Nicolás Castro-Perdomo
Indiana University, 2022
-
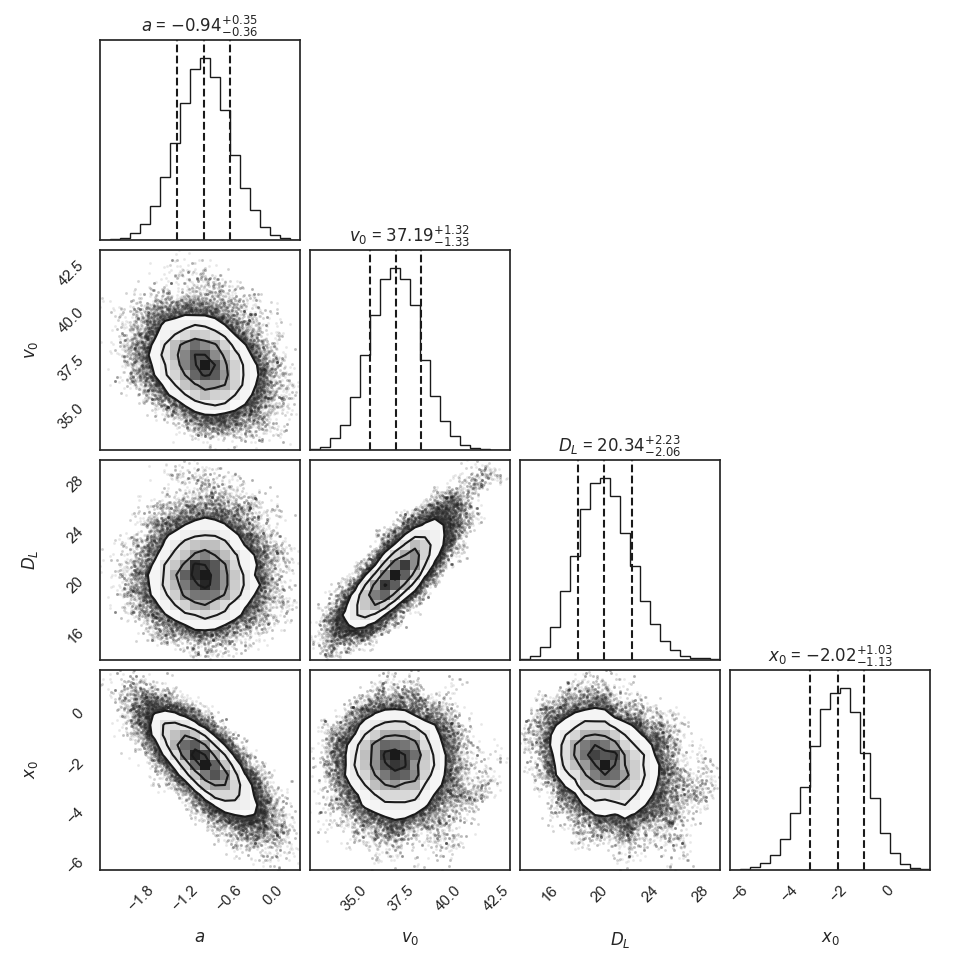
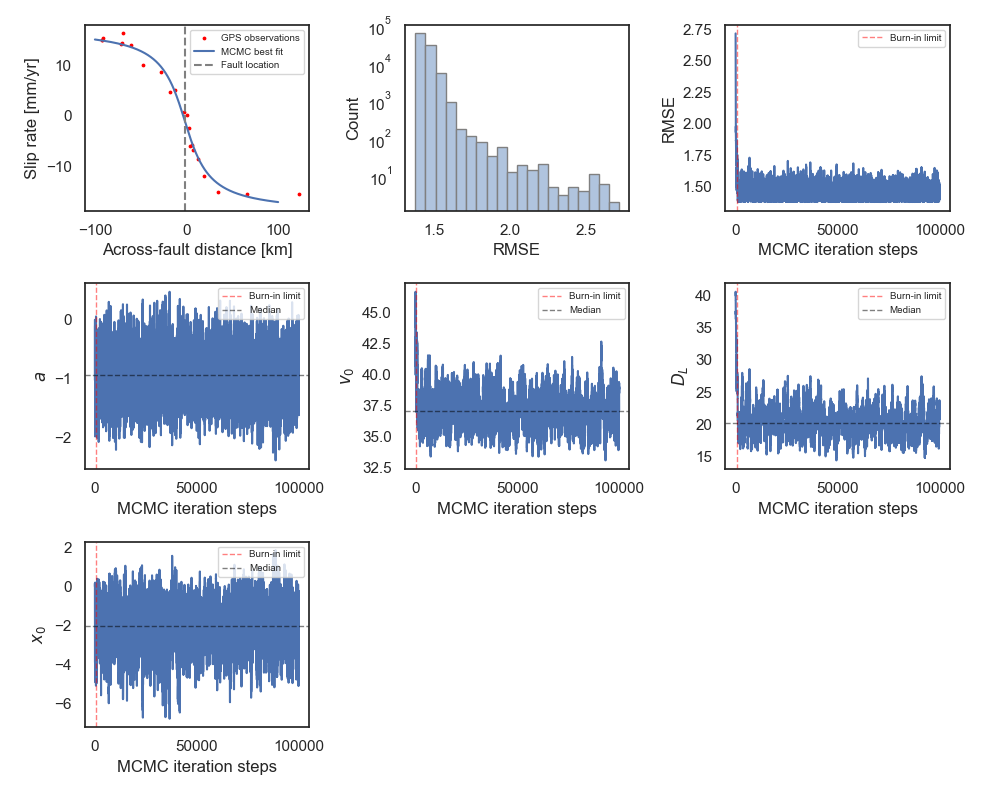
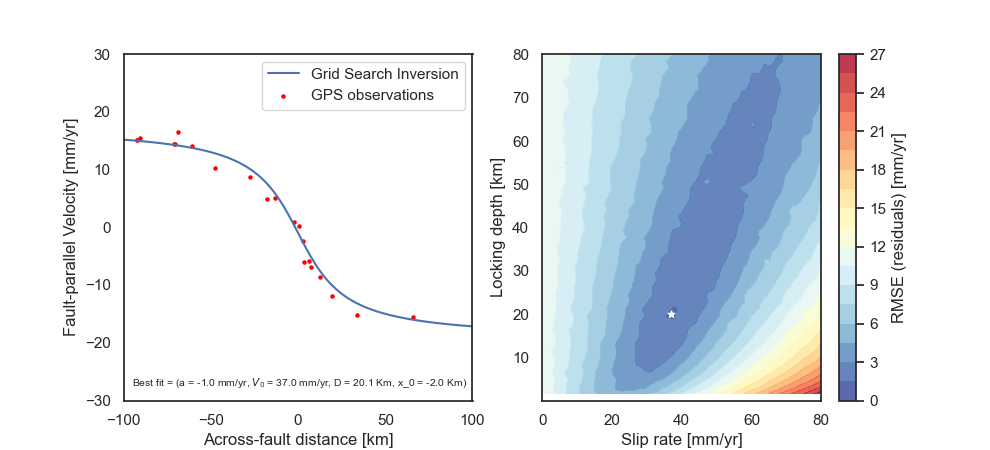
Implement a random walk Metropolis sampling algorithm to estimate fault kinematic parameters
$(a, v_0, D_L, x_0)$ in an elastic half-space dislocation model (e.g., Weertman and Weertman, 1964; Savage and Burford, 1973). -
The model describes the theoretical horizontal velocity profile across a vertical fault as a function of the spatial variable
$x$ :
where
-
The parameter domain is defined as follows:
- x
$\in$ [−150, 150] km - a
$\in$ [-5, 5] mm/yr -
$v_0$ $\in$ [0, 50] mm/yr -
$D_L$ $\in$ [0, 50] km -
$x_0$ $\in$ [−25, 25] km
- x
-
A Gaussian error model will be used, so that at any given location
$x_j$ , fault-parallel velocities satisfy:
where