Source code editor in pure Go.
- This is a know-what-you're-doing source code editor
- As the editor is being developed, the rules of how the UI interacts will become more well defined.
- Primarily developed and tested in Linux.
- Works in MS Windows (native or xserver) and MacOS (xserver).
- Auto-indentation of wrapped lines.
- No code coloring (except comments and strings).
- Many TextArea utilities: undo/redo, replace, comment, ...
- Handles big files.
- Start external processes from the toolbar with a click, capturing the output to a row.
- Drag and drop files/directories to the editor.
- Detects if files opened are changed outside the editor.
- Plugin support
- examples such as
gotodefinitionandautocompletebelow.
- examples such as
- Golang specific:
- Calls goimports if available when saving a .go file.
- Clicking on
.gofiles identifiers will jump to the identifier definition (usesguruand/orgopls queryif installed). - Debug utility for go programs (
GoDebugcmd).- allows to go back and forth in time to consult code values.
- Language Server Protocol (LSP) (code analysis):
-lsprotocmd line option- basic support for gotodefinition and completion
- mostly being tested with
clangdandgopls
- Inline complete
- code completion by hitting the
tabkey (uses LSP).
- code completion by hitting the
Get the latest development:
go get -u github.com/jmigpin/editor@master
Or get the last tagged release (older):
go get -u github.com/jmigpin/editor
Build and run:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/jmigpin/editor
go build
./editor
Windows platform compilation alternatives:
go build # shows one console window (will be hidden, but makes a flash)
go build -ldflags -H=windowsgui # hides the console window, but cmds will popup consoles
go build -tags=xproto # (not native, needs an x11 server to run)
Usage:
Usage of ./editor:
-colortheme string
available: light, dark, acme (default "light")
-commentscolor int
Colorize comments. Can be set to zero to use a percentage of the font color. Ex: 0=auto, 1=Black, 0xff0000=red.
-cpuprofile string
profile cpu filename
-dpi float
monitor dots per inch (default 72)
-font string
font: regular, medium, mono, or a filename (default "regular")
-fonthinting string
font hinting: none, vertical, full (default "full")
-fontsize float
(default 12)
-lsproto value
Language-server-protocol register options. Can be specified multiple times.
Format: language,extensions,network{tcp,tcpclient,stdio},cmd,optional{stderr}
Examples:
go,.go,stdio,"gopls serve"
go,.go,tcp,"gopls serve -listen={{.Addr}}"
c++,".c .h .cpp .hpp",stdio,clangd
python,.py,tcpclient,127.0.0.1:9000
-plugins string
comma separated string of plugin filenames
-scrollbarleft
set scrollbars on the left side (default true)
-scrollbarwidth int
Textarea scrollbar width in pixels. A value of 0 takes 3/4 of the font size.
-sessionname string
open existing session
-shadows
shadow effects on some elements (default true)
-sn string
open existing session
-stringscolor int
Colorize strings. Can be set to zero to not colorize. Ex: 0xff0000=red.
