Temporary installation:
pip install git+https://github.com/nesar/watercolor.gitFuture:
pip install watercolorfrom watercolor.paint import photometry_from_catalogFirst we load the galaxy catalog. The main physical quantities required for painting the colors are the metallicities, stellar mass and age of the star particles of a galaxy.
galaxy_star_catalog_file='../watercolor/data/test_hacc_stellar_catalog/Gal_z0_hbin.txt' # HACC galaxy catalog
final_sed_mJy, final_wave_um, lsst_mags, spherex_mags, cosmos_mags = photometry_from_catalog(galaxy_star_catalog_file)Number of galaxies: 200
# Create the main figure and a gridspec object
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 2, height_ratios=[1,1])
# Create the three subplots
ax0 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, :]) # Top panel spanning both columns
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 0]) # Bottom left panel
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 1]) # Bottom right panel
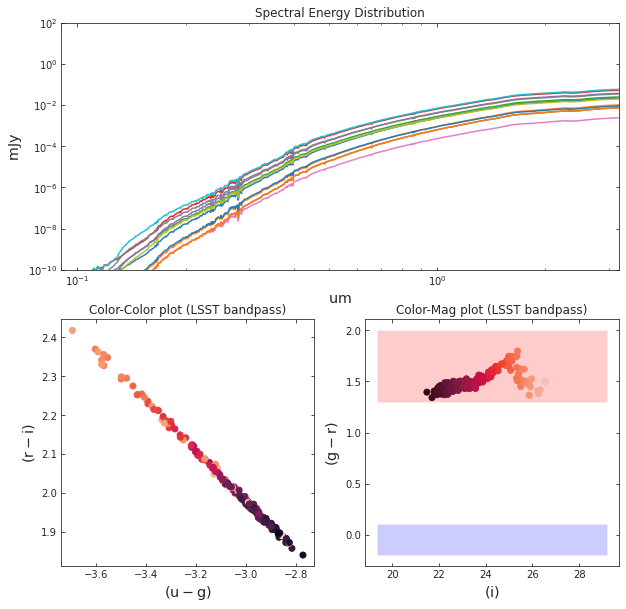
ax0.set_title('Spectral Energy Distribution')
ax1.set_title('Color-Color plot (LSST bandpass)')
ax2.set_title('Color-Mag plot (LSST bandpass)')
np.random.seed(2)
for gal_id in np.random.randint(0, final_sed_mJy.shape[0], 12):
ax0.plot(final_wave_um[gal_id], final_sed_mJy[gal_id], label=str(gal_id), alpha=0.94)
ax0.set_xlim(0.09, 3.2)
ax0.set_ylim(1e-10, 1e2)
ax0.set_xscale('log')
ax0.set_yscale('log')
ax0.set_xlabel(r'${\rm um}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
ax0.set_ylabel(r'${\rm mJy}}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
# ax[0].legend(fontsize='x-large', ncol=3, title='Galaxy number')
u, g, r, i, z, Y = lsst_mags.T
ax1.scatter(u-g, r-i, c=Y)
ax1.set_xlabel(r'${\rm (u-g)}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
ax1.set_ylabel(r'${\rm (r-i)}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
