This repository provides a deployment guide showcasing the application of Google Cloud's Generative AI for marketing scenarios. It offers detailed, step-by-step guidance for setting up and utilizing the Generative AI tools, including examples of their use in crafting marketing materials like blog posts and social media content.
Additionally, supplementary Jupyter notebooks are provided to aid users in grasping the concepts explored in the demonstration.
The architecture of all the demos that are implemented in this application is as follows.

.
├── app
└── notebooks
└── templates
/app: Source code for demo app./notebooks: Sample notebooks demonstrating the concepts covered in this demonstration./templates: Workspace Slides, Docs and Sheets templates used in the demonstration.
In this repository, the following demonstrations are provided:
- Marketing Insights: Utilize Looker Dashboards to access and visualize marketing data, powered by Looker dashboards, marketers can access and visualize marketing data to build data driven marketing campaigns. These features can empower businesses to connect with their target audience more efficiently, thereby improving conversion rates.
- Audience and Insight finder: Conversational interface that translates natural language into SQL queries. This democratizes access to data for non-SQL users removing any bottleneck for marketing teams.
- Trendspotting: Identify emerging trends in the market by analyzing Google Trends data on a Looker dashboard and summarize news related to top search terms. This can help businesses to stay ahead of the competition and to develop products and services that meet the needs and interests of their customers.
- Content Search: Improve search experience for internal or external content with Vertex AI Search for business users.
- Content Generation: Reduce time for content generation with Vertex Foundation Models. Generate compelling and captivating email copy, website articles, social media posts, and assets for PMax. All aimed at achieving specific goals such as boosting sales, generating leads, or enhancing brand awareness. This encompasses both textual and visual elements using Vertex language & vision models.
- Workspace integration: Transfer the insights and assets you've generated earlier to Workspace and visualize in Google Slides, Docs and Sheets.
The notebooks listed below were developed to explain the concepts exposed in this repository:
- Getting Started (1_environment_setup.ipynb): This notebook is part of the deployment guide and helps with dataset preparation.
- Data Q&A with PaLM API and GoogleSQL (data_qa_with_sql.ipynb): Translate questions using natural language to GoogleSQL to interact with BigQuery.
- News summarization with LangChain agents and Vertex AI PaLM text models (news_summarization_langchain_palm.ipynb): Summarize news articles related to top search terms using LangChain agents and the ReAct concept.
- News summarization with PaLM API (simple_news_summarization.ipynb): News summarization related to top search terms using the PaLM API.
The following additional (external) notebooks provide supplementary information on the concepts discussed in this repository:
- Tuning and deploy a foundation model: This notebook demonstrates how to tune a model with your dataset to improve the model's response. This is useful for brand voice because it allows you to ensure that the model is generating text that is consistent with your brand's tone and style.
- Document summarization techniques: Two notebooks explaining different techniques to summarize large documents.
- Document Q&A: Two notebooks explaining different techniques to do document Q&A on a large amount of documents.
- Vertex AI Search - Web search: This demo illustrates how to search through a corpus of documents using Enterprise Search on Vertex AI Search. Additional features include how to search the public Cloud Knowledge Graph using the Enterprise Knowledge Graph API.
- Vertex AI Search - Document search: This demo illustrates how Enterprise Search and the Vertex AI PaLM API help ensure that generated content is grounded in validated, relevant and up-to-date information.
- Getting Started with LangChain and Vertex AI PaLM API: Use LangChain and Vertex AI PaLM API to generate text.
This section outlines the steps to configure the Google Cloud environment that is required in order to run the notebooks and demonstration provided in this repository.
You will be interacting with the following resources:
- A user-managed instance of Vertex AI Workbench serves as your development setting and the main interface to Vertex AI services.
- BigQuery is utilized to house data from Marketing Platforms, while Dataplex is employed to keep their metadata.
- Vertex AI Search & Conversation - Enterprise Search and Generative AI Agent - are used to construct a search engine for an external website.
- Workspace (Google Slides, Google Docs and Google Sheets) are used to visualized the resources generated by you.
In the Google Cloud Console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
As this is a DEMONSTRATION, you need to be a project owner in order to set up the environment.
From Cloud Shell, run the following commands to enable the required Cloud APIs:
export PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud info --format='value(config.project)')
gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
gcloud services enable \
cloudbuild.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com \
cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com \
iam.googleapis.com \
container.googleapis.com \
cloudapis.googleapis.com \
cloudtrace.googleapis.com \
containerregistry.googleapis.com \
iamcredentials.googleapis.com
gcloud services enable \
monitoring.googleapis.com \
logging.googleapis.com \
notebooks.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com \
storage.googleapis.com \
datacatalog.googleapis.com \
appengineflex.googleapis.com \
translate.googleapis.com \
admin.googleapis.com \
docs.googleapis.com \
drive.googleapis.com \
sheets.googleapis.com \
slides.googleapis.comNote: When you work with Vertex AI user-managed notebooks, be sure that all the services that you're using are enabled and white-listed.