-tabwidth int
(default 8)
-usemultikey
use multi-key to compose characters (Ex: [multi-key, ~, a] = ã)
-wraplinerune int
code for wrap line rune, can be set to zero (default 8592)
The editor has no configuration file. Use it within a script with your preferences (example editor.sh):
#!/bin/sh
exec ~/code/jmigpin/editor/editor \
--dpi=143 \
--fontsize=9 \
--colortheme=acme \
--commentscolor=0x008b00 \
--stringscolor=0x8b3100 \
--lsproto=go,.go,stdio,"gopls serve" \
--lsproto=c++,".c .h .cpp .hpp",stdio,clangd,stderr \
"$@"
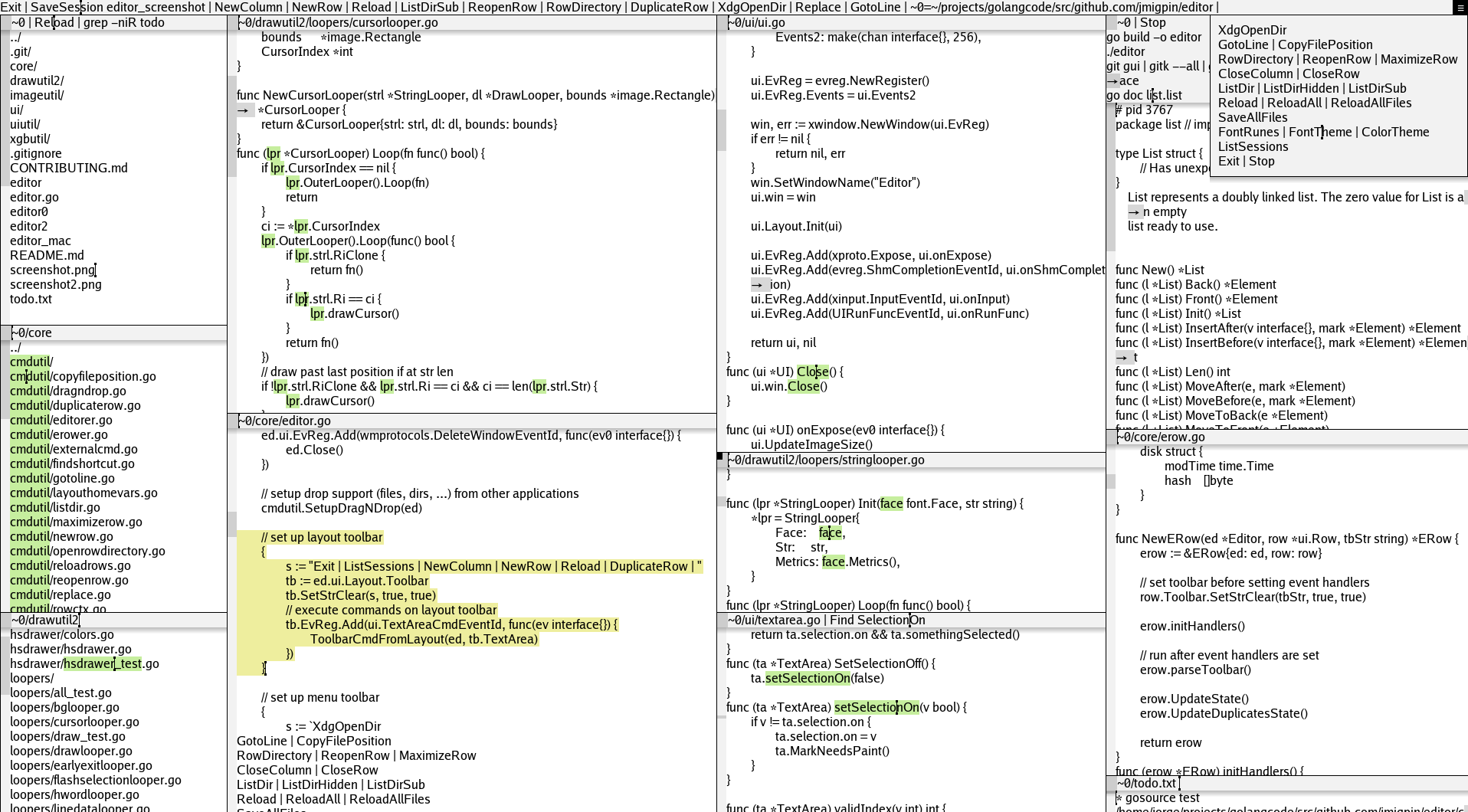
