Nauti connects kubernetes clusters by a new build parallel network securely, it requires no public IP for
child cluster and has no limits of cluster IP CIDR or CNI types of kubernetes clusters and also
provide service discovery ability.
It consists of several parts for networking between clusters:
- ovnmaster it builds an
ovsfor in-cluster traffic manage which is parallel with native cluster CNI and IPAM for second network interface - nri-controller add second network interface when pod created.
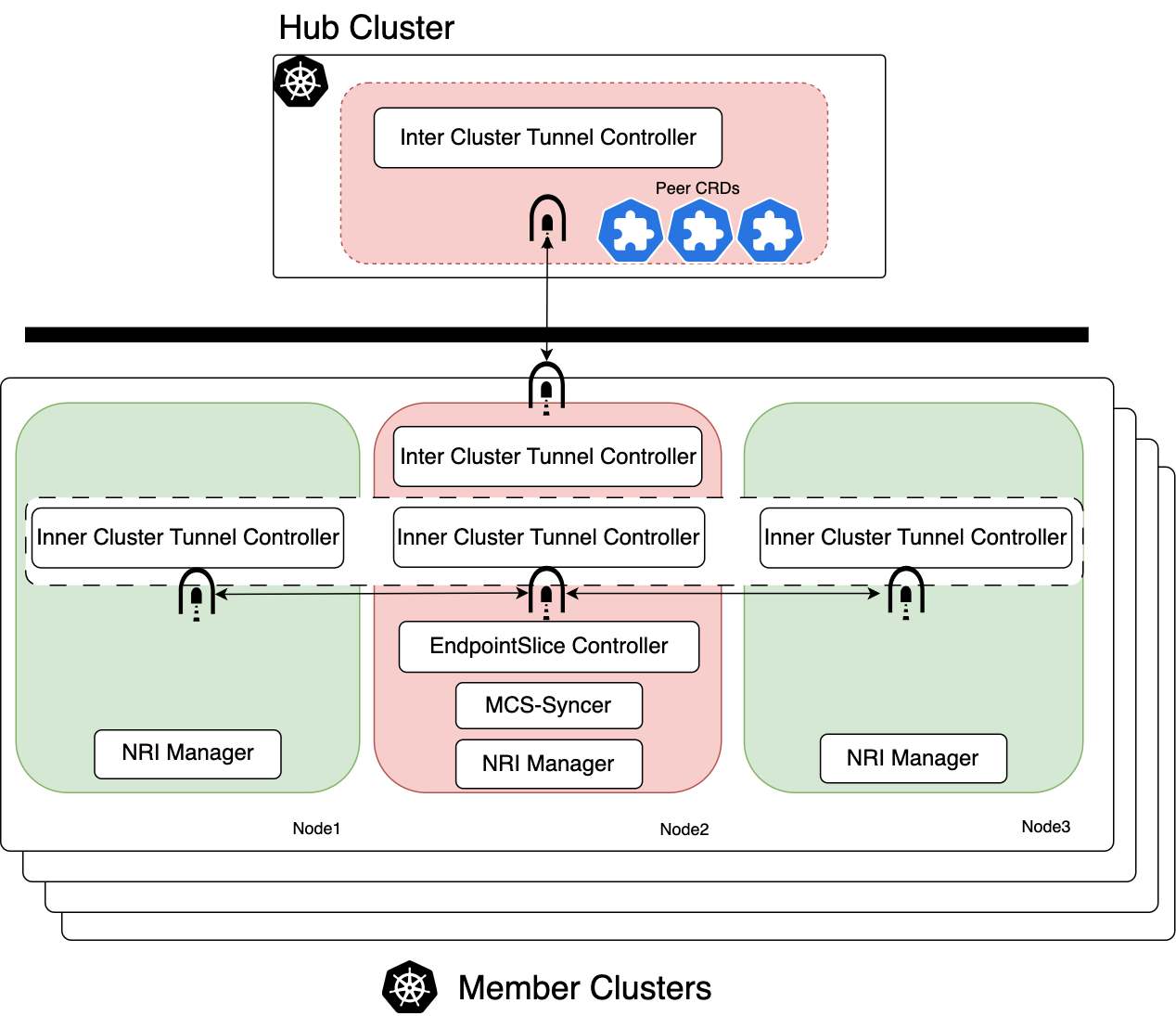
- octopus manages secure tunnels between hub and clusters, sync multi cluster services related resource across clusters
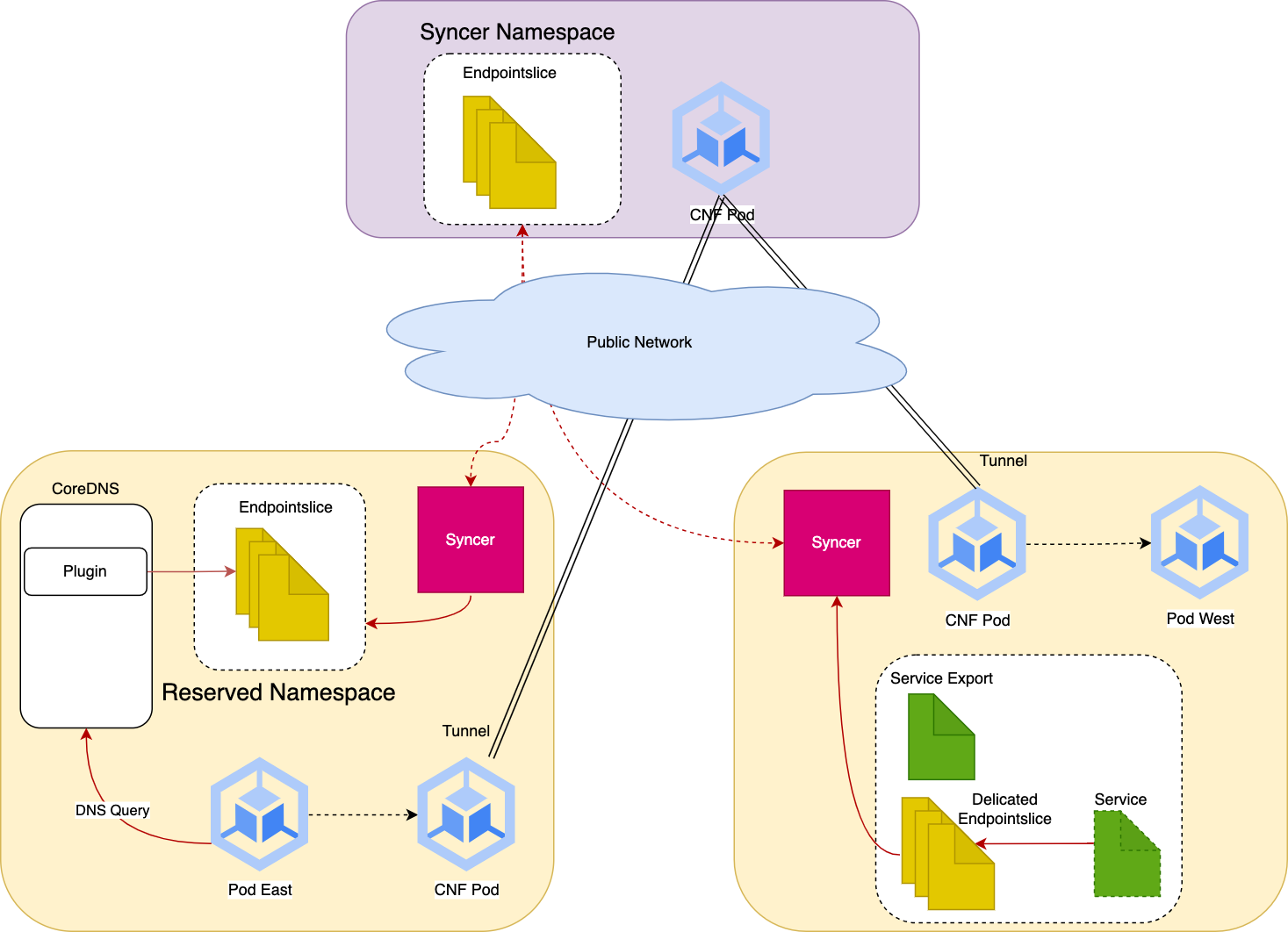
- crossdns provides DNS discovery of Services across clusters.
We use hub cluster to exchange MCS related resources for connecting clusters, and establish secure tunnels with
all other participating clusters. Hub defines a set of ServiceAccount, Secrets and RBAC to enable Syncer and
octopusto securely access the Hub cluster's API.
