Phi-3-MLX is a versatile AI framework that leverages both the Phi-3-Vision multimodal model and the recently updated (July 2, 2024) Phi-3-Mini-128K language model, optimized for Apple Silicon using the MLX framework. This project provides an easy-to-use interface for a wide range of AI tasks, from advanced text generation to visual question answering and code execution.
- Support for the newly updated Phi-3-Mini-128K (language-only) model
- Integration with Phi-3-Vision (multimodal) model
- Optimized performance on Apple Silicon using MLX
- Batched generation for processing multiple prompts
- Flexible agent system for various AI tasks
- Custom toolchains for specialized workflows
- Model quantization for improved efficiency
- LoRA fine-tuning capabilities
- API integration for extended functionality (e.g., image generation, text-to-speech)
Install and launch Phi-3-MLX from command line:
pip install phi-3-vision-mlx
phi3vTo instead use the library in a Python script:
from phi_3_vision_mlx import generategenerate('What is shown in this image?', 'https://collectionapi.metmuseum.org/api/collection/v1/iiif/344291/725918/main-image')# A list of prompts for batch generation
prompts = [
"Explain the key concepts of quantum computing and provide a Rust code example demonstrating quantum superposition.",
"Write a poem about the first snowfall of the year.",
"Summarize the major events of the French Revolution.",
"Describe a bustling alien marketplace on a distant planet with unique goods and creatures."
"Implement a basic encryption algorithm in Python.",
]
# Generate responses using Phi-3-Vision (multimodal model)
generate(prompts, max_tokens=100)
# Generate responses using Phi-3-Mini-128K (language-only model)
generate(prompts, max_tokens=100, blind_model=True)# Model quantization
generate("Describe the water cycle.", quantize_model=True)
# Cache quantization
generate("Explain quantum computing.", quantize_cache=True)Training a LoRA Adapter
from phi_3_vision_mlx import train_lora
train_lora(
lora_layers=5, # Number of layers to apply LoRA
lora_rank=16, # Rank of the LoRA adaptation
epochs=10, # Number of training epochs
lr=1e-4, # Learning rate
warmup=0.5, # Fraction of steps for learning rate warmup
dataset_path="JosefAlbers/akemiH_MedQA_Reason"
)Generating Text with LoRA
generate("Describe the potential applications of CRISPR gene editing in medicine.",
blind_model=True,
quantize_model=True,
use_adapter=True)Comparing LoRA Adapters
from phi_3_vision_mlx import test_lora
# Test model without LoRA adapter
test_lora(adapter_path=None)
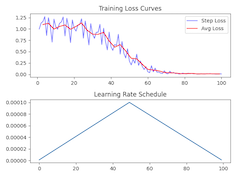
# Output score: 0.6 (6/10)
# Test model with the trained LoRA adapter (using default path)
test_lora(adapter_path=True)
# Output score: 0.8 (8/10)
# Test model with a specific LoRA adapter path
test_lora(adapter_path="/path/to/your/lora/adapter")from phi_3_vision_mlx import Agent
# Create an instance of the Agent
agent = Agent()
# First interaction: Analyze an image
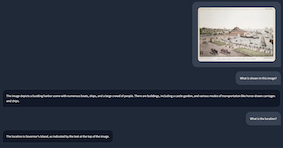
agent('Analyze this image and describe the architectural style:', 'https://images.metmuseum.org/CRDImages/rl/original/DP-19531-075.jpg')
# Second interaction: Follow-up question
agent('What historical period does this architecture likely belong to?')
# End the conversation
# This clears the agent's memory and prepares it for a new conversation
agent.end()# Ask the agent to generate and execute code to create a plot
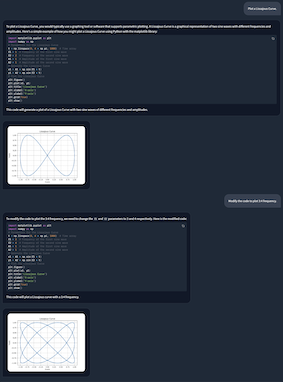
agent('Plot a Lissajous Curve.')
# Ask the agent to modify the generated code and create a new plot
agent('Modify the code to plot 3:4 frequency')
agent.end()# Request the agent to generate an image
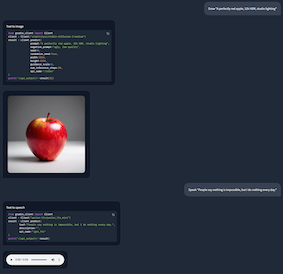
agent('Draw "A perfectly red apple, 32k HDR, studio lighting"')
agent.end()
# Request the agent to convert text to speech
agent('Speak "People say nothing is impossible, but I do nothing every day."')
agent.end()from phi_3_vision_mlx import _load_text
# Create a custom tool named 'add_text'
def add_text(prompt):
prompt, path = prompt.split('@')
return f'{_load_text(path)}\n<|end|>\n<|user|>{prompt}'
# Define the toolchain as a string
toolchain = """
prompt = add_text(prompt)
responses = generate(prompt, images)
"""
# Create an Agent instance with the custom toolchain
agent = Agent(toolchain, early_stop=100)
# Run the agent
agent('How to inspect API endpoints? @https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gradio-app/gradio/main/guides/08_gradio-clients-and-lite/01_getting-started-with-the-python-client.md')from phi_3_vision_mlx import VDB
import datasets
# Simulate user input
user_input = 'Comparison of Sortino Ratio for Bitcoin and Ethereum.'
# Create a custom RAG tool
def rag(prompt, repo_id="JosefAlbers/sharegpt_python_mlx", n_topk=1):
ds = datasets.load_dataset(repo_id, split='train')
vdb = VDB(ds)
context = vdb(prompt, n_topk)[0][0]
return f'{context}\n<|end|>\n<|user|>Plot: {prompt}'
# Define the toolchain
toolchain_plot = """
prompt = rag(prompt)
responses = generate(prompt, images)
files = execute(responses, step)
"""
# Create an Agent instance with the RAG toolchain
agent = Agent(toolchain_plot, False)
# Run the agent with the user input
_, images = agent(user_input)# Continued from Example 2 above
agent_writer = Agent(early_stop=100)
agent_writer(f'Write a stock analysis report on: {user_input}', images)from phi_3_vision_mlx import benchmark
benchmark()| Task | Vanilla Model | Quantized Model | Quantized Cache | LoRA Adapter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text Generation | 8.46 tps | 51.69 tps | 6.94 tps | 8.58 tps |
| Image Captioning | 7.72 tps | 33.10 tps | 1.75 tps | 7.11 tps |
| Batched Generation | 103.47 tps | 182.83 tps | 38.72 tps | 101.02 tps |
(On M1 Max 64GB)
API references and additional information are available at:
https://josefalbers.github.io/Phi-3-Vision-MLX/
This project is licensed under the MIT License.