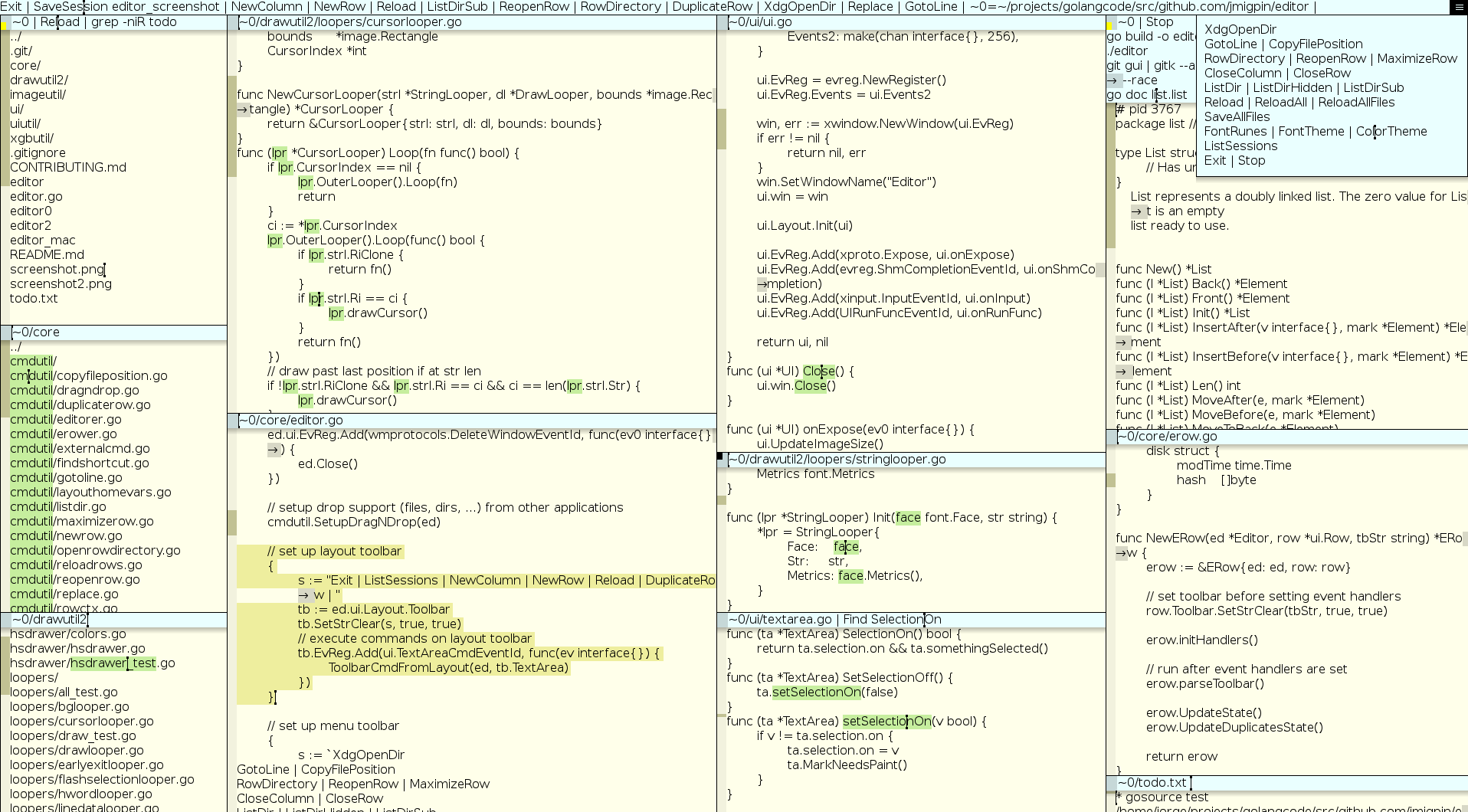
The editor has a top toolbar and columns. Columns have rows. Rows have a toolbar and a textarea.
These row toolbars are also textareas where clicking on the text will run that text as a command.
The row toolbar has a square showing the state of the row.
Commands in toolbars are separated by "|" (not to be confused with the shell pipe). If a shell pipe is needed it should be escaped with a backslash.
All internal commands start with an Uppercase letter. Otherwise it tries to run an existent external program.
