Basic Ansible Learning Project
Requirements:
- Vagrant
- Virtualbox/VMware
- WSL / Native Linux / Mac
- First create the VM's
cd ubuntu/
vagrant up
cd centos/
vagrant up- Create ssh-key to login on the target-machines
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "Ansible" -f ~/.ssh/ansible- Edit hosts file of the "ManagerHost" In my case WLS
# Ansible
192.168.1.126 node-6
192.168.1.125 node-5
192.168.1.124 node-4
192.168.1.123 node-3
192.168.1.122 node-2
192.168.1.121 node-1
- Install ansible on Controler machine and add ssh on each of the machines
apt install ansible -y &&
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/ansible.pub vagrant@node-1 &&
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/ansible.pub vagrant@node-2 &&
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/ansible.pub vagrant@node-3 &&
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/ansible.pub vagrant@node-4 &&
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/ansible.pub vagrant@node-5 &&
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/ansible.pub vagrant@node-6 &&- First ANSIBLE command
ansible all --key-file ~/.ssh/ansible -i inventory -m ping -u vagrantnode-3 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
node-2 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
node-1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}- Ansible gather_facts
ansible all -m gather_facts --limit node-1This module is automatically called by playbooks to gather useful variables about remote hosts that can be used in playbooks.
- ansible adhoc commands
An Ansible ad hoc command uses the /usr/bin/ansible command-line tool to automate a single task on one or more managed nodes. "Privilege permitions for exec commands on target machines. Context: For the apt module we're using is possible to look at the official DOC for it Here is the link: https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.9/modules/apt_module.html"
NOK:
ansible all -m apt -a update_cache=truenode-3 | FAILED! => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "Failed to lock apt for exclusive operation: Failed to lock /var/lib/apt/lists/lock"
}
node-1 | FAILED! => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "Failed to lock apt for exclusive operation: Failed to lock /var/lib/apt/lists/lock"
}
node-2 | FAILED! => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "Failed to lock apt for exclusive operation: Failed to lock /var/lib/apt/lists/lock"To work we need to add --become and --ask-become-me-pass
ansible all -m apt -a update_cache=true --become --ask-become-passBECOME password:
node-2 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"cache_update_time": 1699108086,
"cache_updated": true,
"changed": true
}
node-1 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"cache_update_time": 1699108087,
"cache_updated": true,
"changed": true
}
node-3 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"cache_update_time": 1699108087,
"cache_updated": true,
"changed": true
}The command bellow we can install vim-nox editor, vagrant does not has sudo pass So you can use the command without --ask-become-pass.
ansible all -m apt -a name=vim-nox --becomeTo upgrade the system
ansible all -m apt -a "upgrade=dist" --become- Playbooks
A playbook is a multiple-machine deployment system, reusable and repeatable
touch install_apache.yml---
- hosts: all # Run in all Hosts on inventary
become: true # Run with sudo privileges
tasks: # The tasks to run
- name: Update Repository Index # Simple indicative name
apt: # Module apt
update_cache: yes # update index Cache
- name: install apache2 package # Indicative Name
apt: # Module APT
name: apache2 # The module to installansible-playbook install_apache.yml
PLAY [all] ****************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ****************************************************************************************************
ok: [node-1]
ok: [node-3]
ok: [node-2]
TASK [install apache2 package] ********************************************************************************************
changed: [node-2]
changed: [node-3]
changed: [node-1]
PLAY RECAP ****************************************************************************************************************
node-1 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-2 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-3 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=09.We can bind hosts by groups, like the example bellow:
[web_servers]
node-1
node-2
[db_servers]
node-3
node-4
[file_servers]
node-5
node-6- Now is possible to group tasks
ansible db_servers -m ping
ansible web_servers -m ping
ansible file_servers -m ping- Tags are metadata you canb attach to the tasks in an Ansible playbook
- name: Install MariDB package
tags: mariadb,db,ubuntu
apt:
name: mariadb-server
state: latest
when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu'How to list Tags available
ansible-playbook --list-tags site.yml
playbook: site.yml
play #1 (all): all TAGS: []
TASK TAGS: [always]
play #2 (web_servers): web_servers TAGS: []
TASK TAGS: [apache, apache2, centos, httpd, ubuntu]
play #3 (db_servers): db_servers TAGS: []
TASK TAGS: [centos, db, mariadb, ubuntu]
play #4 (file_servers): file_servers TAGS: []
TASK TAGS: [samba]Now we'll target centos only
ansible-playbook --tags centos site.yml
PLAY [all] *******************************************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *******************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [node-4]
ok: [node-5]
ok: [node-3]
ok: [node-1]
ok: [node-2]
ok: [node-6]
TASK [Install Updates (CentOS)] **********************************************************************************************************************************
skipping: [node-1]
skipping: [node-2]
skipping: [node-3]
ok: [node-5]
ok: [node-4]
ok: [node-6]
TASK [Install Update (Ubuntu)] ***********************************************************************************************************************************
skipping: [node-5]
skipping: [node-4]
skipping: [node-6]
ok: [node-3]
ok: [node-1]
ok: [node-2]
PLAY [web_servers] ***********************************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *******************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [node-5]
ok: [node-2]
ok: [node-1]
TASK [update and install httpd, php package for CentOS] **********************************************************************************************************
skipping: [node-1]
skipping: [node-2]
ok: [node-5]