ax2.scatter(i, g-r, c=u)
ax2.set_xlabel(r'${\rm (i)}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
ax2.set_ylabel(r'${\rm (g-r)}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
# ax[2].axhline(y=1.3, color='red')
# ax[2].axhline(y=0.1, color='blue')
ax2.fill_between( np.linspace(0.9*i.min(), 1.1*i.max(), 100), 1.3, 2.0, facecolor='red', alpha=0.2, interpolate=True)
ax2.fill_between( np.linspace(0.9*i.min(), 1.1*i.max(), 100), -0.2, 0.1, facecolor='blue', alpha=0.2, interpolate=True)
plt.show()import watercolor
from watercolor.load_sim_stellar_catalog import load_hacc_galaxy_data
from watercolor.calculate_csp import calc_fluxes_for_galaxy
from watercolor.load_sps_library import LIBRARY_FLUX_FILE, LIBRARY_WAVE_FILE, LIBRARY_AGE_FILE, LIBRARY_METAL_FILE
from watercolor.dust_attenuation import spectrum_dusted, log_total_stellar_metal, log_total_stellar_mass
from watercolor.cosmic_distance_effects import combine_redshift_and_dimming_effect
from watercolor.filter_convolution import load_survey_pickle, photometry_from_spectrafof_halo_tag, if_satellite, galaxy_tags, stellar_idx, metal_hydro, mass, age_hydro, x, y, z , vx, vy, vz = watercolor.load_sim_stellar_catalog.load_hacc_galaxy_data(galaxy_star_catalog_file)galaxy_number = 4 # Choosing one of the galaxies in the catalog
unique_galaxy_tag = np.unique(galaxy_tags)[galaxy_number]
print('Number of galaxies: %d'%np.unique(galaxy_tags).shape[0])
mstar_i = mass[galaxy_tags == unique_galaxy_tag]
metal_i = metal_hydro[galaxy_tags == unique_galaxy_tag]
if_satellite_i = if_satellite[galaxy_tags == unique_galaxy_tag]
logZ = log_total_stellar_metal(metal_i, mstar_i)
logmstar = log_total_stellar_mass(mstar_i)Number of galaxies: 200
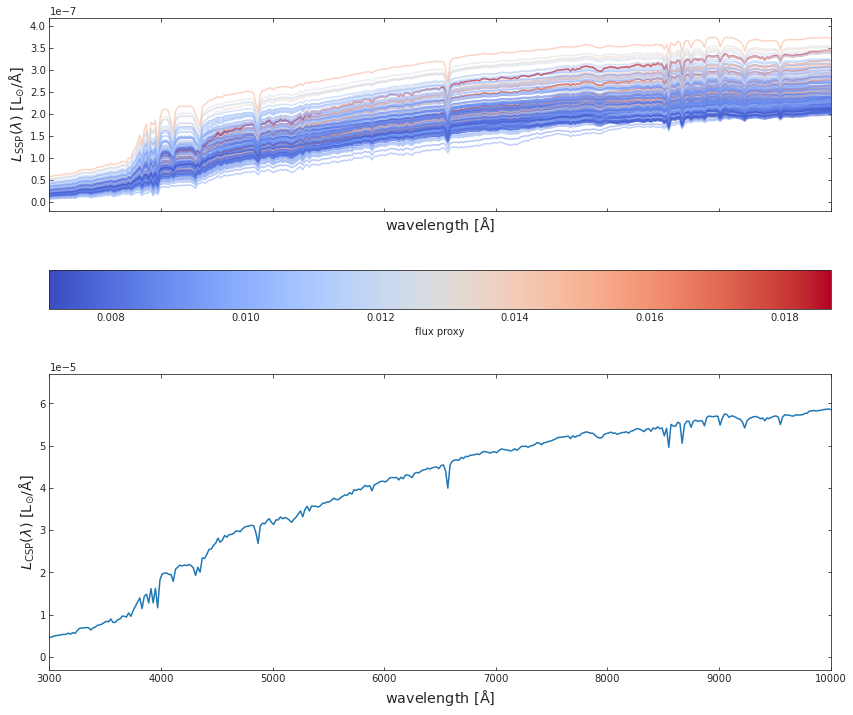
3. After selecting a unique galaxy tag, we calculate the SED. This is the rest-frame SED is due to spectral emission alone, and without dust attenuation.