Examples:
~/tmp/subdir/file1.txt | lsClicking atlswill runlsat~/tmp/subdir~/tmp/subdir/file1.txt | ls -l \| grep fiNotice how "|" is escaped, allowing to runls -l | grep fi~/tmp/subdir/file1.txtClicking atfile1.txtopens a new row to edit the same file. Clicking at~/tmpopens a new row located at that directory.gorename -offset $edFileOffset -to abcUsage of external command with active row position as argument. gorename godoc, go tools.guru -scope fmt callers $edFileOffsetUsage of external command with active row position as argument. guru godoc, go tools.grep -niIR somewordGrep results with line positions that are clickable.xdg-open $edDirOpen favorite external application with active row directory.xtermOpen an xterm at the active row directory.$font=monoUse monospaced font in this row textarea (see more at internal variables).
Top toolbar commands
ListSessions: lists saved sessionsSaveSession <name>: save session to ~/.editor_sessions.jsonDeleteSession <name>: deletes the session from the sessions fileNewColumn: opens new columnNewRow: opens new empty row located at the active-row directory, or if there is none, the current directory. Useful to run commands in a directory.ReopenRow: reopen a previously closed rowSaveAllFiles: saves all filesReloadAll: reloads all filepathsReloadAllFiles: reloads all filepaths that are filesColorTheme: cycles through available color themes.FontTheme: cycles through available font themes.Exit: exits the program
Row toolbar commands
These commands run on a row toolbar, or on the top toolbar with the active-row.
Save: save fileReload: reload contentCloseRow: close rowCloseColumn: closes row columnFind: find string (ignores case)GotoLine <num>: goes to line numberReplace <old> <new>: replaces old string with new, respects selectionsStop: stops current process (external cmd) running in the rowListDir [-sub] [-hidden]: lists directory-sub: lists directory and sub directories-hidden: lists directory including hidden
MaximizeRow: maximize row. Will push other rows up/down.CopyFilePosition: output the cursor file position in the format "file:line:col". Useful to get a clickable text with the file position.RuneCodes: output rune codes of the current row text selection.FontRunes: output the current font runes.XdgOpenDir: callsxdg-opento open the row directory with the preferred external application (ex: a filemanager).LSProtoCloseAll: closes all running lsp client/server connections. Next call will auto start again. Useful to stop a misbehaving server that is not responding.GoRename [-all] <new-name>: Renames the identifier under the text cursor. Uses the row/active-row filename, and the cursor index as the "offset" argument. Reloads the calling row at the end if there are no errors.- default: calls
gopls(limited scope in renaming, but faster). -all: callsgorenameto rename across packages (slower).
- default: calls
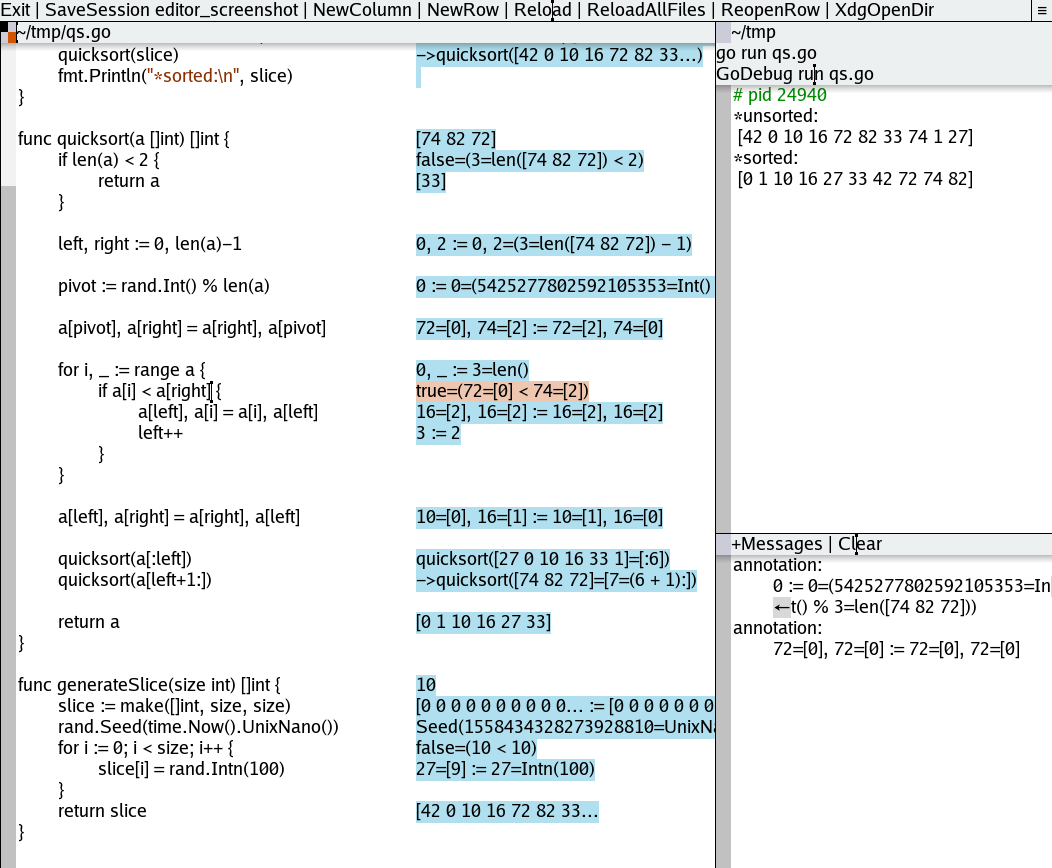
GoDebug <command> [arguments]: debugger utility for go programs (more at commands:godebug)
Row name at the toolbar (usually the filename)
