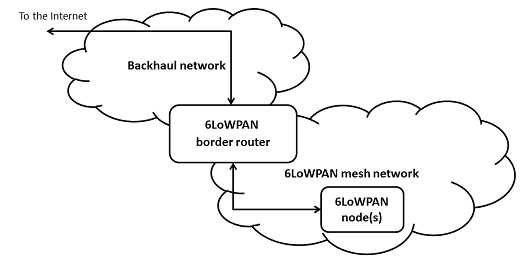
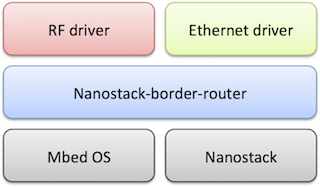
Modified Nanostack Border Router to work with Silicon Labs BRD4001A board with a BRD4170A radio. It use 6LoWPAN mesh network on the 2.4 GHz band and a SLIP interface using flow control for communicating with the backhaul network.
This application runs on Mbed OS and uses PHY drivers and Nanostack to form a border router.
The code layout is organized like this:
configs/ Contains example configuration files
drivers/ Contains PHY drivers
mbed-os/ Contains Mbed OS, itself
source/ Contains the application code
mbed_app.json Build time configuration file
- Clone this repository.
- Run
mbed deploy. - Build.
The target is already set for BRD4001A board with a BRD4170A radio.
Applications using Nanostack Border Router need to use a .json file for the configuration. You can find the example configurations in the configs/ folder.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
backhaul-dynamic-bootstrap |
Defines whether the manually configured backhaul prefix and default route are used, or whether they are learnt automatically via the IPv6 neighbor discovery. False means static and true means automatic configuration. |
backhaul-prefix |
The IPv6 prefix (64 bits) assigned to and advertised on the backhaul interface. Example format: fd00:1:2:: |
backhaul-default-route |
The default route (prefix and prefix length) where packets should be forwarded on the backhaul device, default: ::/0. Example format: fd00:a1::/10 |
backhaul-next-hop |
The next-hop value for the backhaul default route; should be a link-local address of a neighboring router, default: empty (on-link prefix). Example format: fe80::1 |
backhaul-mld |
Enable sending Multicast Listener Discovery reports to backhaul network when a new multicast listener is registered in mesh network. Values: true or false |
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
security-mode |
The 6LoWPAN mesh network traffic (link layer) can be protected with the Private Shared Key (PSK) security mode, allowed values: NONE and PSK. |
psk-key |
A 16-bytes long private shared key to be used when the security mode is PSK. Example format (hexadecimal byte values separated by commas inside brackets): {0x00, ..., 0x0f} |
multicast-addr |
Multicast forwarding is supported by default. This defines the multicast address to which the border router application forwards multicast packets (on the backhaul and RF interface). Example format: ff05::5 |
ra-router-lifetime |
Defines the router advertisement interval in seconds (default 1024 if left out). |
beacon-protocol-id |
Is used to identify beacons. This should not be changed (default 4 if left out). |
To learn more about 6LoWPAN and the configuration parameters, please read the 6LoWPAN overview.
See configs/6lowpan_Atmel_RF.json for an example configuration file.
Nanostack Border Router uses RPL as the routing protocol on the mesh network side (RF interface) when in 6LoWPAN-ND mode. Currently, only the grounded/non-storing operation mode is supported.
Nanostack Border Router offers the following configuration options for RPL:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| rpl-instance-id | The RPL instance ID value that identifies the RPL instance, default: 1 |
| rpl-idoublings | RPL Trickle parameter: DIOIntervalDoublings value, default: 12 |
| rpl-imin | RPL Trickle parameter: DIOIntervalMin value, default: 9 |
| rpl-k | RPL Trickle parameter: the redundacy constant k, default: 10 |
| rpl-max-rank-inc | Maximum rank increase value, default: 2048 |
| rpl-min-hop-rank-inc | Minimum rank increase value, default: 128 |
| rpl-default-lifetime | Default lifetime for the RPL routes, default: 64 |
| rpl-lifetime-unit | The value of the unit that describes the lifetime (in seconds), default: 60 |
| rpl-pcs | The number of bits that may be allocated to the path control field. |
| rpl-ocp | The Objective Function (OF) to use, values: 1=OF0 (default), 2=MRHOF |
The Nanostack border router application can be connected to a backhaul network with a SLIP interface. https://github.com/ARMmbed/mbed-access-point provide images for Raspberry Pi 2B and 3 for routing between SLIP and Ethernet.
