| page_type | languages | products | description | urlFragment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
sample |
|
|
Deploy Spring microservices using Azure Spring Cloud and MySQL |
spring-petclinic-microservices |
Azure Spring Cloud enables you to easily run a Spring Boot based microservices application on Azure.
This quickstart shows you how to deploy an existing Java Spring Cloud application to Azure. When you're finished, you can continue to manage the application via the Azure CLI or switch to using the Azure Portal.
- Deploy Spring Microservices using Azure Spring Cloud and MySQL
- What will you experience
- What you will need
- Install the Azure CLI extension
- Clone and build the repo
- CREATE Azure Spring Cloud service instance using Azure CLI
- CREATE microservice applications
- Create MySQL Database
- DEPLOY applications and set environment variables
- MONITOR microservice applications
- AUTOMATE deployments using GitHub Actions
- Manage application secrets using Azure KeyVault
- Next Steps
You will:
- Build existing Spring microservices applications
- Provision an Azure Spring Cloud service instance. If you prefer Terraform, you may also provision using Terraform, see
README-terraform - Deploy applications to Azure
- Bind applications to Azure Database for MySQL
- Open the application
- Monitor applications
- Automate deployments using GitHub Actions
- Manage application secrets using Azure KeyVault
In order to deploy a Java app to cloud, you need an Azure subscription. If you do not already have an Azure subscription, you can activate your MSDN subscriber benefits or sign up for a free Azure account.
In addition, you will need the following:
| Azure CLI version 2.0.67 or higher | Java 8 | Maven | MySQL CLI | Git |
Install the Azure Spring Cloud extension for the Azure CLI using the following command
az extension add --name spring-cloudNote - spring-cloud CLI extension 2.1.0 or later is a pre-requisite to enable the
latest Java in-process agent for Application Insights. If you already
have the CLI extension, you may need to upgrade to the latest using --
az extension update --name spring-cloud mkdir source-code
git clone https://github.com/azure-samples/spring-petclinic-microservices cd spring-petclinic-microservices
mvn clean package -DskipTests -Denv=cloudThis will take a few minutes.
Create a bash script with environment variables by making a copy of the supplied template:
cp .scripts/setup-env-variables-azure-template.sh .scripts/setup-env-variables-azure.shOpen .scripts/setup-env-variables-azure.sh and enter the following information:
export SUBSCRIPTION=subscription-id # customize this
export RESOURCE_GROUP=resource-group-name # customize this
...
export SPRING_CLOUD_SERVICE=azure-spring-cloud-name # customize this
...
export MYSQL_SERVER_NAME=mysql-servername # customize this
...
export MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_NAME=admin-name # customize this
...
export MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD=SuperS3cr3t # customize this
...Then, set the environment:
source .scripts/setup-env-variables-azure.shLogin to the Azure CLI and choose your active subscription. Be sure to choose the active subscription that is whitelisted for Azure Spring Cloud
az login