spec_wave_ssp, spec_flux_ssp, spec_csp, flux_proxy, gal_stellar_mass = watercolor.calculate_csp.calc_fluxes_for_galaxy(galaxy_star_catalog_file,
unique_galaxy_tag,
LIBRARY_FLUX_FILE,
LIBRARY_WAVE_FILE,
LIBRARY_AGE_FILE,
LIBRARY_METAL_FILE)fig, a = plt.subplots(2,1, figsize=(14, 12), sharex=True, sharey=False)
c_norm = mpl.colors.Normalize(vmin=np.min(flux_proxy), vmax=np.max(flux_proxy))
c_map = mpl.cm.coolwarm
s_map = mpl.cm.ScalarMappable(cmap=c_map, norm=c_norm)
s_map.set_array([])
for idx in range(spec_flux_ssp.shape[0]):
# spec_flux_ssp[idx] = spec_ssp(age_hydro[ssp_id], metal_hydro[ssp_id], mass[ssp_id])
a[0].plot(spec_wave_ssp, spec_flux_ssp[idx],
# color=s_map.to_rgba(np.log10(mass[ssp_id])),
color=s_map.to_rgba(flux_proxy[idx]),
alpha=0.5)
fig.colorbar(s_map, ax = a[0],
orientation = 'horizontal',
# label=r'stellar mass', pad=0.2)
label=r'flux proxy', pad=0.2)
#####################################################################
a[1].plot(spec_wave_ssp, spec_csp)
# a[0].set_ylim(1e-9, 1e-6)
# a[0].set_yscale('log')
# a[1].set_yscale('log')
# a[1].set_xscale('log')
a[1].set_xlim(3e3, 1e4)
a[0].set_xlabel(r'${\rm wavelength\ [\AA]}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
a[1].set_xlabel(r'${\rm wavelength\ [\AA]}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
a[0].set_ylabel(r'$L_{\rm SSP}(\lambda)\ {\rm [L_{\odot}/\AA]}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
a[1].set_ylabel(r'$L_{\rm CSP}(\lambda)\ {\rm [L_{\odot}/\AA]}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
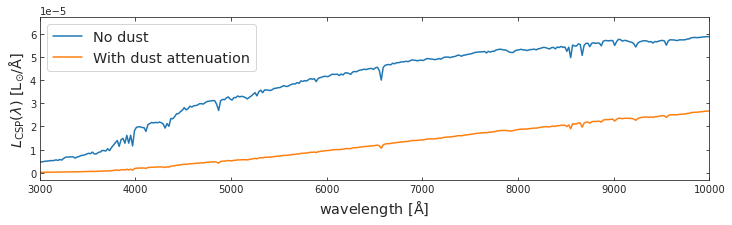
plt.show()spec_wave_csp_dusted = spectrum_dusted(spec_csp, spec_wave_ssp, logmstar, logZ, 0.01)f, a = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 3))
a.plot(spec_wave_ssp, spec_csp, label='No dust')
a.plot(spec_wave_ssp, spec_wave_csp_dusted, label='With dust attenuation')
a.set_xlim(3e3, 1e4)
a.set_xlabel(r'${\rm wavelength\ [\AA]}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
a.set_ylabel(r'$L_{\rm CSP}(\lambda)\ {\rm [L_{\odot}/\AA]}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
a.legend(fontsize='x-large')<matplotlib.legend.Legend>
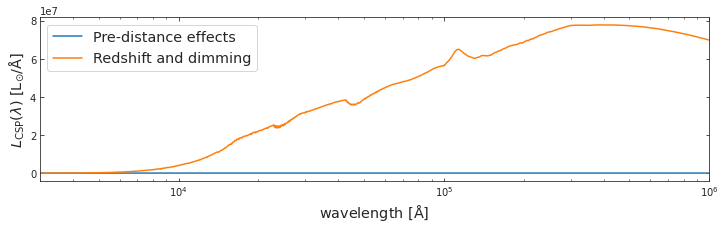
redsh_wave, redsh_spec = combine_redshift_and_dimming_effect(wave=spec_wave_ssp,