| Raspberry Pi | <-> | BRD4001A | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UART0_TXD | GPIO14 | J8_8 | --> | EXP14 | PC5 | USART3_RX |
| UART0_RXD | GPIO15 | J8_10 | <-- | EXP12 | PC4 | USART3_TX |
| UART0_CTS | GPIO16 | J8_36 | <-- | EXP10 | PC3 | USART3_RTS |
| UART0_RTS | GPIO17 | J8_11 | --> | EXP8 | PC2 | USART3_CTS |
| GND | J8_6 | <-> | EXP1 | GND |
Information come from https://forums.raspberrypi.com/viewtopic.php?t=241623
- Download "miniuart-ctsrts.dtbo" from https://github.com/HiassofT/AtariSIO/tree/master/contrib/rpi
- Upload "miniuart-ctsrts.dtbo" to mbedap with sftp (with Windows, use winSCP)
- cp miniuart-ctsrts.dtbo /boot/overlays/
- Add "dtoverlay=miniuart-ctsrts" to /boot/config.txt
The application can use the file system as instructed in Mbed OS storage documentation. The file system is not enabled by default due to a variety of possible configurations.
File system activation happens by telling the file system the root path to Nanostack. To set the root path, use the function:
ns_file_system_set_root_path(root-path)
After you have set the root path, Wi-SUN stack reads the configuration settings from the file system. Wi-SUN stack writes the configuration back to the file system after the configuration changes.
- Find the binary file
nanostack-border-router.binin theBUILDfolder. - Copy the binary to the USB mass storage root of the development board. It is automatically flashed to the target MCU. When the flashing is complete, the board restarts itself. Press the Reset button of the development board if it does not restart automatically.
- The program begins execution.
- Open the serial connection, for example PuTTY.
Serial connection settings for the Nanorouter are as follows:
- Baud-rate = 921600.
- Data bits = 8.
- Stop bits = 1.
If there is no input from the serial terminal, press the Reset button of the development board.
In the PuTTY main screen, save the session, and click Open. This opens a console window showing debug messages from the application. If the console screen is blank, you may need to press the Reset button of the board to see the debug information. The serial output from the 6LoWPAN border router looks something like this in the console:
[INFO][app ]: Starting Nanostack border router...
[INFO][brro]: NET_IPV6_BOOTSTRAP_AUTONOMOUS
[INFO][app ]: Using ETH backhaul driver...
[INFO][Eth ]: Ethernet cable is connected.
[INFO][addr]: Tentative Address added to IF 1: fe80::ac41:dcff:fe37:72c4
[INFO][addr]: DAD passed on IF 1: fe80::ac41:dcff:fe37:72c4
[INFO][addr]: Tentative Address added to IF 1: 2001:999:21:9ce:ac41:dcff:fe37:72c4
[INFO][addr]: DAD passed on IF 1: 2001:999:21:9ce:ac41:dcff:fe37:72c4
[INFO][brro]: Backhaul bootstrap ready, IPv6 = 2001:999:21:9ce:ac41:dcff:fe37:72c4
[INFO][brro]: Backhaul interface addresses:
[INFO][brro]: [0] fe80::ac41:dcff:fe37:72c4
[INFO][brro]: [1] 2001:999:21:9ce:ac41:dcff:fe37:72c4
[INFO][addr]: Address added to IF 0: fe80::ff:fe00:face
[INFO][br ]: BR nwk base ready for start
[INFO][br ]: Refresh Contexts
[INFO][br ]: Refresh Prefixs
[INFO][addr]: Address added to IF 0: 2001:999:21:9ce:0:ff:fe00:face
[INFO][addr]: Address added to IF 0: fe80::fec2:3d00:4:a0cd
[INFO][brro]: RF bootstrap ready, IPv6 = 2001:999:21:9ce:0:ff:fe00:face
[INFO][brro]: RF interface addresses:
[INFO][brro]: [0] fe80::ff:fe00:face
[INFO][brro]: [1] fe80::fec2:3d00:4:a0cd
[INFO][brro]: [2] 2001:999:21:9ce:0:ff:fe00:face
[INFO][brro]: 6LoWPAN Border Router Bootstrap Complete.
The software is provided under Apache-2.0 license. Contributions to this project are accepted under the same license. Please see contributing.md for more info.
This project contains code from other projects. The original license text is included in those source files. They must comply with our license guide.