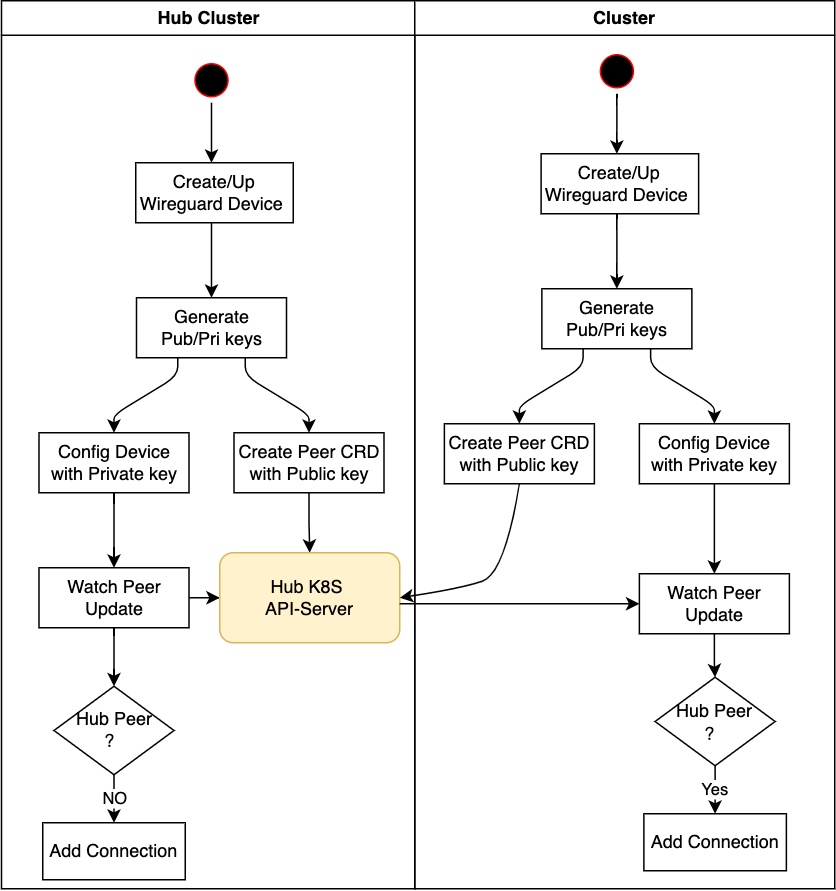
Octopus maintains the tunnels by using of WireGuard, a performant and secure VPN
inCNF pod. The CNF pod can run on any node without specifically designated. CNF pod will generate key pairs
every time it starts, creates and up wiregurad network interface and config the wireguard device with peer CRD.
For develop guide, workflow show as.
We may merge the two components into one Service Discovery Component.
For every service in cluster which has ServiceExport created for it. A new EndpointSlice will be generated to represent
the running pods contain references to endpoint's secondary IP. These endpointSlice resources will be exported to
Hub Cluster and will be copied to other clusters.
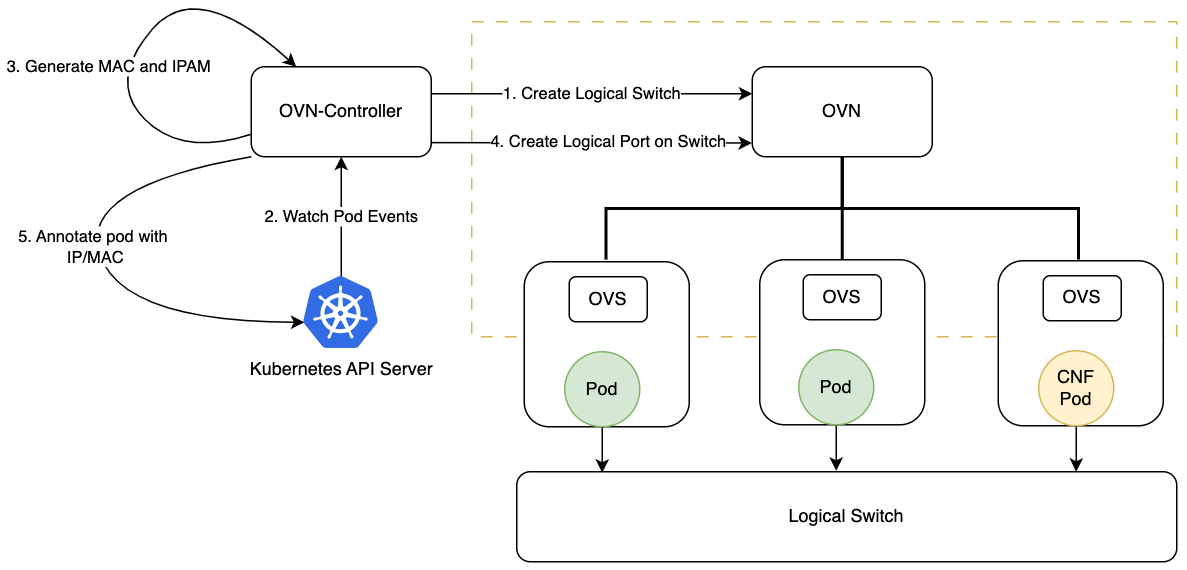
OvnMaster deploy OVN/OVS components to create a virtual switch for all pods’ secondary network, so that we can route
all inner cluster traffic to CNF pod in L2 level, without any specifically modification on Kubernetes Node.