spec=spec_wave_csp_dusted,
galaxy_redshift=0.001)f, a = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 3))
a.plot(spec_wave_ssp, spec_csp, label='Pre-distance effects')
a.plot(redsh_wave, redsh_spec*1e6, label='Redshift and dimming')
# a.set_xlim(3e3, 1e4)
a.set_xlim(3e3, 1e6)
a.set_xscale('log')
# a.set_yscale('log')
a.set_xlabel(r'${\rm wavelength\ [\AA]}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
a.set_ylabel(r'$L_{\rm CSP}(\lambda)\ {\rm [L_{\odot}/\AA]}$', fontsize = 'x-large')
a.legend(fontsize='x-large')<matplotlib.legend.Legend>
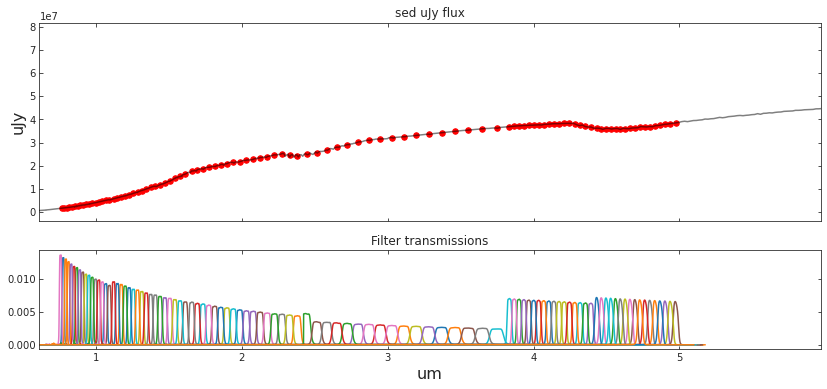
##### Load survey filters
SURVEY_STRING = 'SPHEREx'
central_wavelengths, bandpass_wavs, bandpass_vals, bandpass_names = load_survey_pickle(SURVEY_STRING)
##### Compute bandpasses
# sed_um_wave = spec_wave_ssp/1e4
# sed_mJy_flux = spec_csp*1e3
sed_um_wave = redsh_wave/1e4
sed_mJy_flux = redsh_spec*1e3
flux_survey, appmag_ext_survey, band_fluxes_survey = photometry_from_spectra(central_wavelengths,
sed_um_wave,
sed_mJy_flux,
bandpass_wavs,
bandpass_vals,
bandpass_names,
interp_kind='linear',
plot=True,
clip_bandpass=True)##### Load survey filters
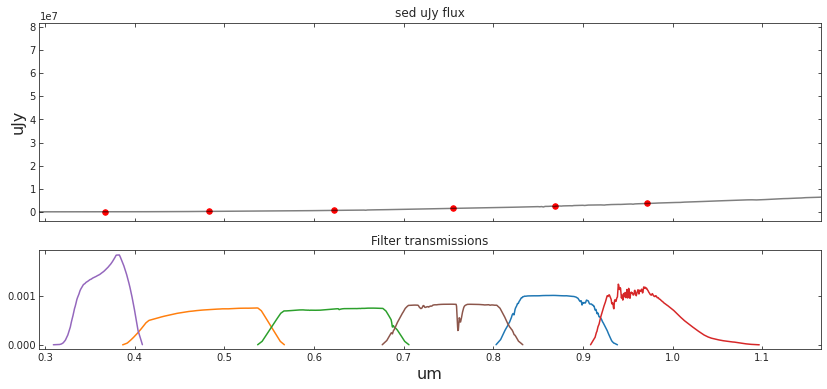
SURVEY_STRING = 'LSST'
central_wavelengths, bandpass_wavs, bandpass_vals, bandpass_names = load_survey_pickle(SURVEY_STRING)
##### Compute bandpasses
# sed_um_wave = spec_wave_ssp/1e4
# sed_mJy_flux = spec_csp*1e3
sed_um_wave = redsh_wave/1e4
sed_mJy_flux = redsh_spec*1e3
flux_survey, appmag_ext_survey, band_fluxes_survey = photometry_from_spectra(central_wavelengths,
sed_um_wave,
sed_mJy_flux,
bandpass_wavs,
bandpass_vals,
bandpass_names,
interp_kind='linear',
plot=True,
clip_bandpass=True)##### Load survey filters
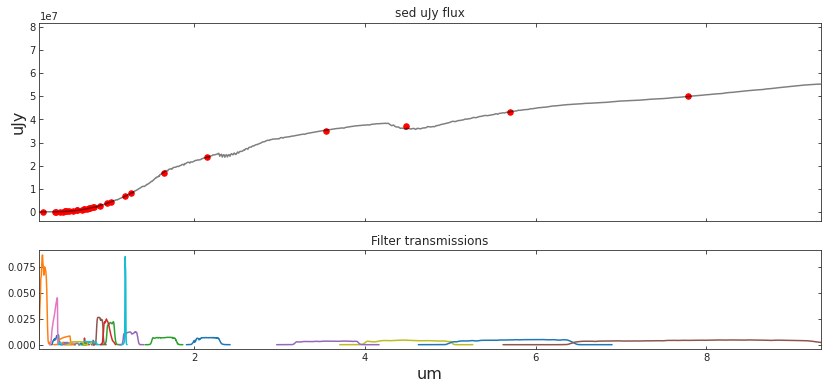
SURVEY_STRING = 'COSMOS'
central_wavelengths, bandpass_wavs, bandpass_vals, bandpass_names = load_survey_pickle(SURVEY_STRING)
##### Compute bandpasses
# sed_um_wave = spec_wave_ssp/1e4
# sed_mJy_flux = spec_csp*1e3
sed_um_wave = redsh_wave/1e4
sed_mJy_flux = redsh_spec*1e3
flux_survey, appmag_ext_survey, band_fluxes_survey = photometry_from_spectra(central_wavelengths,
sed_um_wave,
sed_mJy_flux,
bandpass_wavs,
bandpass_vals,
bandpass_names,
interp_kind='linear',
plot=True,
clip_bandpass=True)def radial_luminosity_profile(data,
