The code in this repository has been migrated to the Nautobot ChatOps Repository as an integration - read more about it in the ChatOps Docs! As of July 2023 this repository has been FROZEN - all development / issues / discussions for this integration are in the Nautobot ChatOps Repository going forward.
Using the Nautobot ChatOps base framework, this Nautobot app (plugin) adds the ability to gather data as well as make basic changes communicating directly with the Meraki portal using Slack, Webex Teams, MS Teams, and Mattermost changing the way IT organizations support their Meraki infrastructure.
Add a slash command to Slack called /meraki.
See the nautobot-chatops installation guide for instructions on adding a slash command to your Slack channel.
You may need to adjust your Access Grants in Nautobot depending on your security requirements.
The following commands are available:
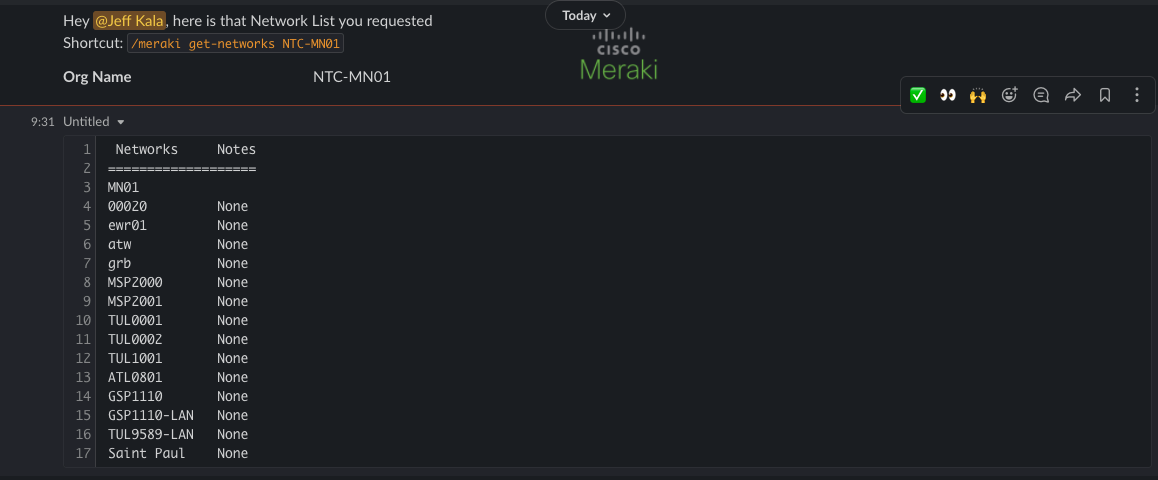
/meraki get-organizations: Gather all the Meraki Organizations./meraki get-admins [org-name]: Based on an Organization Name Return the Admins./meraki get-devices [org-name] [device-type]: Gathers devices from Meraki./meraki get-networks [org-name]: Gathers networks from Meraki./meraki get-switchports [org-name] [device-name]: Gathers switch ports from a MS switch device./meraki get-switchports-status [org-name] [device-name]: Gathers switch ports status from a MS switch device./meraki get-firewall-performance [org-name] [device-name]: Query Meraki with a firewall to device performance./meraki get-network-ssids [org-name] [net-name]: Query Meraki for all SSIDs for a given Network./meraki get-camera-recent [org-name] [device-name]: Query Meraki Recent Camera Analytics./meraki get-clients [org-name] [device-name]: Query Meraki for List of Clients./meraki get-lldp-cdp [org-name] [device-name]: Query Meraki for List of LLDP or CDP Neighbors./meraki configure-basic-access-port [org-name] [device-name] [port-number] [enabled] [vlan] [port-desc]: Configure an access port with description, VLAN and state./meraki cycle-port [org-name] [device-name] [port-number]: Cycles a port on a given switch.
Running /meraki get-organizations.

Running /meraki get-switchports-status.