az account list -o table
az account set --subscription ${SUBSCRIPTION}Prepare a name for your Azure Spring Cloud service. The name must be between 4 and 32 characters long and can contain only lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens. The first character of the service name must be a letter and the last character must be either a letter or a number.
Create a resource group to contain your Azure Spring Cloud service.
az group create --name ${RESOURCE_GROUP} \
--location ${REGION}Create an instance of Azure Spring Cloud.
az spring-cloud create --name ${SPRING_CLOUD_SERVICE} \
--sku standard --enable-java-agent \
--resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} \
--location ${REGION}The service instance will take around five minutes to deploy.
Set your default resource group name and cluster name using the following commands:
az configure --defaults \
group=${RESOURCE_GROUP} \
location=${REGION} \
spring-cloud=${SPRING_CLOUD_SERVICE}Use the application.yml in the root of this project to load configuration into the Config Server in Azure Spring Cloud.
az spring-cloud config-server set \
--config-file application.yml \
--name ${SPRING_CLOUD_SERVICE}Create 5 microservice apps.
az spring-cloud app create --name ${API_GATEWAY} --instance-count 1 --is-public true \
--memory 2 \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m'
az spring-cloud app create --name ${ADMIN_SERVER} --instance-count 1 --is-public true \
--memory 2 \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m'
az spring-cloud app create --name ${CUSTOMERS_SERVICE} --instance-count 1 \
--memory 2 \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m'
az spring-cloud app create --name ${VETS_SERVICE} --instance-count 1 \
--memory 2 \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m'
az spring-cloud app create --name ${VISITS_SERVICE} --instance-count 1 \
--memory 2 \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m'Create a MySQL database in Azure Database for MySQL.
// create mysql server
az mysql server create --resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} \
--name ${MYSQL_SERVER_NAME} --location ${REGION} \
--admin-user ${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_NAME} \
--admin-password ${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD} \
--sku-name GP_Gen5_2 \
--ssl-enforcement Disabled \
--version 5.7
// allow access from Azure resources
az mysql server firewall-rule create --name allAzureIPs \
--server ${MYSQL_SERVER_NAME} \
--resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} \
--start-ip-address 0.0.0.0 --end-ip-address 0.0.0.0
// allow access from your dev machine for testing
az mysql server firewall-rule create --name devMachine \
--server ${MYSQL_SERVER_NAME} \
--resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} \
--start-ip-address <ip-address-of-your-dev-machine> \
--end-ip-address <ip-address-of-your-dev-machine>
// increase connection timeout
az mysql server configuration set --name wait_timeout \
--resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} \
--server ${MYSQL_SERVER_NAME} --value 2147483
// SUBSTITUTE values
mysql -u ${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_LOGIN_NAME} \
-h ${MYSQL_SERVER_FULL_NAME} -P 3306 -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 64379