Create a user-managed notebooks instance from the command line.
Note: Make sure that you're following these steps in the same project as before.
In Cloud Shell, enter the following command.
- For
<YOUR_INSTANCE_NAME>, enter a name starting with a lower-case letter followed by lower-case letters, numbers or dash sign. - For
<YOUR_LOCATION>, add a zone (for example,us-central1-aoreurope-west4-a).
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config list --format 'value(core.project)')
INSTANCE_NAME=<YOUR_INSTANCE_NAME>
LOCATION=<YOUR_LOCATION>
gcloud notebooks instances create $INSTANCE_NAME \
--vm-image-project=deeplearning-platform-release \
--vm-image-family=common-cpu-notebooks \
--machine-type=n1-standard-4 \
--location=$LOCATIONVertex AI Workbench creates a user-managed notebook instance based on the properties that you specified and then automatically starts the instance. When the instance is ready to use, Vertex AI Workbench activates an Open JupyterLab link next to the instance name in the Vertex AI Workbench Cloud Console page. To connect to your user-managed notebooks instance, click Open JupyterLab.
On Jupyterlab Launcher Page, click on Terminal to start a new terminal.
Clone the repository to your notebook instance:
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/genai-for-marketing
Open notebook /genai-for-marketing/notebooks/1_environment_setup.ipynb and follow the instructions in it.
It will execute the following steps:
- Install dependecies to run the notebook
- Create a dataset on BigQuery
- Create a synthetic CDP dataset and load it to BigQuery
- Create Tag Template on Dataplex
- Tag dataset columns with metadata
- Test the deployment
Make sure all the steps are executed successfully and you can retrieve the metadata from Dataplex.
The metadata should look like this:
Table: transactions - Column: app_purchase_qnt - Data Type: INT64 - Primary Key: False - Foreing Key: False - Description: The value of the in-app purchase.
...
Table: customers - Column: total_value - Data Type: INT64 - Primary Key: False - Foreing Key: False - Description: The total value of all purchases made by the customer.
Follow the steps below to create a search engine for a website using Enterprise Search.
- Make sure the Enterprise Search APIs are enabled here and you activated Generative AI App Builder here.
- Create and preview the website search engine as described here and here.
After you finished creating the Enterprise Search datastore, navigate back to the Apps page and copy the ID of the datastore you just created.
Example:
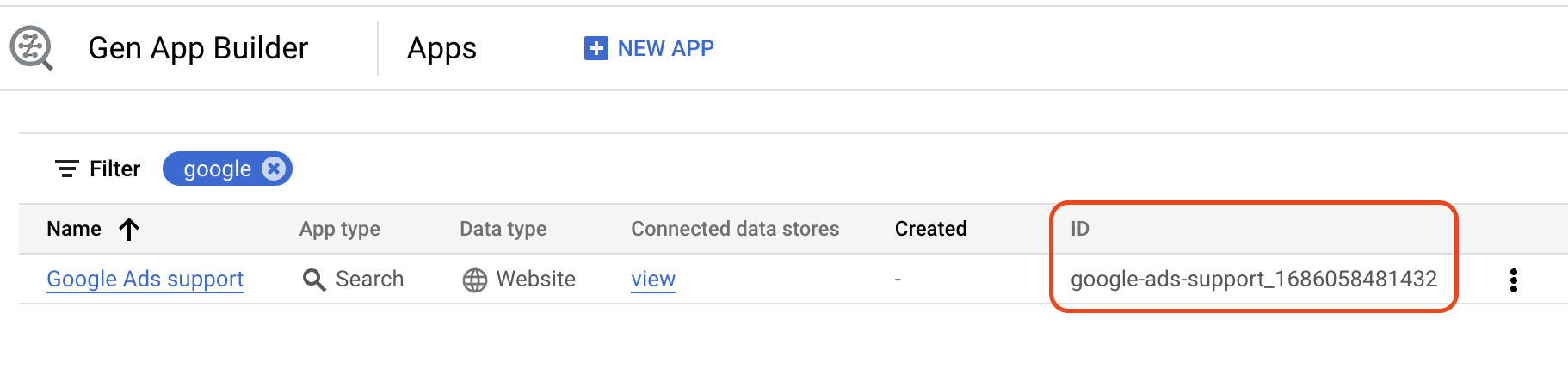
Open this configuration file - line 40 and paste the ID of your newly created datastore in the DATASTORES dictionary.