- Clicking on a section of the path of the filename will open a new row with that content. Ex: if a row filename is "/a/b/c.txt" clicking on "/a" will open a new row with that directory listing, while clicking on "/a/b/c.txt" will open another row to edit the same file.
Textarea commands
OpenSession <name>: opens previously saved session<url>: opens url in preferred application.<filename(:number?)(:number?)>: opens filename, possibly at line/column (usual output from compilers). Check common locations like$GOROOTand C include directories.- If text is selected, only the selection will be considered as the filename to open.
<identifier-in-a-.go-file>: opens definition of the identifier. Ex: clicking inPrintlnonfmt.Printlnwill open the file at the line that contains thePrintlnfunction definition.
Usage:
GoDebug <command> [arguments]
The commands are:
run build and run program with godebug data
test test packages compiled with godebug data
build build binary with godebug data (allows remote debug)
connect connect to a binary built with godebug data (allows remote debug)
Examples:
GoDebug -help
GoDebug run -help
GoDebug run main.go -arg1 -arg2
GoDebug run -dirs=dir1,dir2 -files=f1.go,f2.go main.go -arg1 -arg2
GoDebug test -help
GoDebug test
GoDebug test -run mytest
GoDebug build -addr=:8080 main.go
GoDebug connect -addr=:8080
- Annotate files
-
By default, the current directory will be annotated. Other files/directories can be added with the
-dirsand-filescommand line options, but it is also possible to annotate by inserting one of the following comments in the code (notice the lack of space)://godebug:annotateblock //godebug:annotatefile //godebug:annotatepackage //godebug:annotatemodule //godebug:annotateimport # use before an "import" line # or specify a target //godebug:annotatefile:<file> # absolute or relative to the current //godebug:annotatepackage:<pkg-path> //godebug:annotatemodule:<pkg-path> # any pkg path inside will annotate allThe annotator will detect these comments and annotate accordingly.
A pkg path can be given to annotatepackage, but beware that pkgs located in $GOROOT are not annotated. Example:
//godebug:annotatepackage:golang.org/x/tools/godoc/utilHigher level
//godebug:*comments will override lower ones. To disable annotating for the current code block, insert://godebug:annotateoffThis is helpful to bypass loops that would become too slow with debug messages being sent. Example:
func fn(){ a:=0 // annotated if a==0{ a++ // annotated //godebug:annotateoff a+=2 // *not* annotated a+=3 // *not* annotated for i:=0; i<10000;i++{ // *not* annotated } } println(a) // annotated, not part of the disabled block }
-
- Limitations:
Stringmethods are not annotated to avoid endless loops (the annotation would recursively call the String method again).- Go supports multi-value function assignment. These statements are annotated but give a compilation error later:
The annotator assumes myfunc1 returns 1 value. For this to be solved the annotator would have to become substantially slower with type analysis.