num_bins=15):
# Calculate the radial distances for each point
data[:, 0] = data[:, 0] - np.mean(data[:, 0])
data[:, 1] = data[:, 1] - np.mean(data[:, 1])
r = np.sqrt(data[:, 0]**2 + data[:, 1]**2)
# Bin data and sum luminosities within each bin
bin_edges = np.linspace(0, r.max(), num_bins+1)
luminosity, _ = np.histogram(r, bins=bin_edges, weights=data[:, 2])
# Return the bin centers and corresponding luminosities
bin_centers = (bin_edges[:-1] + bin_edges[1:]) / 2
return bin_centers, luminosity
def radial_mass_density_from_lum(data,
num_bins=15):
data[:, 0] = data[:, 0] - np.mean(data[:, 0])
data[:, 1] = data[:, 1] - np.mean(data[:, 1])
# Calculate the radial distances for each point
r = np.sqrt(data[:, 0]**2 + data[:, 1]**2)
# Bin data and sum "masses" (luminosities) within each bin
bin_edges = np.linspace(0, r.max(), num_bins+1)
total_mass, _ = np.histogram(r, bins=bin_edges, weights=data[:, 3])
# Calculate the area of each annulus: π(R_outer^2 - R_inner^2)
areas = np.pi * (bin_edges[1:]**2 - bin_edges[:-1]**2)
# Compute mass density
mass_density = total_mass / areas
# Return the bin centers and corresponding mass densities
bin_centers = (bin_edges[:-1] + bin_edges[1:]) / 2
return bin_centers, mass_densitygal_tag_cond = np.where(galaxy_tags == unique_galaxy_tag)
x_select = (x[gal_tag_cond])# - np.mean(x[gal_tag_cond]))/(np.max(x[gal_tag_cond]) - np.min(x[gal_tag_cond]))
y_select = (y[gal_tag_cond])# - np.mean(y[gal_tag_cond]))/(np.max(y[gal_tag_cond]) - np.min(y[gal_tag_cond]))
z_select = np.trapz(spec_flux_ssp, spec_wave_ssp)
m_select = mass[gal_tag_cond]bin_centers, mass_densities_direct = radial_mass_density_from_lum(np.array([x_select, y_select, z_select, m_select]).T)
# # Plotting the radial mass density profile (direct from luminosity)
f, a = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 4))
# Plotting the radial mass density profile
a[0].plot(bin_centers, mass_densities_direct, '-ko', label='Mass Density Profile')
a[0].set_xlabel('Radial Distance (kpc)')
a[0].set_ylabel('Mass Density (M_solar/kpc^2)')
a[0].set_title('Radial Mass Density Profile')
a[0].legend()
bin_centers, luminosities = radial_luminosity_profile(np.array([x_select, y_select, z_select, m_select]).T)
