Báo cáo cuối kỳ môn Chuyên đề nghiên cứu về máy học và trí tuệ nhân tạo - CS2310.CH1801 Đại học Công nghệ thông tin
MSHV: Nguyễn Hoa – 220101044 Nguyễn Trung Thu – 230101034
GV: TS. Lương Ngọc Hoàng
T4/2024
python run_fsc.py dataset=[sst-2, yelp-2, mr, cr, agnews, sst-5, yelp-5] dataset_seed=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4] prompt_length=[any integer (optional, default:5)] task_lm=[distilroberta-base, roberta-base, roberta-large, distilgpt2, gpt2, gpt2-medium, gpt2-large, gpt2-xl] random_seed=[any integer (optional)]
{'SQL_ON/rewards/acc': tensor(0.5000, device='cuda:0'), 'SQL_ON/rewards/gap_reward_class_0': tensor(-163.1316), 'SQL_ON/rewards/gap_reward_class_1': tensor(188.6110), 'SQL_ON/rewards/gap_reward': tensor(12.7397), 'SQL_ON/rewards/resized_reward': tensor(0.)}
logits.shape==torch.Size([2, 3, 50257]) logits_ --->softmx [['Price', 'Size', 'Size'], ['Price', 'Product', 'ĠQuantity']]
tensor([-1.0000, 1.0000], device='cuda:0')
tensor(416.1516, device='cuda:0', grad_fn=)
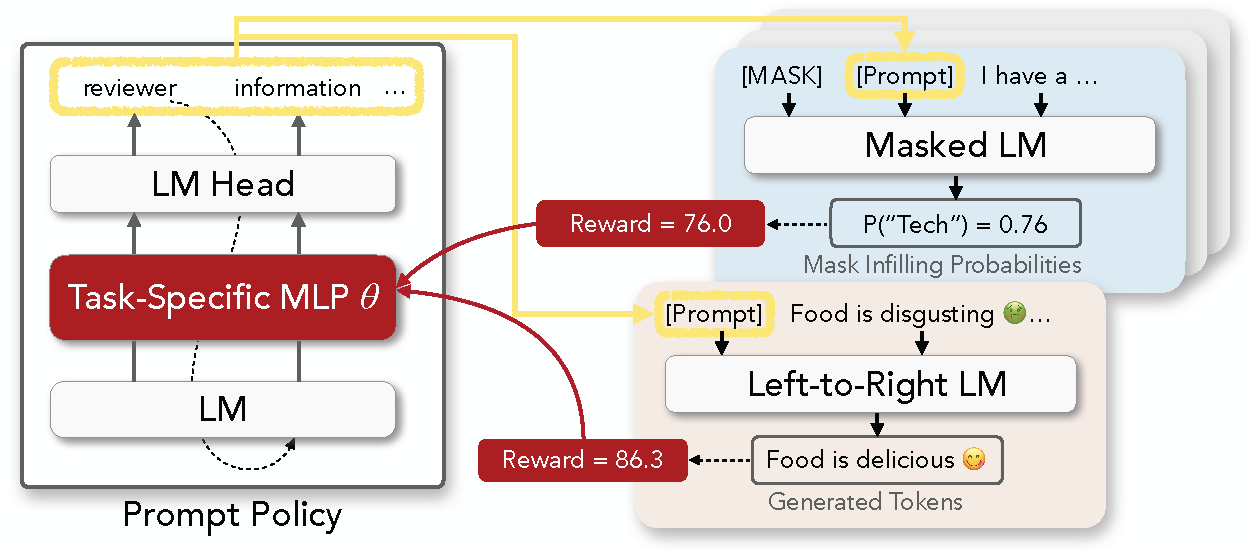
This repo contains the code of the discrete prompt optimization framework described in the paper
RLPrompt: Optimizing Discrete Text Prompts With Reinforcement Learning
Mingkai Deng*, Jianyu Wang*, Cheng-Ping Hsieh* (equal contribution), Yihan Wang, Han Guo, Tianmin Shu, Meng Song, Eric P. Xing, Zhiting Hu
We will keep updating the codebase for easier usage and adaptation for your own tasks, so please stay tuned by starring or watching our repo!
- Extensive recent work (e.g., this) has shown that prompting pre-trained LMs with specific text can steer them to perform various NLP tasks, without needing to update the model
- Previous work has typically tuned soft prompts with gradient-based optimization or searched for discrete text prompts using various heuristics
- In our paper, we propose to formulate discrete prompt optimization as an RL problem, and train a policy network to generate the prompt that optimizes a reward function
- Compared to typical soft prompts, our discrete prompts are lightweight, interpretable, and transferrable across model types (e.g., RoBERTa to GPT-2) and sizes (e.g., small to large)
- Check out more analyses at our paper here
Our codebase requires the following Python and PyTorch versions:
- Python >= 3.7
- PyTorch >= 1.10.1 (install from the official website)
Install our core modules with
pip install -e .
Please refer to the folders in examples, which contains our implementations of 1) few-shot classification and 2) text style transfer, as described in our paper.
In short, the code in rlprompt provides the core components for prompt optimization. The task-specific folders in examples simply implement the reward functions and use the core modules to run experiments.