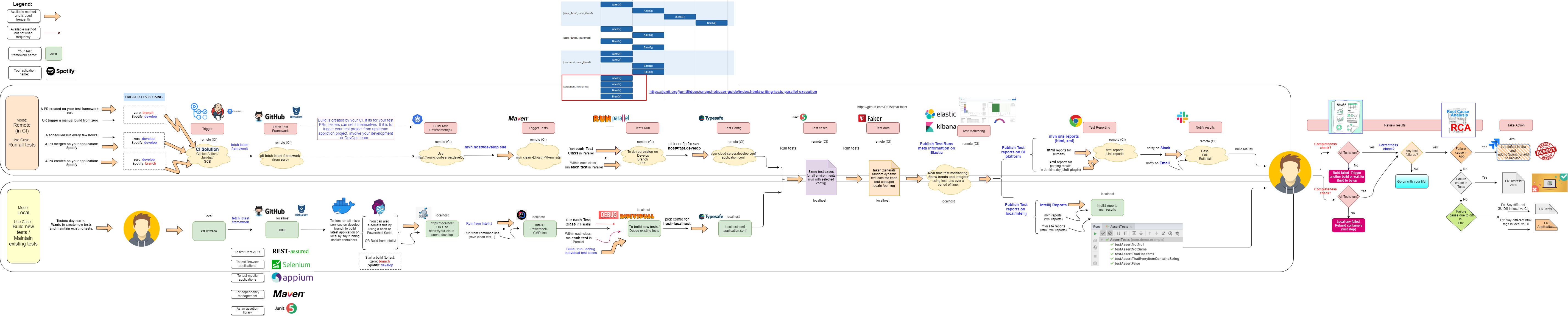
Zero is our feature rich, core test automation framework, that can be used as an underlying automation framework for any/and all kind of test automation frameworks (such as API, Browser, Mobile App).
- JDK 11 - as language of choice for writing this test framework.
- Maven 3.8.6+ - for project dependency management and running tests in CI.
- git-crypt - to encrypt/decrypt secrets. One time set up instructions here.
- Problem solving based learning (Learn something when a problem comes. This way, you will remember it better).
- First make it work, then make it better (Specially when working with new tools or tech, don't worry about getting it right the first time. First focus on making it work, then refactor to make it better)
A good guideline to test any project is:
Test the right things, in the right order, at the right time.
- Risk based testing (Test the right things and avoid testing 3rd party/low risk software).
- Follow test pyramid (in the right order)
- Fail fast, fail early (at the right time)
- Prevent breaking changes from merging (Run fast and stable API tests as a part of application pull requests).
- If cannot prevent, test immediately on merge Run slower and flaky Mobile/Browser tests immediately on merge of pull requests on new deployed env.
- Test asap, if cannot test on merge Use your creative imagination to do exploratory tests, UX testing post merge.
Some of the key goals and objectives of our test framework are:
- Easy to understand (Separate test intentions from implementation)
- Easy to maintain (Separation of concerns between data, config, code and tests).
- Easy to scale (Prefer composition over inheritance. Follow SOLID principles).
- Fast execution time (Create atomic, independent tests that can run in parallel to cut down on execution times).
- Test at right moment (Have various CI workflows that allow testing as soon as possible).
- Reliable, robust tests (Create generic classes that have methods that wait for the right state before acting on elements)
- Flexible tests that can run on any test env (Move all env related information to its own config files, so that tests can flexibly run on any test environment)
There are some standard files, there deserves a section of their own. These are:
- README.md file (This is where you tell what your project is all about and how others can use it.).
- junit-platform.properties file (This is where you specify your projects execution mode i.e. serial, or any of the available parallel execution modes)
- .log4j properties file. (This specifies the log level for your project)
- application.conf and other conf file. (This is where we specify common application config and config for each test environment)
- .gitignore file. (This contains everything that you are not interested in version controlling.)
- .gitattributes file. (This is where you specify attributes of any files that are being version controlled.)
- .editorconfig file. (This provides a way to have a common formatting rules within your team. In absence of this, your PRs would be a mess to review.)
- pom.xml file. (This is where you define all your maven project dependencies.)
- LICENSE file. (This is where you give permission to others to make use of your open source project.)
- Dockerfile. (This is where you automate your test environment. i.e. all the parts that your project depends on; such as having a machine, JDK, Maven, setting up system environments, any other tools, etc all.)
- .dockerignore file. (Like gitignore file, here we specify everything that we want to be ignored from passing to docker build context.)
- docker-compose.yml file. (A convenient way to set up a local instance of your dockerized application on your localhost machine. )
Key tools to be used in this core framework are:
- Java (As the core programming language)
- Maven (for automatic dependency management)
- Junit 5 (for assertions)
- Slf4J/Log4J (for logging interface and as a logging library)
- Typesafe (for application configuration for multiple test environments)
- Git crypt (for managing secrets)
- Surefire (for xml reports in CI)
- Surefire Site plugin (for html reports in CI)
- Github (for version control)
- Github actions (for continuous integration)
- Faker library (for generating random test data for different locales - germany, france, netherlands, english)
- Slack integration (for giving notifications on pull requests)
- Elastic and Kibana (for test monitoring)
- Docker (for automating test framework's environment)
- Powershell or bash Script (for automating building test environment)
- SonarQube/SonarLint (for keeping your code clean and safe)
- Badges (for a quick view on your project meta and build status)
Key tools that we will use in other frameworks, that will all extend this core framework are:
- RestAssured (library for Rest API automation)
- Selenium (library for Browser automation)
- Appium (library for Mobile ios/android automation)
- README-wiki
- how-to-write-a-good-readme-file
- another-good-readme-example
- java-gitignore-file-example
- manage multiple github accounts
- manage multiple git configs for different accounts
- logout/login in multiple accounts
- adding ssh key to the ssh agent
- adding-a-new-ssh-key-to-your-github-account
- auto launching ssh keys for git on windows
- GitCredentialManager