func myfunc1() (int,int) { return 1, 2} func myfunc2(a int, b int) {} ... myfunc2(myfunc1()) // assumes myfunc1 returns 1 arg (compilation err) - Constants bigger then
intget theinttype when assigned to aninterface{}https://golang.org/ref/spec#Constants. Consider the following code that compiles and runs:But, the following gives a compile error:a:=uint64(0) a=math.MaxUint64When the code is annotated, there are debug functions that havevar a interface{} a=math.MaxUint64 // compilation err: constant 18446744073709551615 overflows intinterface{}arguments. So if an argument is aconstbigger thenint, it won't work. A solution is to use//godebug:annotateoffbefore the offending line. For this to be solved, the types need to be analysed but that would become substantially slower (compiles are not cached).
- Notes:
- Use
esckey to stop the debug session. Check related shortcuts at the key/buttons shortcuts section. - Supports remote debugging (check help usage with
GoDebug -h).- The annotated executable pauses if a client is not connected. In other words, it stops sending debug messages until a client connects.
- A client can connect/disconnect any number of times, but there can be only one client at a time.
- Example usage of setting the env var in a godebug session:
The example below builds a binary for windows in another platform, for later remote debug:
GoDebug run -env=GO111MODULE=off main.goGoDebug build -env=GOOS=windows -addr=:8080 main.go
- Use
~<digit>=path: Replaces long row filenames with the variable. Ex.: a file named/a/b/c/d/e.txtwith~0=/a/b/cdefined in the top toolbar will be shortened to~0/d/e.txt.$font=<name>: sets the row textarea font when set on the row toolbar. Useful when using a proportional font in the editor but a monospaced font is desired for a particular program output running in a row. Ex.:$font=mono.$termFilter: when set on a row toolbar, filters terminal escape sequences. Currently only theclearescape sequenceesc[Jis interpreted to clear the textarea. Other escape sequences are removed from the output.
$edName: row name.$edDir: row directory.$edFileOffset: filename with offset position from active row cursor. Ex: "filename:#123".$edLine: line from active row cursor. Ex: "12".
- background colors:
blue: row file has been edited.orange: row file doesn't exist.
- dot colors:
black: row currently active. There is only one active row.red: row file was edited outside (changed on disk) and doesn't match last known save. UseReloadcmd to update.blue: there are other rows with the same filename (2 or more).yellow: there are other rows with the same filename (2 or more). Color will change when the pointer is over one of the rows.
Plugins allow extra functionality to be added to the editor without changing the binary.
A plugin can be compiled and run with (will output a *.so):
go build -buildmode=plugin plugin1.go
go build -buildmode=plugin plugin2.go
editor --plugins plugin1.so,plugin2.so
Functions that can be implemented by a plugin are (subject to changes - work-in-progress ):
func OnLoad(ed *core.Editor)
func AutoComplete(ctx context.Context, ed *core.Editor, cfb *ui.ContextFloatBox) (err error, handled bool) // error` is only considered if `handled` is true
func ToolbarCmd(ed *core.Editor, erow *core.ERow, part *toolbarparser.Part) bool
Note that plugins might need to be recompiled everytime there are changes in the libraries provided by the editor.
Editor events currently implemented (subject to changes - work-in-progress ):
PostNewERowEEventId // on erow creation
PostFileSaveEEventId // after a file is saved
PreRowCloseEEventId // before a row is closed
RowStateChangeEEventId // on row state change (duplicate rows also emit).
Plugins located at: ./plugins.
gotodefinition_godef.go: plugin that shows how to override the textarea click action and use godef instead of the default.autocomplete_gocode.go: plugin that shows a context with suggestions for.gofiles (uses gocode).rownames.go: example plugin that shows how to access row names.eevents.go: example plugin on how to access editor events.