Also, it creates logical switch, watches the Pod creation and deletion events, manage the address and create logical ports. Finally, it writes the assigned address to the annotation of the Pod.
Nauti is pretty easy to install with Helm. Make sure you already have at least 2 Kubernetes clusters,
please refer to this installation guide.
Global CIDR is used in parallel network connection, it should not be conflict or overlap with cluster Pod
or Service CIDR, it's 10.112.0.0/12 by default.
Hub is a kubernetes which has a public IP exposed,
$ helm repo add mcs http://122.96.144.180:30088/charts/mcs
"mcs" has been added to your repositories
$ helm repo list
NAME URL
mcs http://122.96.144.180:30088/charts/mcs
$ helm search repo mcs
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
mcs/nauti 0.1.0 1.16.0 A Helm chart for Tunnel across clusters.
mcs/nauti-agent 0.1.0 1.0.0 A Helm chart for Tunnel across clusters.
$ helm install nauti mcs/nauti --namespace nauti-system --create-namespace \
--set tunnel.endpoint=10.115.217.212 --set tunnel.cidr=10.112.0.0/12
NAME: nauti
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Mar 31 12:43:43 2024
NAMESPACE: nauti-system
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
Thank you for installing nauti.
Your release is named nauti.
Continue to install nauti-agent on clusters, with bootstrap token: re51os.131tn13kek2iaqoz
And install nauti-agent in cluster by:
helm install nauti-agent mcs/nauti-agent --namespace nauti-system --create-namespace \
--set hub.hubURL=https://10.115.217.212:6443 --set cluster.clusterID=cluster1Add a PV (Be careful, the PV below is just for demo):
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: ovn-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
storageClassName: local-storage
local:
path: /home/ubuntu/pv
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- child-node-0$ kubectl create -f local-pv.yamlJoining a cluster, make sure clusterID and tunnel.cidr is unique. We don't require cluster has a public IP.
$ helm repo add mcs http://122.96.144.180:30088/charts/mcs
"mcs" has been added to your repositories
$ helm install nauti-agent mcs/nauti-agent --namespace nauti-system --create-namespace \
--set hub.hubURL=https://10.115.217.212:6443 --set cluster.clusterID=cluster1Add cross cluster DNS config segment, in coredns configmap, and restart coredns pods.
hyperos.local:53 {
forward . 10.96.0.11
}$ kubectl delete pod -n kube-system --selector=k8s-app=kube-dnsCreate this example in one cluster.
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nauti-io/nauti/main/examples/nginx-deploy.yamlTest it in another cluster.
$ kubectl exec -it nginx-app-xxx -c alpine -- curl nginx-svc.default.svc.hyperos.local
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
body {
width: 35em;
margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>$ helm uninstall nauti -n nauti-system
$ kubectl delete -f local-pv.yaml
$ kubectl delete ns nauti-system
$ for ns in $(kubectl get ns -o name |cut -c 11-); do
echo "annotating pods in ns:$ns"
kubectl annotate pod --all nauti.io/cidr- -n "$ns"
kubectl annotate pod --all nauti.io/gateway- -n "$ns"
kubectl annotate pod --all nauti.io/ip_address- -n "$ns"
kubectl annotate pod --all nauti.io/logical_switch- -n "$ns"
kubectl annotate pod --all nauti.io/mac_address- -n "$ns"
kubectl annotate pod --all nauti.io/allocated- -n "$ns"
kubectl annotate pod --all nauti.io/pod_nic_type- -n "$ns"
kubectl annotate pod --all nauti.io/routes- -n "$ns"
done