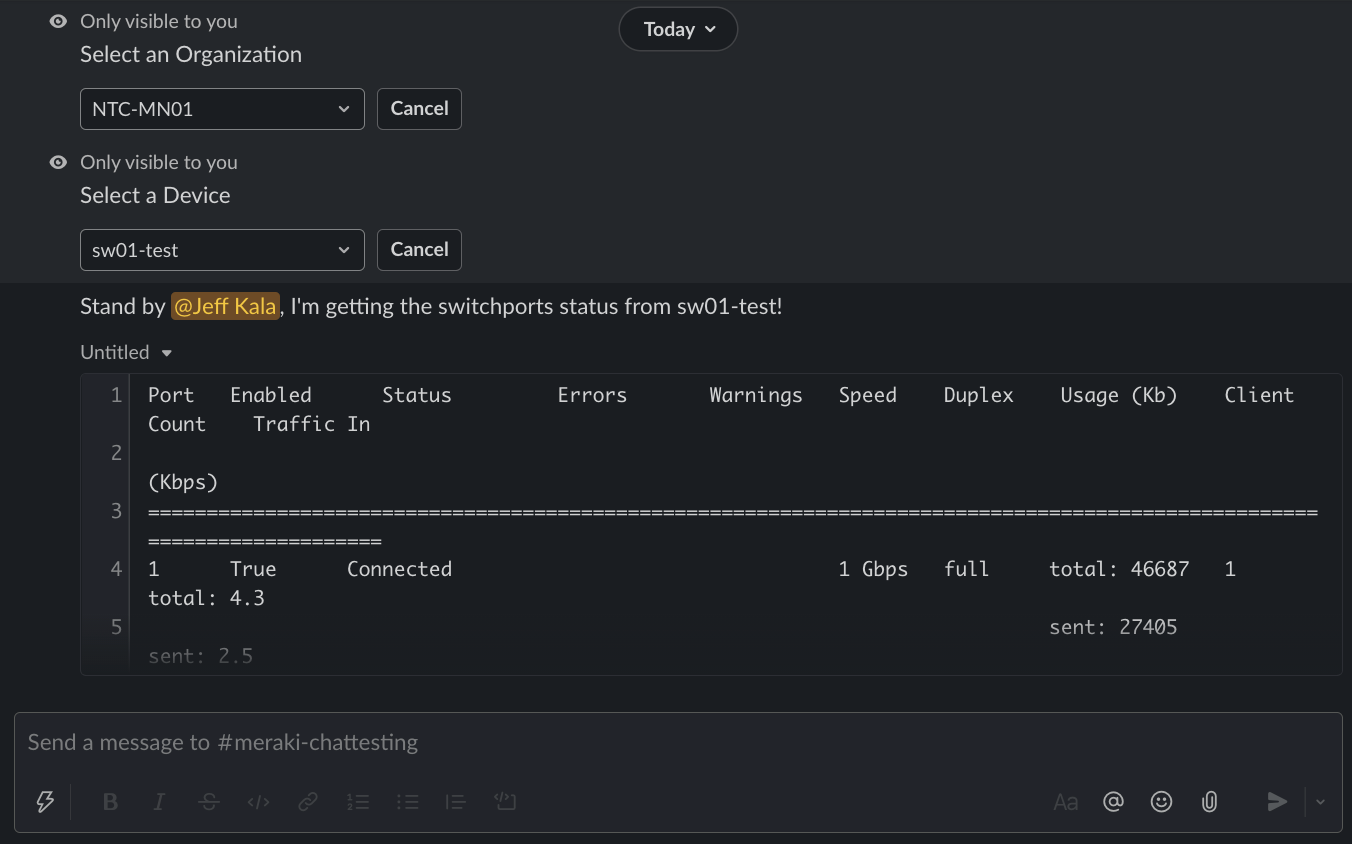
Since the output was cut off the output example is below:
Port Enabled Status Errors Warnings Speed Duplex Usage (Kb) Client Count Traffic In
(Kbps)
========================================================================================================================
1 True Connected 1 Gbps full total: 46687 1 total: 4.3
sent: 27405 sent: 2.5
recv: 19282 recv: 1.8
2 True Connected 1 Gbps full total: 10086 1 total: 1.0
sent: 9481 sent: 0.9
recv: 605 recv: 0.1
3 True Disconnected Port total: 0 0 total: 0
disconnected sent: 0 sent: 0
recv: 0 recv: 0
4 True Disconnected Port total: 0 0 total: 0
disconnected sent: 0 sent: 0
recv: 0 recv: 0
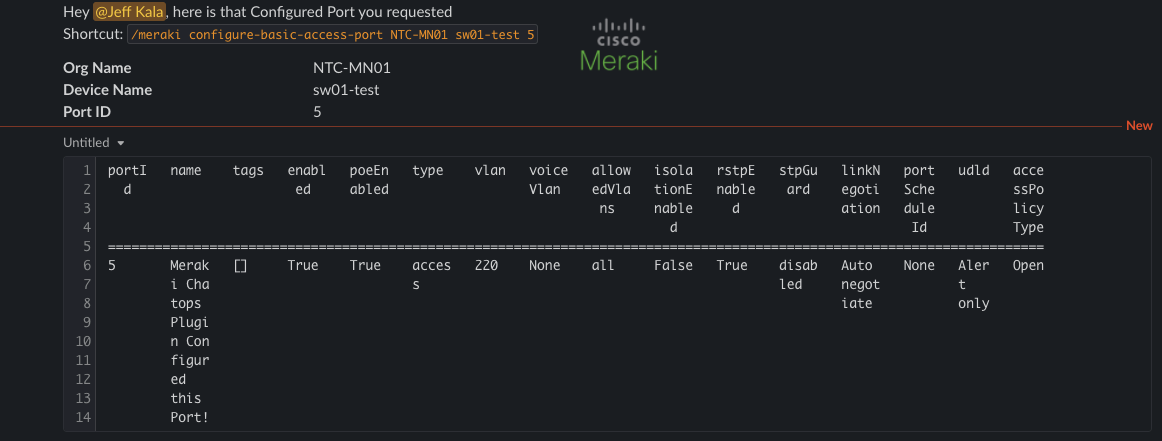
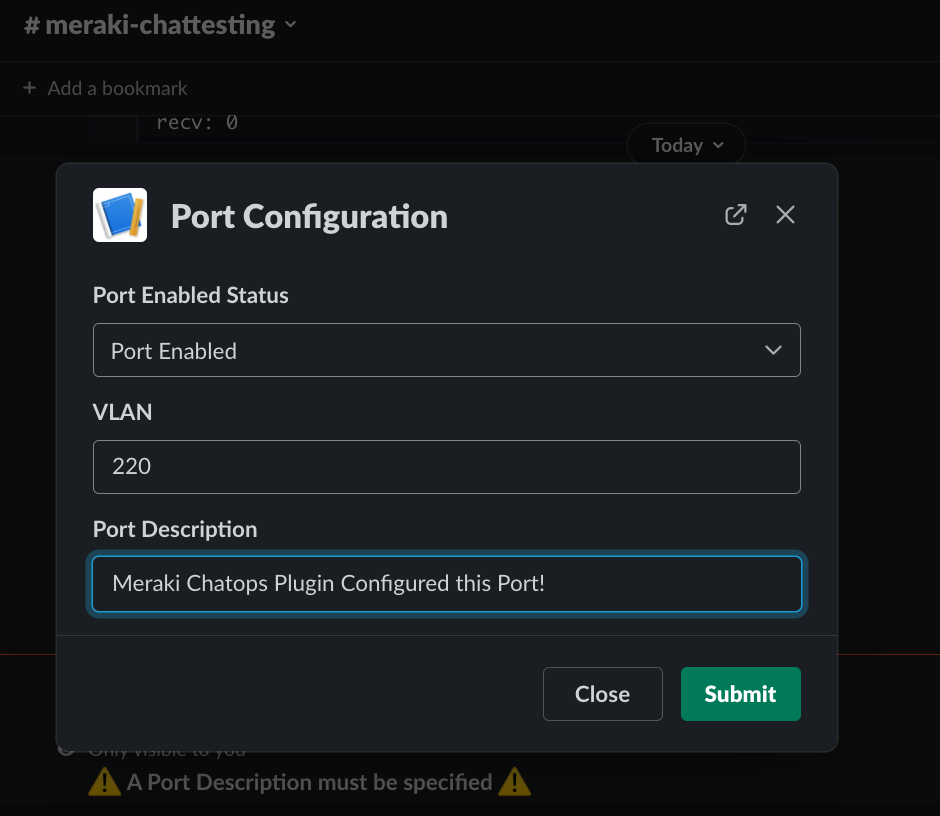
To demonstrate a example of configuration updates. There is a simple configuration ability for access ports.
/meraki configure-basic-access-port
Specify Org, Switch, and Port ID.
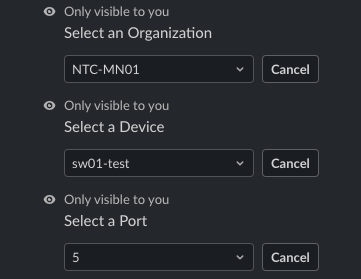
Fill out the Port Specific Configuration.
This plugin requires installation of the Nautobot ChatOps plugin. Follow this link to the installation instructions for that plugin.
The plugin is available as a Python package in PYPI and can be installed with pip
pip install git+https://github.com/networktocode-llc/nautobot-plugin-chatops-meraki.gitThe plugin is compatible with Nautobot 1.0.1 and higher
To ensure Nautobot Plugin Chatops Meraki is automatically re-installed during future upgrades, create a file named local_requirements.txt (if not already existing) in the Nautobot root directory (alongside requirements.txt) and list the nautobot-plugin-chatops-meraki package:
# echo nautobot-plugin-chatops-meraki >> local_requirements.txt
Once installed, the plugin needs to be enabled in your nautobot_config.py
# In your configuration.py
PLUGINS = ["nautobot_chatops", "nautobot_plugin_chatops_meraki"]
PLUGINS_CONFIG = {
"nautobot_chatops": {
# ADD SLACK/MS-TEAMS/WEBEX-TEAMS/MATTERMOST SETTINGS HERE
}
}To connect to the Meraki Dashboard API, you need to define Meraki Dashboard API key. See Meraki Dashboard API Documentation.