Global key/button shortcuts
esc:- stop debugging session
- close context float box
f1: toggle context float box- triggers call to plugins that implement
AutoComplete esc: close context float box
- triggers call to plugins that implement
Column key/button shortcuts
buttonLeft:- on left border: drag to move/resize
- on square-button: close
Row key/button shortcuts
ctrl+s: save filectrl+f: warp pointer to "Find" cmd in row toolbarbuttonLefton square-button: close row- on top border:
buttonLeft: drag to move/resize rowbuttonMiddle: close rowbuttonWheelUp: adjust row vertical position, pushing other rows upbuttonWheelDown: adjust row vertical position, pushing other rows down
- Any button/key press: make row active to layout toolbar commands
Textarea key/button shortcuts
- basic keyboard navigation
left: move cursor leftright: move cursor rightup: move cursor updown: move cursor downhome: start of lineend: end of linedelete: delete current runebackspace: delete previous runepageUp: page uppageDown: page down
- basic mouse navigation
buttonLeft: move cursor to point- drag: selects text - works as copy making it available for paste (primary selection).
- double-click: selects word
- triple-click: selects line
shift+buttonLeft: move cursor to point adding to selectionbuttonRight: move cursor to point + text area cmdbuttonWheelUp: scroll upbuttonWheelDown: scroll downbuttonWheelUpon scrollbar: page upbuttonWheelDownon scrollbar: page down
- selection
shift+left: move cursor left adding to selectionshift+right: move cursor right adding to selectionshift+up: move cursor up adding to selectionshift+down: move cursor down adding to selectionshift+home: start of string adding to selectionshift+end: end of string adding to selectionctrl+a: select all
- copy/paste
ctrl+c: copy to clipboardctrl+v: paste from clipboardctrl+x: cutbuttonMiddle: paste from primary
- undo/redo
ctrl+z: undoctrl+shift+z: redo
- utils
tab(if selection is on): insert tab at beginning of linesshift+tab: remove tab from beginning of linesctrl+k: remove linesctrl+alt+up: move line(s) upctrl+alt+down: move line(s) downctrl+alt+shift+down: duplicate linesctrl+d: comment linesctrl+shift+d: uncomment lines
- godebug
ctrl+buttonLeft: select annotationctrl+buttonRight: over an annotation: print the annotation value.ctrl+buttonWheelUp:- on textarea: show previous debug step
- over an annotation: show line previous annotation
ctrl+buttonWheelDown:- on textarea: show next debug step
- over an annotation: show line next annotation
ctrl+f5:- on textarea: show last debug step
ctrl+f9:- on textarea: clear debug messages (continues debugging)
esc: stop the debug session.
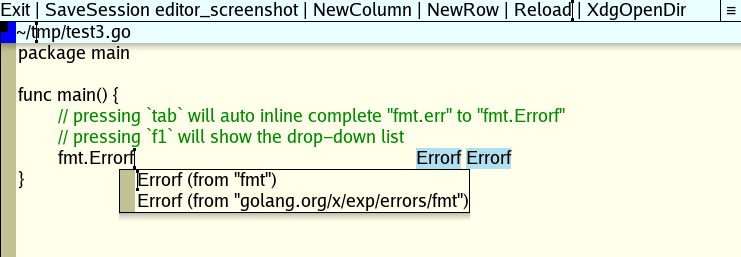
- inline complete
tab: inline code completion for file extensions registered with LSP.- if the previous rune is not a space, it runs code completion. To force
tabinsertion, amod-key+tabcan be pressed (ex:ctrl,alt, ...).
- if the previous rune is not a space, it runs code completion. To force
When a new row is created, it is placed either below the current row (measuring available space), or in a "good position".
The "good position" measures the available space between all rows, and uses the position with the most space.
The measuring of space is done as follows:
- if the cursor is visible, measure space after visible cursor to the end of the textarea and use it if not smaller than two lines in height, otherwise use 2)
- about 2/3 of the textarea
- Notable projects that inspired many features:
- Oberon OS: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UTIJaKO0iqU
- Acme editor: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dP1xVpMPn8M