Server version: 5.6.39.0 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> CREATE DATABASE petclinic;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.10 sec)
mysql> CREATE USER 'root' IDENTIFIED BY 'petclinic';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON petclinic.* TO 'root';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1.29 sec)
mysql> CALL mysql.az_load_timezone();
Query OK, 3179 rows affected, 1 warning (6.34 sec)
mysql> SELECT name FROM mysql.time_zone_name;
...
mysql> quit
Bye
az mysql server configuration set --name time_zone \
--resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} \
--server ${MYSQL_SERVER_NAME} --value "US/Pacific"Deploy microservice applications to Azure.
az spring-cloud app deploy --name ${API_GATEWAY} \
--jar-path ${API_GATEWAY_JAR} \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m -Dspring.profiles.active=mysql'
az spring-cloud app deploy --name ${ADMIN_SERVER} \
--jar-path ${ADMIN_SERVER_JAR} \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m -Dspring.profiles.active=mysql'
az spring-cloud app deploy --name ${CUSTOMERS_SERVICE} \
--jar-path ${CUSTOMERS_SERVICE_JAR} \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m -Dspring.profiles.active=mysql' \
--env MYSQL_SERVER_FULL_NAME=${MYSQL_SERVER_FULL_NAME} \
MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME=${MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME} \
MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_LOGIN_NAME=${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_LOGIN_NAME} \
MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD=${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD}
az spring-cloud app deploy --name ${VETS_SERVICE} \
--jar-path ${VETS_SERVICE_JAR} \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m -Dspring.profiles.active=mysql' \
--env MYSQL_SERVER_FULL_NAME=${MYSQL_SERVER_FULL_NAME} \
MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME=${MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME} \
MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_LOGIN_NAME=${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_LOGIN_NAME} \
MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD=${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD}
az spring-cloud app deploy --name ${VISITS_SERVICE} \
--jar-path ${VISITS_SERVICE_JAR} \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m -Dspring.profiles.active=mysql' \
--env MYSQL_SERVER_FULL_NAME=${MYSQL_SERVER_FULL_NAME} \
MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME=${MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME} \
MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_LOGIN_NAME=${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_LOGIN_NAME} \
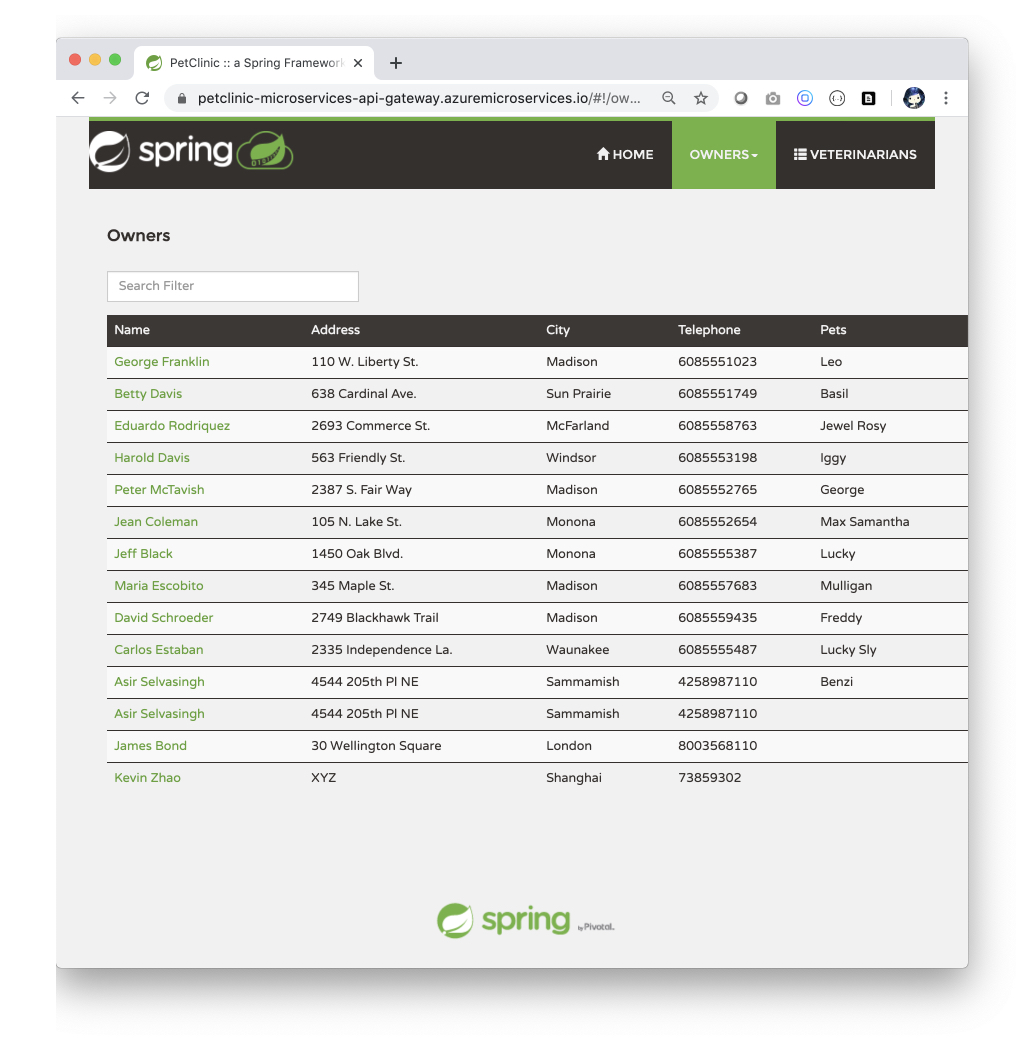
MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD=${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD} az spring-cloud app show --name ${API_GATEWAY} | grep urlNavigate to the URL provided by the previous command to open the Pet Clinic microservice application.
Open the Application Insights created by Azure Spring Cloud and start monitoring microservice applications.
Navigate to the Application Map blade:
![]()
Navigate to the Performance blade:

Navigate to the Performance/Dependenices blade - you can see the performance number for dependencies,
particularly SQL calls:

Click on a SQL call to see the end-to-end transaction in context:

Navigate to the Failures/Exceptions blade - you can see a collection of exceptions:

Click on an exception to see the end-to-end transaction and stacktrace in context:

Navigate to the Metrics blade - you can see metrics contributed by Spring Boot apps,
Spring Cloud modules, and dependencies.
The chart below shows gateway-requests (Spring Cloud Gateway), hikaricp_connections
(JDBC Connections) and http_client_requests.
Spring Boot registers a lot number of core metrics: JVM, CPU, Tomcat, Logback...
The Spring Boot auto-configuration enables the instrumentation of requests handled by Spring MVC.
All those three REST controllers OwnerResource, PetResource and VisitResource have been instrumented by the @Timed Micrometer annotation at class level.
customers-serviceapplication has the following custom metrics enabled:- @Timed:
petclinic.owner - @Timed:
petclinic.pet
- @Timed:
visits-serviceapplication has the following custom metrics enabled:- @Timed:
petclinic.visit
- @Timed:
You can see these custom metrics in the Metrics blade:

You can use the Availability Test feature in Application Insights and monitor
the availability of applications:

Navigate to the Live Metrics blade - you can see live metrics on screen with low latencies < 1 second:

If you do not have a Key Vault yet, run the following commands to provision a Key Vault:
export KEY_VAULT=your-keyvault-name # customize this
az keyvault create --name ${KEY_VAULT} -g ${RESOURCE_GROUP}Add the MySQL secrets to your Key Vault:
az keyvault secret set --vault-name ${KEY_VAULT} --name "MYSQL-SERVER-FULL-NAME" --value ${MYSQL_SERVER_FULL_NAME}
az keyvault secret set --vault-name ${KEY_VAULT} --name "MYSQL-DATABASE-NAME" --value ${MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME}
az keyvault secret set --vault-name ${KEY_VAULT} --name "MYSQL-SERVER-ADMIN-LOGIN-NAME" --value ${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_LOGIN_NAME}
az keyvault secret set --vault-name ${KEY_VAULT} --name "MYSQL-SERVER-ADMIN-PASSWORD" --value ${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD}Create a service principal with enough scope/role to manage your Azure Spring Cloud instance:
az ad sp create-for-rbac --role contributor --scopes /subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION_ID> --sdk-authWith results:
{
"clientId": "<GUID>",
"clientSecret": "<GUID>",
"subscriptionId": "<GUID>",
"tenantId": "<GUID>",
"activeDirectoryEndpointUrl": "https://login.microsoftonline.com",
"resourceManagerEndpointUrl": "https://management.azure.com/",
"sqlManagementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net:8443/",
"galleryEndpointUrl": "https://gallery.azure.com/",
"managementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net/"
}Add them as secrets to your Key Vault:
az keyvault secret set --vault-name ${KEY_VAULT} --name "AZURE-CREDENTIALS-FOR-SPRING" --value "<results above>"To generate a key to access the Key Vault, execute command below:
az ad sp create-for-rbac --role contributor --scopes /subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE_GROUP>/providers/Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/<KEY_VAULT> --sdk-authThen, follow the steps here to add access policy for the Service Principal.
In the end, add this service principal as secrets named "AZURE_CREDENTIALS" in your forked GitHub repo following the steps here.
Finally, edit the workfolw file .github/workflows/action.yml in your forked repo to fill in the names of resource group and the Azure Spring Cloud instance name that you just created:
env:
RESOURCE_GROUP: resource-group-name # customize this
SPRING_CLOUD_SERVICE: azure-spring-cloud-name # customize thisAfter you commited this change, you will see GitHub Actions triggered to build and deploy all the apps in the repo to your Azure Spring Cloud instance.

