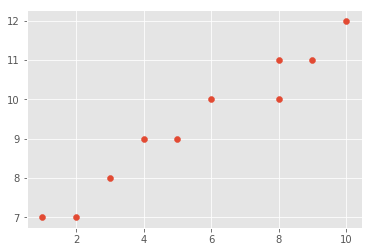
Regression analysis forms the basis of machine learning experiments. Understanding regression will help you to get the foundations of most machine learning algorithms. Ever wondered what's at the heart of an artificial neural network processing unstructured data like music and graphics? It can be linear regression!
You will be able to:
- Calculate the slope of a line using standard slope formula
- Calculate the y-intercept using the slope value
- Draw a regression line based on calculated slope and intercept
- Predict the label of a previously unseen data element
A first step towards understanding regression is getting a clear idea about "linear" regression and basic linear algebra.
In the lesson, we showed the best-fit line's slope
With
You'll use the latter formula in this lab. As in our previous lab, let's break down the formula into its parts. First, you'll import the required libraries and define some data points to work with. Next, you'll use some pre-created toy data in numpy arrays. Let's do this for you to give you a head start.
# import necessary libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import style
style.use('ggplot')
# Initialize vectors X and Y with given values and create a scatter plot
X = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9,10], dtype=np.float64)
Y = np.array([7,7,8,9,9,10,10,11,11,12], dtype=np.float64)# Scatter plot# Your observations about relationship in X and Y
#In a data analysis context, we can think of these points as two vectors:
- vector X: The independent variable or predictor
- vector Y: The dependent variable or target variable
Write a function calc_slope() that takes in x and y vectors and calculates the slope using the formula shown above.
# Write the function to calculate slope as:
# (mean(x) * mean(y) – mean(x*y)) / ( mean (x)^2 – mean( x^2))
def calc_slope(xs,ys):
pass
calc_slope(X,Y)
# 0.5393518518518512Great, so we have our slope. Next we calculate the intercept.
As a reminder, the calculation for the best-fit line's y-intercept is:
Write a function best_fit() that takes in X and Y, calculates the slope and intercept using the formula. The function should return slope and intercept values.
# use the slope function with intercept formula to return calculate slope and intercept from data points
def best_fit(xs,ys):
pass
# Uncomment below to test your function
#m, c = best_fit(X,Y)
#m, c
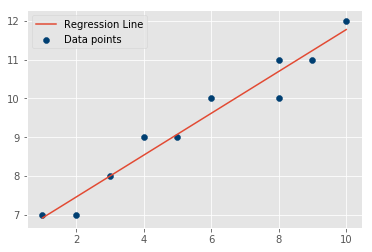
# (0.5393518518518512, 6.379629629629633)We now have a working model with m and c as model parameters. We can create a line for the data points using the calculated slope and intercept:
- Recall that
$y = mx + c$ . We can now use slope and intercept values along with X data points (features) to calculate the Y data points (labels) of the regression line.
Write a function reg_line() that takes in slope, intercept and X vector and calculates the regression line using
def reg_line (m, c, xs):
pass
# Uncomment below
#regression_line = reg_line(m,c,X)# Plot data and regression lineSo there we have it, our least squares regression line. This is the best fit line and does describe the data pretty well (still not perfect though).
# Your answer here
So, how might you go about actually making a prediction based on this model you just made?
Now that we have a working model with m and b as model parameters. We can fill in a value of x with these parameters to identify a corresponding value of
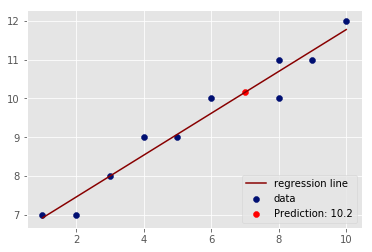
Let's try to find a y prediction for a new value of
x_new = 7
y_predicted = None
y_predicted
# 10.155092592592592# Plot as above and show the predicted valueYou now know how to create your own models, which is great, but you still haven't answered one very important question: how accurate is our model? This will be discussed next.
In this lesson, you learned how to draw a best fit line for given data labels and features, by first calculating the slope and intercept. The calculated regression line was then used to predict the label (