PLAY [db_servers] ************************************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *******************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [node-4]
ok: [node-3]
TASK [Install MariDB package] ************************************************************************************************************************************
skipping: [node-3]
ok: [node-4]
PLAY [file_servers] **********************************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *******************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [node-6]
PLAY RECAP *******************************************************************************************************************************************************
node-1 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-2 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-3 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-4 : ok=4 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-5 : ok=4 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-6 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0 You can run tasks plays on specifics tags listed on the first command. If you want to use multiple tags make sure to use double quotes: "samba,db,httpd"
- You can use copy module to transfer files to target machines.
- name: Copy Default html file for site
tags: httpd, centos, apache
copy:
src: default_site.html
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644ansible-playboot site.ymlAt the example before the task will send the default_site.html to all webservers:
- Is possible to use "service" module to modify status of any service
Below we use httpd service as example
- name: Start httpd (CENTOS)
tags: httpd, centos, apache
service:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes # This the option to enable service on reboot.
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'TASK [Start httpd (CENTOS)] **************************************************************************************************************************************
skipping: [node-1]
skipping: [node-2]
changed: [node-5]
PLAY RECAP *******************************************************************************************************************************************************
node-1 : ok=5 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=3 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-2 : ok=5 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=3 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-3 : ok=4 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-4 : ok=4 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-5 : ok=6 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-6 : ok=4 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0Note: use "enable: yes" to ensure the service starts on reboot
- On the example below we can use the restart state of service module to restart the httpd service together with lineinfile module.
- name: Change Email Addres for admin
tags: apache, centos, httpd
lineinfile:
path: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
regexp: '^ServerAdmin'
line: ServerAdmin test@gmail.com'
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
register: httpd # Simple stores a variable to use in the next task
- name: restart httpd (CENTOS)
tags: apache, centos, httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
when: httpd.changed # VAriable from register httpdTASK [Change Email Addres for admin] *****************************************************************************************************************************
skipping: [node-1]
skipping: [node-2]
changed: [node-5]
TASK [restart httpd (CENTOS)] ************************************************************************************************************************************
skipping: [node-1]
skipping: [node-2]
changed: [node-5]
PLAY RECAP *******************************************************************************************************************************************************
node-1 : ok=5 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=5 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-2 : ok=5 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=5 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-3 : ok=4 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-4 : ok=4 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-5 : ok=8 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-6 : ok=4 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0 First we change a line on httpd.conf file the confirm that with register and restarted service on next task.
- With the task below we can create users using the "user" module.
- hosts: all
become: true
tasks:
- name: Create zuka user
tags: always
user:
user: zuka
group: root ansible-playbook site.yml
TASK [Create zuka user] ******************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [node-5]
changed: [node-2]
changed: [node-4]
changed: [node-1]
changed: [node-3]
changed: [node-6]
PLAY RECAP *******************************************************************************************************************************************************
node-1 : ok=7 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=5 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-2 : ok=7 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=5 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-3 : ok=6 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-4 : ok=6 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-5 : ok=9 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=3 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-6 : ok=6 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0 - Create an ssh-key to an specific user, give it root acess at sudoers
Modules:
- copy
- authorized_keys
- user
- name: Create an sshkey to zuka user
tags: always
authorized_key:
user: zuka
key: "ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIOXbwVjReKVrC18mlTzbOFu5Ncz6VlwcjoaKjNTeWRs+ Ansible"
- name: add sudoers file for zuka user
tags: always
copy:
src: sudoer_zuka
dest: /etc/sudoers.d/zuka
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0440TASK [add sudoers file for zuka user] ****************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [node-1]
changed: [node-5]
changed: [node-2]
changed: [node-4]
changed: [node-3]
changed: [node-6]
TASK [add sudoers file for zuka user] ****************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [node-1]
changed: [node-5]
changed: [node-2]
changed: [node-4]
changed: [node-3]
changed: [node-6]
now you can run playbooks with zuka user /or whatever name you want yo use.