# Plotting the radial luminosity profile
a[1].plot(bin_centers, luminosities, '-ko', label='Luminosity Profile')
a[1].set_xlabel('Radial Distance (kpc)')
a[1].set_ylabel('Luminosity (Jansky)')
a[1].set_title('Radial Luminosity Profile')
a[1].legend()
plt.show()from scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filterdef canvas_plot(data,
canvas_size = 256,
gauss_sigma = 8):
# Create a blank canvas
# size of the canvas for the image
canvas = np.zeros((canvas_size, canvas_size))
# Translate the x, y values to fit the canvas
x_scaled = ((data[:, 0] - data[:, 0].min()) / (data[:, 0].max() - data[:, 0].min()) * canvas_size).astype(int)
y_scaled = ((data[:, 1] - data[:, 1].min()) / (data[:, 1].max() - data[:, 1].min()) * canvas_size).astype(int)
# Adjust the scaling to ensure values are within the bounds of the canvas
x_scaled = np.clip(x_scaled, 0, canvas_size - 1)
y_scaled = np.clip(y_scaled, 0, canvas_size - 1)
# Reset the canvas
canvas = np.zeros((canvas_size, canvas_size))
# Place stars on the canvas using their luminosity
for x_ind, y_ind, quant_ind in zip(x_scaled, y_scaled, data[:, 2]):
canvas[y_ind, x_ind] += quant_ind
# Apply a Gaussian blur to emulate the glow of stars
blurred_canvas = gaussian_filter(canvas, sigma=gauss_sigma)
return blurred_canvasblurred_canvas_lum = canvas_plot(np.array([x_select, y_select, z_select]).T)
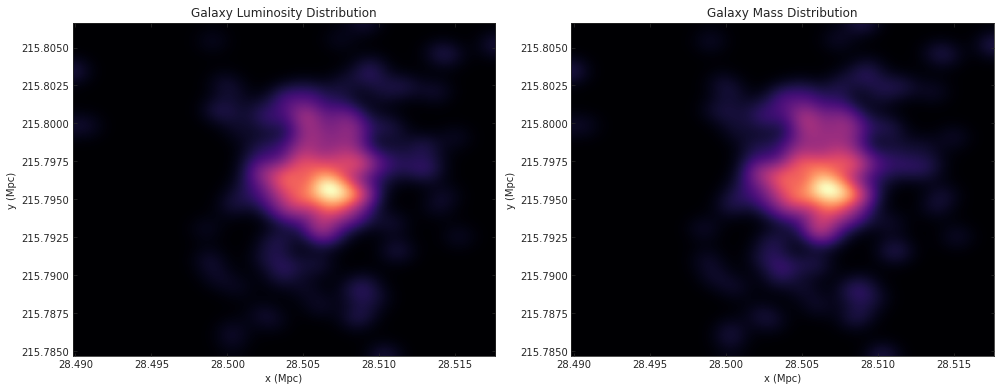
blurred_canvas_mass = canvas_plot(np.array([x_select, y_select, m_select]).T)f, a = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 8))
cmap_select = 'magma'
a[0].imshow(blurred_canvas_lum, cmap=cmap_select, origin='lower', extent=[x_select.min(), x_select.max(), y_select.min(), y_select.max()])
# a[0].colorbar(label='Luminosity (Jansky)')
a[0].set_title('Galaxy Luminosity Distribution')
a[0].set_xlabel('x (Mpc)')
a[0].set_ylabel('y (Mpc)')
a[0].set_aspect('equal', 'box')
a[1].imshow(blurred_canvas_mass, cmap=cmap_select, origin='lower', extent=[x_select.min(), x_select.max(), y_select.min(), y_select.max()])
# a[1].colorbar(label='Mass (Msol)')
# a[1].scatter(x_scaled, y_scaled, s=1)
a[1].set_title('Galaxy Mass Distribution')
a[1].set_xlabel('x (Mpc)')
a[1].set_ylabel('y (Mpc)')
a[1].set_aspect('equal', 'box')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()