Use Azure Key Vault to store and load secrets to connect to MySQL database.
If you skipped the Automation step, create an Azure Key Vault and store database connection secrets.
az keyvault create --name ${KEY_VAULT} -g ${RESOURCE_GROUP}
export KEY_VAULT_URI=$(az keyvault show --name ${KEY_VAULT} | jq -r '.properties.vaultUri')Store database connection secrets in Key Vault.
az keyvault secret set --vault-name ${KEY_VAULT} \
--name "MYSQL-SERVER-FULL-NAME" --value ${MYSQL_SERVER_FULL_NAME}
az keyvault secret set --vault-name ${KEY_VAULT} \
--name "MYSQL-DATABASE-NAME" --value ${MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME}
az keyvault secret set --vault-name ${KEY_VAULT} \
--name "MYSQL-SERVER-ADMIN-LOGIN-NAME" --value ${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_LOGIN_NAME}
az keyvault secret set --vault-name ${KEY_VAULT} \
--name "MYSQL-SERVER-ADMIN-PASSWORD" --value ${MYSQL_SERVER_ADMIN_PASSWORD}Enable System Assigned Identities for applications and export identities to environment.
az spring-cloud app identity assign --name ${CUSTOMERS_SERVICE}
export CUSTOMERS_SERVICE_IDENTITY=$(az spring-cloud app show --name ${CUSTOMERS_SERVICE} | jq -r '.identity.principalId')
az spring-cloud app identity assign --name ${VETS_SERVICE}
export VETS_SERVICE_IDENTITY=$(az spring-cloud app show --name ${VETS_SERVICE} | jq -r '.identity.principalId')
az spring-cloud app identity assign --name ${VISITS_SERVICE}
export VISITS_SERVICE_IDENTITY=$(az spring-cloud app show --name ${VISITS_SERVICE} | jq -r '.identity.principalId')Add an access policy to Azure Key Vault to allow Managed Identities to read secrets.
az keyvault set-policy --name ${KEY_VAULT} \
--object-id ${CUSTOMERS_SERVICE_IDENTITY} --secret-permissions get list
az keyvault set-policy --name ${KEY_VAULT} \
--object-id ${VETS_SERVICE_IDENTITY} --secret-permissions get list
az keyvault set-policy --name ${KEY_VAULT} \
--object-id ${VISITS_SERVICE_IDENTITY} --secret-permissions get listActivate applications to load secrets from Azure Key Vault.
# DO NOT FORGET to replace the value for "azure.keyvault.uri" JVM startup parameter with your Key Vault URI
az spring-cloud app update --name ${CUSTOMERS_SERVICE} \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m -Dspring.profiles.active=mysql,key-vault -Dazure.keyvault.uri=https://petclinic-keyvault.vault.azure.net/' \
--env
# DO NOT FORGET to replace the value for "azure.keyvault.uri" JVM startup parameter with your Key Vault URI
az spring-cloud app update --name ${VETS_SERVICE} \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m -Dspring.profiles.active=mysql,key-vault -Dazure.keyvault.uri=https://petclinic-keyvault.vault.azure.net/' \
--env
# DO NOT FORGET to replace the value for "azure.keyvault.uri" JVM startup parameter with your Key Vault URI
az spring-cloud app update --name ${VISITS_SERVICE} \
--jvm-options='-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m -Dspring.profiles.active=mysql,key-vault -Dazure.keyvault.uri=https://petclinic-keyvault.vault.azure.net/' \
--envIn this quickstart, you've deployed an existing Spring microservices app using Azure CLI, Terraform and GitHub Actions. To learn more about Azure Spring Cloud, go to:
- Azure Spring Cloud
- Azure Spring Cloud docs
- Deploy Spring microservices from scratch
- Deploy existing Spring microservices
- Azure for Java Cloud Developers
- Spring Cloud Azure
- Spring Cloud
This Spring microservices sample is forked from spring-petclinic/spring-petclinic-microservices - see Petclinic README.
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.