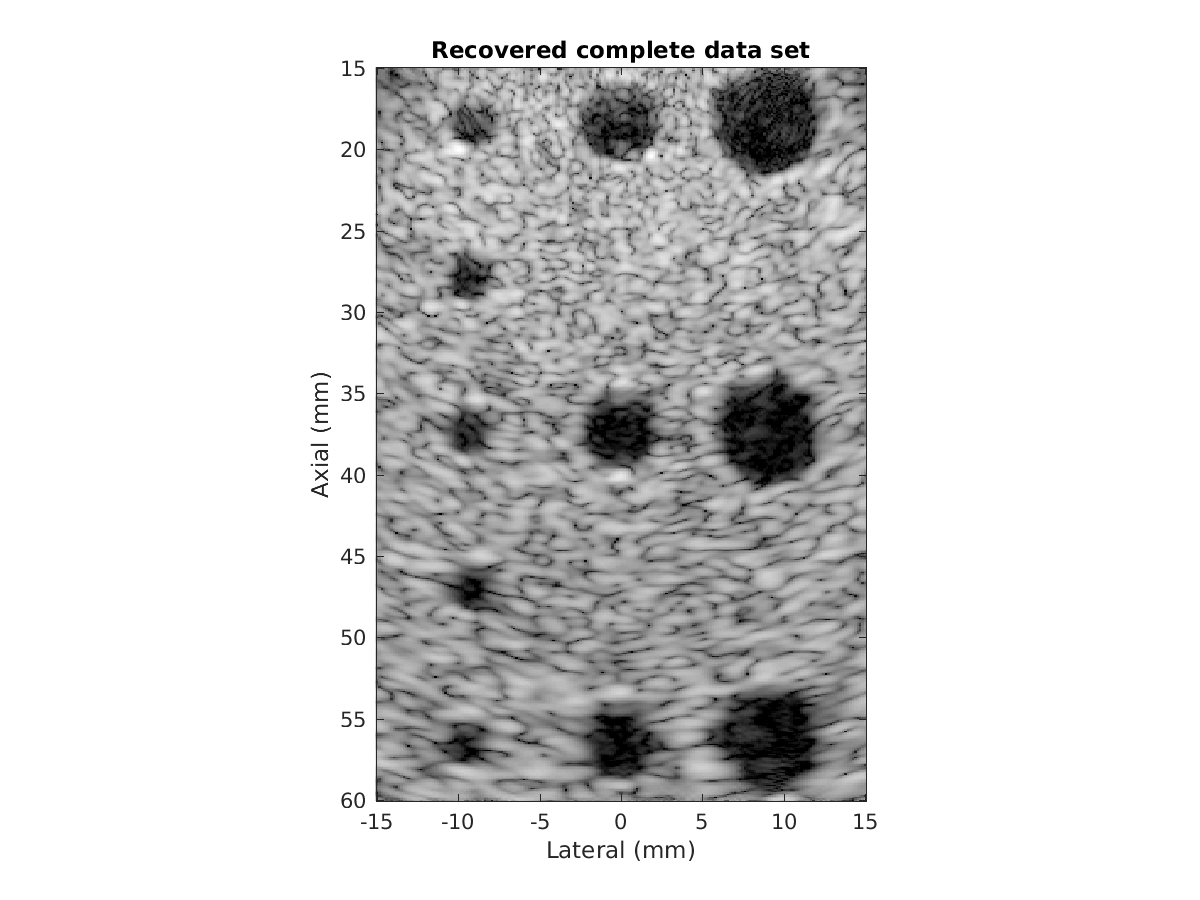
Decode a set of focused transmit ultrasound beams into the "complete data set", indexed by individual transmit elements and receive channels. This decoding has many benefits for image quality:
- Improved electronic signal-to-noise ratio
- Synthetic transmit focusing, providing diffraction-limited resolution at all depths
- Uniform field response from the recovered diverging waves (as opposed to focal gain at a fixed depth)
- Flexibility to apply transmit apodization, phase aberration correction, or other aperture-domain processing
This code is based on the algorithm proposed in:
Bottenus, N. "Recovery of the complete data set from focused transmit beams". IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, vol. 65, no. 1, pp. 30-38, Jan. 2018.
If you use the code/algorithm for research, please cite the above paper. For commercial use, please contact me at nick.bottenus@duke.edu to discuss the related IP.