There are two options to define the API key.
The first option is to define the API key in the nautobot_config.py:
PLUGINS_CONFIG = {
"nautobot_plugin_chatops_meraki": {
"meraki_dashboard_api_key": <API KEY>
},Note: You would probably want to read the API key from the env variable like this:
os.environ.get("MERAKI_API_KEY")
The alternative option is to set the environmental variable:
MERAKI_DASHBOARD_API_KEY: Is set to the dashboard API key.
For the local development and testing add this variable and its value in the creds.env file.
If both options are used, the plugin will read the key from the settings.
Pull requests are welcomed and automatically built and tested against multiple version of Python and multiple version of Nautobot through TravisCI.
The project is packaged with a light development environment based on docker-compose to help with the local development of the project and to run the tests within TravisCI.
The project is following Network to Code software development guideline and is leveraging:
- Black, Pylint, Bandit and pydocstyle for Python linting and formatting.
- Django unit test to ensure the plugin is working properly.
The development environment can be used in 2 ways. First, with a local poetry environment if you wish to develop outside of Docker. Second, inside of a docker container.
The PyInvoke library is used to provide some helper commands based on the environment. There are a few configuration parameters which can be passed to PyInvoke to override the default configuration:
nautobot_ver: the version of Nautobot to use as a base for any built docker containers (default: latest)project_name: the default docker compose project name (default: nautobot-plugin-chatops-meraki)python_ver: the version of Python to use as a base for any built docker containers (default: 3.6)local: a boolean flag indicating if invoke tasks should be run on the host or inside the docker containers (default: False, commands will be run in docker containers)compose_dir: the full path to a directory containing the project compose filescompose_files: a list of compose files applied in order (see Multiple Compose files for more information)
Using PyInvoke these configuration options can be overridden using several methods. Perhaps the simplest is simply setting an environment variable INVOKE_NAUTOBOT-PLUGIN-CHATOPS-MERAKI_VARIABLE_NAME where VARIABLE_NAME is the variable you are trying to override. The only exception is compose_files, because it is a list it must be overridden in a yaml file. There is an example invoke.yml in this directory which can be used as a starting point.
- Copy
development/creds.env.exampletodevelopment/creds.env(This file will be ignored by git and docker) - Uncomment the
POSTGRES_HOST,REDIS_HOST, andNAUTOBOT_ROOTvariables indevelopment/creds.env - Create an invoke.yml with the following contents at the root of the repo:
---
nautobot_plugin_chatops_meraki:
local: true
compose_files:
- "docker-compose.requirements.yml"- Run the following commands:
poetry shell
poetry install
export $(cat development/dev.env | xargs)
export $(cat development/creds.env | xargs)- You can now run nautobot-server commands as you would from the Nautobot documentation for example to start the development server:
nautobot-server runserver 0.0.0.0:8080 --insecureNautobot server can now be accessed at http://localhost:8080.
This project is managed by Python Poetry and has a few requirements to setup your development environment:
- Install Poetry, see the Poetry Documentation for your operating system.
- Install Docker, see the Docker documentation for your operating system.
Once you have Poetry and Docker installed you can run the following commands to install all other development dependencies in an isolated python virtual environment:
poetry shell
poetry install
invoke startNautobot server can now be accessed at http://localhost:8080.
The project is coming with a CLI helper based on invoke to help setup the development environment. The commands are listed below in 3 categories dev environment, utility and testing.
Each command can be executed with invoke <command>. Environment variables INVOKE_NAUTOBOT-PLUGIN-CHATOPS-MERAKI_PYTHON_VER and INVOKE_NAUTOBOT-PLUGIN-CHATOPS-MERAKI_NAUTOBOT_VER may be specified to override the default versions. Each command also has its own help invoke <command> --help
build Build all docker images.
debug Start Nautobot and its dependencies in debug mode.
destroy Destroy all containers and volumes.
restart Restart Nautobot and its dependencies.
start Start Nautobot and its dependencies in detached mode.
stop Stop Nautobot and its dependencies.
cli Launch a bash shell inside the running Nautobot container.
create-user Create a new user in django (default: admin), will prompt for password.
makemigrations Run Make Migration in Django.
nbshell Launch a nbshell session.
bandit Run bandit to validate basic static code security analysis.
black Run black to check that Python files adhere to its style standards.
flake8 This will run flake8 for the specified name and Python version.
pydocstyle Run pydocstyle to validate docstring formatting adheres to NTC defined standards.
pylint Run pylint code analysis.
tests Run all tests for this plugin.
unittest Run Django unit tests for the plugin.
For any questions or comments, please check the FAQ first and feel free to swing by the Network to Code slack channel (channel #networktocode). Sign up here