs minimally read privileges at both the cluster and namespace level to display resources and metrics.
These rules below are just suggestions. You will need to customize them based on your environment policies. If you need to edit/delete resources extra Fu will be necessary.
NOTE! Cluster/Namespace access may change in the future as K9s evolves. NOTE! We expect K9s to keep running even in atrophied clusters/namespaces. Please file issues if this is not the case!
---
# K9s Reader ClusterRole
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: k9s
rules:
# Grants RO access to cluster resources node and namespace
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes", "namespaces"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
# Grants RO access to RBAC resources
- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["clusterroles", "roles", "clusterrolebindings", "rolebindings"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
# Grants RO access to CRD resources
- apiGroups: ["apiextensions.k8s.io"]
resources: ["customresourcedefinitions"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
# Grants RO access to metric server (if present)
- apiGroups: ["metrics.k8s.io"]
resources: ["nodes", "pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
---
# Sample K9s user ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: k9s
subjects:
- kind: User
name: fernand
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: k9s
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioIf your users are constrained to certain namespaces, K9s will need to following role to enable read access to namespaced resources.
---
# K9s Reader Role (default namespace)
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: k9s
namespace: default
rules:
# Grants RO access to most namespaced resources
- apiGroups: ["", "apps", "autoscaling", "batch", "extensions"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
# Grants RO access to metric server
- apiGroups: ["metrics.k8s.io"]
resources: ["pods", "nodes"]
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
# Sample K9s user RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: k9s
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: User
name: fernand
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: k9s
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioYou can style K9s based on your own sense of look and style. This is very much an experimental feature at this time, more will be added/modified if this feature has legs so thread accordingly!
By default a K9s view displays resource information using the following coloring scheme:
- Blue - All good.
- Orange/Red - Represents a potential issue with the resource ie a pod is not in a running state.
- Green - Indicates a row has changed. A change delta indicator indicates which column changed.
Skins are YAML files, that enable a user to change K9s presentation layer. K9s skins are loaded from $HOME/.k9s/skin.yml. If a skin file is detected then the skin would be loaded if not the current stock skin remains in effect.
You can also change K9s skins based on the cluster you are connecting too. In this case, you can specify the skin file name as $HOME/.k9s/mycluster_skin.yml
Below is a sample skin file, more skins are available in the skins directory in this repo, just simply copy any of these in your user's home dir as skin.yml.
# InTheNavy Skin...
k9s:
# General K9s styles
body:
fgColor: dodgerblue
bgColor: white
logoColor: blue
# ClusterInfoView styles.
info:
fgColor: lightskyblue
sectionColor: steelblue
frame:
# Borders styles.
border:
fgColor: dodgerblue
focusColor: aliceblue
# MenuView attributes and styles.
menu:
fgColor: darkblue
keyColor: cornflowerblue
# Used for favorite namespaces
numKeyColor: cadetblue
# CrumbView attributes for history navigation.
crumbs:
fgColor: white
bgColor: steelblue
activeColor: skyblue
# Resource status and update styles
status:
# You can also use hex colors!
newColor: #0000ff
modifyColor: powderblue
addColor: lightskyblue
errorColor: indianred
highlightcolor: royalblue
killColor: slategray
completedColor: gray
# Border title styles.
title:
fgColor: aqua
bgColor: white
highlightColor: skyblue
counterColor: slateblue
filterColor: slategray
# TableView attributes.
table:
fgColor: blue
bgColor: darkblue
cursorColor: aqua
# Header row styles.
header:
fgColor: white
bgColor: darkblue
sorterColor: orange
views:
# YAML info styles.
yaml:
keyColor: steelblue
colonColor: blue
valueColor: royalblue
# Logs styles.
logs:
fgColor: white
bgColor: blackAvailable color names are defined below:
| Color Names | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| black | maroon | green | olive | navy |
| purple | teal | silver | gray | red |
| lime | yellow | blue | fuchsia | aqua |
| white | aliceblue | antiquewhite | aquamarine | azure |
| beige | bisque | blanchedalmond | blueviolet | brown |
| burlywood | cadetblue | chartreuse | chocolate | coral |
| cornflowerblue | cornsilk | crimson | darkblue | darkcyan |
| darkgoldenrod | darkgray | darkgreen | darkkhaki | darkmagenta |
| darkolivegreen | darkorange | darkorchid | darkred | darksalmon |
| darkseagreen | darkslateblue | darkslategray | darkturquoise | darkviolet |
| deeppink | deepskyblue | dimgray | dodgerblue | firebrick |
| floralwhite | forestgreen | gainsboro | ghostwhite | gold |
| goldenrod | greenyellow | honeydew | hotpink | indianred |
| indigo | ivory | khaki | lavender | lavenderblush |
| lawngreen | lemonchiffon | lightblue | lightcoral | lightcyan |
| lightgoldenrodyellow | lightgray | lightgreen | lightpink | lightsalmon |
| lightseagreen | lightskyblue | lightslategray | lightsteelblue | lightyellow |
| limegreen | linen | mediumaquamarine | mediumblue | mediumorchid |
| mediumpurple | mediumseagreen | mediumslateblue | mediumspringgreen | mediumturquoise |
| mediumvioletred | midnightblue | mintcream | mistyrose | moccasin |
| navajowhite | oldlace | olivedrab | orange | orangered |
| orchid | palegoldenrod | palegreen | paleturquoise | palevioletred |
| papayawhip | peachpuff | peru | pink | plum |
| powderblue | rebeccapurple | rosybrown | royalblue | saddlebrown |
| salmon | sandybrown | seagreen | seashell | sienna |
| skyblue | slateblue | slategray | snow | springgreen |
| steelblue | tan | thistle | tomato | turquoise |
| violet | wheat | whitesmoke | yellowgreen | grey |
| dimgrey | darkgrey | darkslategrey | lightgrey | lightslategrey |
| slategrey |
This initial drop is brittle. K9s will most likely blow up...
- You're running older versions of Kubernetes. K9s works best Kubernetes 1.15+.
- You don't have enough RBAC fu to manage your cluster.
This is still work in progress! If there is enough interest in the Kubernetes community, we will enhance per your recommendations/contributions. Also if you dig this effort, please let us know that too!
K9s sits on top of many open source projects and libraries. Our sincere appreciations to all the OSS contributors that work nights and weekends to make this project a reality!
![]() © 2019 Imhotep Software LLC. All materials licensed under Apache v2.0
© 2019 Imhotep Software LLC. All materials licensed under Apache v2.0