The resulting code should look like this:
# Enterprise Search datastores and location
DATASTORES = {
'google-ads-support_1688070625722': 'default_config'
}
Don't forget to save the configuration file.
In order to render your Looker Dashboards in the UI, you need to update a configuration file with the links to them.
Open the configuration file - line 33 and paste the name and link of your Looker Dashboards in the DASHBOARDS dictionary.
The resulting code should look like this:
# Looker Dashboards
# The link of the looker Dashboard must follow this format:
# https://<LOOKER INSTANCE URL>/embed/dashboards/<DASHBOARD NUMBER>?allow_login_screen=true
DASHBOARDS = {
'Overview': 'https://mydomain.looker.com/embed/dashboards/1111?allow_login_screen=true'
}
The allow_login_screen=true will open the authentication page from Looker to secure the access to your account.
[Optional] If you have your Google Ads and Google Analytics 4 accounts in production, you can deploy our Marketing Data Engine solution to your project, build the Dashboards and link them to the demonstration UI.
Next you will create a Generative AI Agent that will assist the users to answer questions about Google Ads, etc.
- Follow the steps described in this Codelab to build your own Generative AI Agent.
- Execute these steps in the same project you will deploy this demo.
- In step 3 of this Codelab you can provide a different URL to be indexed by the Generative AI Agent, for example
support.google.com/google-ads/*. - [Optional] Use LLMs to generate answers when no answer is found. If you have questions, please refer to this documentation.
- Enable Dialogflow Messenger integration and copy the HTML code snippet provided by the platform.
- The HTML code snippet looks like this:

- Open the configuration file - line 47 and replace the HTML code snipped with the one created in your deployment.
- The HTML code snippet looks like this:
Follow the steps below to setup the Workspace integration with this demonstration.
- Create a Service Account (SA) in the same project you are deploying the demo and download the JSON API Key. This SA doesn't need any roles / permissions.
- Follow this documentation to create the service account. Take note of the service account address; it will look like this:
name-of-the-sa@my-project.iam.gserviceaccount.com. - Follow this documentation to dowload the key JSON file with the service account credentials.
- Rename the JSON file to
credentials.jsonand copy it under /app folder. - [Optional] If your file has a different name and/or you copied it to a different location, change line 66 in utils_config.py to reflect these changes.
- Follow this documentation to create the service account. Take note of the service account address; it will look like this:
- When you deploy the app to AppEngine, the JSON file will be copied inside the docker image.
- IMPORTANT: For security reasons, DON'T push this credentials to a public Github repository.
- Navigate to Google Drive and create a folder.
- This folder will be used to host the templates and assets created in the demo.
- Share this folder with the service account address you created in the previous step. Give "Editor" rights to the service account. The share will look like this:

- Take note of the folder ID. Go into the folder you created and you will be able to find the ID in the URL. The URL will look like this:

- Open the configuration file utils_config.py - line 69 and change to your folder ID.
- IMPORTANT: Also share this folder with people who will be using the demonstration.
- Copy the content of templates to this newly created folder.
- For the Google Slides template (
[template] Marketing Assets):- From the Google Drive folder, open the Google Slides and take note of the Slides ID from the URL.
- Open the configuration file utils_config.py - line 70 and change to your Slides ID.
- For the Google Docs template (
[template] Gen AI for Marketing Google Doc Template):- From the Google Drive folder, open the Google Docs and take note of the Docs ID from the URL.
- Open the configuration file utils_config.py - line 71 and change to your Docs ID.
- For the Google Sheets template (
[template] GenAI for Marketing):- From the Google Drive folder, open the Google Sheets and take note of the Sheets ID from the URL.
- Open the configuration file utils_config.py - line 72 and change to your Sheets ID.
- On Jupyterlab
Launcher Page(in the Workbench managed instance), click onTerminalto start a new terminal by clicking the Terminal icon. - Navigate to
genai-for-marketingfolder
cd genai-for-marketing
- Open the
app.yamlconfiguration file and include your service account (Compute Engine default service account) in line 19:
service_account: <REPLACE WITH YOUR SERVICE ACCOUNT ADDRESS>
The service account has the following format: PROJECT_NUMBER-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com
You can check the available service accounts in your project by running the following command:
gcloud iam service-accounts list
- Deploy the solution to AppEngine
gcloud app deploy
Wait for the application to be deployed and open the link generated by AppEngine.
If you have any questions or if you found any problems with this repository, please report through GitHub issues.