You can reference a static version of this code released with the paper by its DOI number:
Output of the sample code:
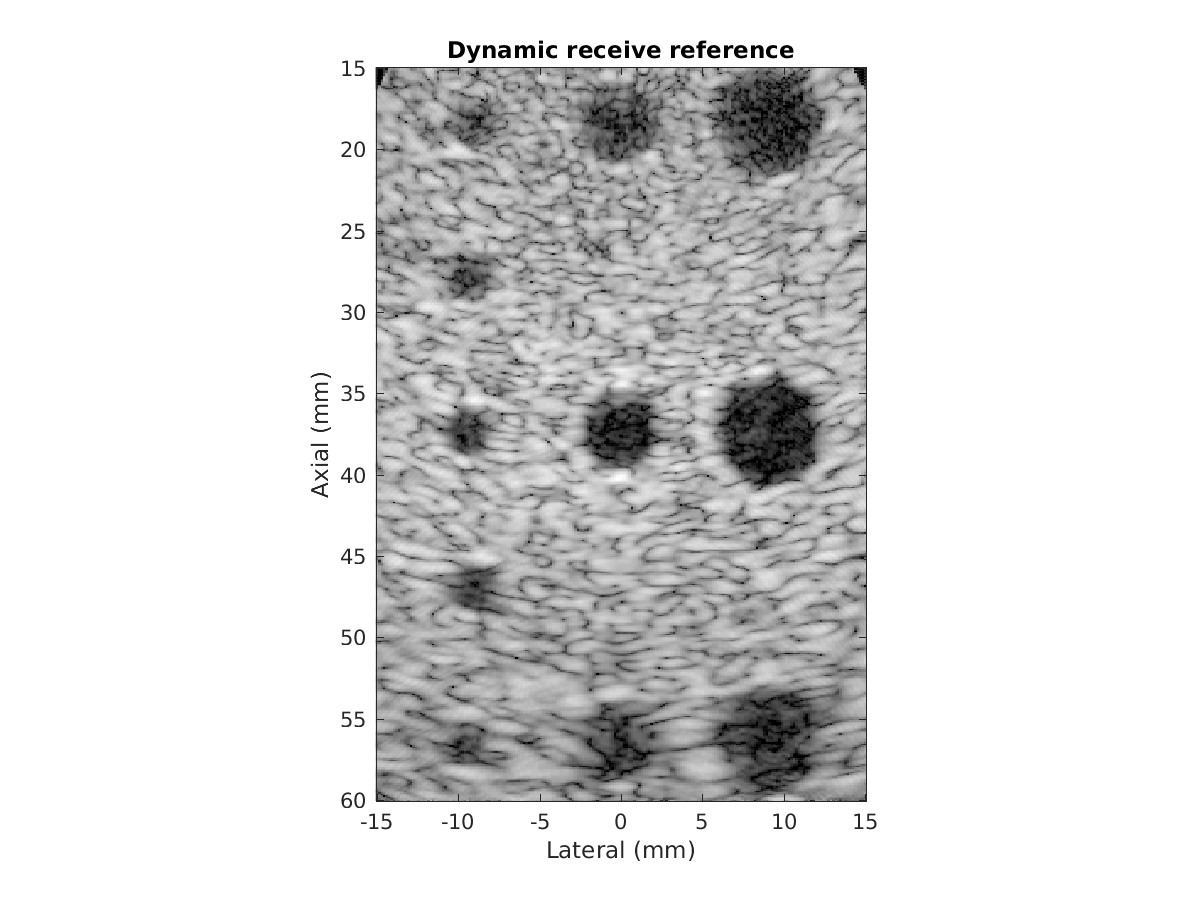
Dynamic receive (conventional) processing of the same data set for reference:
This repository provides both a MATLAB and Python implementation of the decoding method.
sample_data.mat is saved in Matlab v7 format for compatibility with Python. This data was acquired using the Verasonics Vantage research scanner.
- rf - RF channel data (samples x receive channels x transmit events)
- transmit_delays - The applied focal delays (transmit events x elements)
- params:
- c - Speed of sound
- fs - Sampling frequency (Hz)
- f0 - Transmit center frequency (Hz)
- tx_pos - Array transmit position (x,y,z) (all zero)
- rx_pos - Array element locations (x,y,z) (meters)
- theta - Beam steering angles (degrees)
- apex - Axial distance behind the array for the steered beams (meters)
- focus - Transmit focal points relative to the array position (x,y,z) (meters)
- t0 - Sample index of the first data point (negative indicates that recording started before transmission was finished)
- samples - Number of axial samples in the data set
Both the frequency domain and time domain algorithms are implemented in decode_focused_beams.m.
See demo.m for an example of how to use the code with the provided sample experimental data. The provided demo code should run in several seconds on most modern computers.
The frequency domain algorithm is implemented in decode_focused_beams.py in the decode(rf, delays) function.
See the main() function for an example of how to use the code with the provided sample experimental data. The demo code can be run as python decode_focused_beams.py.