- Now we're going to use roles to simplify our ansible-playbook since is full and not organized.
roles/
├── base
│ └── tasks
│ └── main.yml
├── db_servers
│ └── tasks
│ └── main.yml
├── file_servers
│ └── tasks
│ └── main.yml
├── web_servers
│ ├── files
│ │ ├── default_site.html
│ │ └── sudoer_zuka
│ └── tasks
│ └── main.yml
└── workstations
└── tasks
└── main.yml
Each role has it's own tasks contianing it's own main.yml If you have your tasks has to move or copy files you should put into the role it-self like web_servers role.
- You define the roles as the examples bellow:
- hosts: all
become: true
roles:
- base
- hosts: web_servers
become: true
roles:
- web_servers
- hosts: db_servers
become: true
roles:
- db_servers
- hosts: file_servers
become: true
roles:
- file_servers- We can ping hosts in two ways comand-line and playbook
ansible-playbook all -m ping---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: This is a ping to all Hosts
ping:- Now we can create hosts variables
mkdir host_vars
for i in {1..6};do touch node-$i.yml;done
ls -lrth
-rw-r--r-- 1 nerdevops nerdevops 0 Nov 13 18:29 node-1.yml
-rw-r--r-- 1 nerdevops nerdevops 0 Nov 13 18:29 node-6.yml
-rw-r--r-- 1 nerdevops nerdevops 0 Nov 13 18:29 node-5.yml
-rw-r--r-- 1 nerdevops nerdevops 0 Nov 13 18:29 node-4.yml
-rw-r--r-- 1 nerdevops nerdevops 0 Nov 13 18:29 node-3.yml
-rw-r--r-- 1 nerdevops nerdevops 0 Nov 13 18:29 node-2.yml- Centos vars for apache:
apache_package_name: httpd
apache_service: httpd
php_package_name: php- Ubuntu vars:
apache_package_name: apache2
apache_service: apache2
php_package_name: libapache2-mod-php- Now it's easy to call the as variables on tasks main.yml of web_servers
- name: update and install apache2, php package for Ubuntu # Indicative Name
tags: apache,httpd,php
package: # Module APT
name:
- "{{ apache_package_name }}"
- "{{ php_package_name }}" # The package
state: latest
- name: Start httpd (CENTOS)
tags: apache,httpd
service:
name: "{{ apache_service }}"
state: started
enabled: yesNote: In brackets we have our variables witch we already defined on host_vars files.
- Templates allow us to modify any variable.
- Each webserver host_variables files must contain the following lines to use as variables:
html_host: "node-1"
html_template: default_site.html.j2
note: # Change for the other ondes, node-2 and node-5
- Then create the templates folder
cd roles/web_severs
mkdir templates
cp ../files/default_site.html default_site.html.j2- Insert the variable:
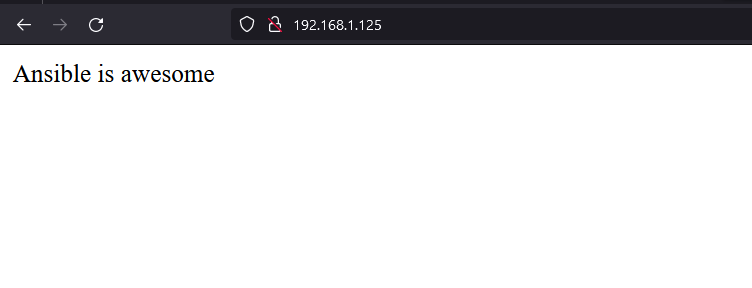
<html>
<title>
Website Teste
</title>
<body>
<p> Ansible is awesome on host "{{ html_host }}"</p>
</body>
</html>- Now lets change the task to contain templates instead of copy module.
- name: Copy Default html file for site
tags: httpd, centos, apache
template: # Use to be copy, let's test template module
src: "{{ html_template }}"
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644We have the ""{{ html_template }}"" Variable and "{{ html_host }}" defined and used.
- Running playbook:
ansible-playbook site.yml
TASK [web_servers : Copy Default html file for site] *********************************************************************************
changed: [node-5]
changed: [node-2]
changed: [node-1]
PLAY RECAP ***************************************************************************************************************************
node-1 : ok=8 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-2 : ok=8 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-3 : ok=6 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-4 : ok=6 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-5 : ok=9 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0
node-6 : ok=6 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0That's how we use tamplates to change unic values.