In this work, we propose a multi-evidence, position-aware, and scalable benchmark for evaluating long-context LLMs, named Counting-Stars, which evaluates long-context LLMs by using two tasks: multi-evidence acquisition and multi-evidence reasoning.
- Multi-evidence: Counting-Stars is the most evidence-intensive evaluation in known long-context benchmarks.
- Position-aware: The position of the evidence in the context can be adjusted as desired and tested in a targeted manner.
- Scalable: Both the context length and the amount of evidence can be expanded arbitrarily.
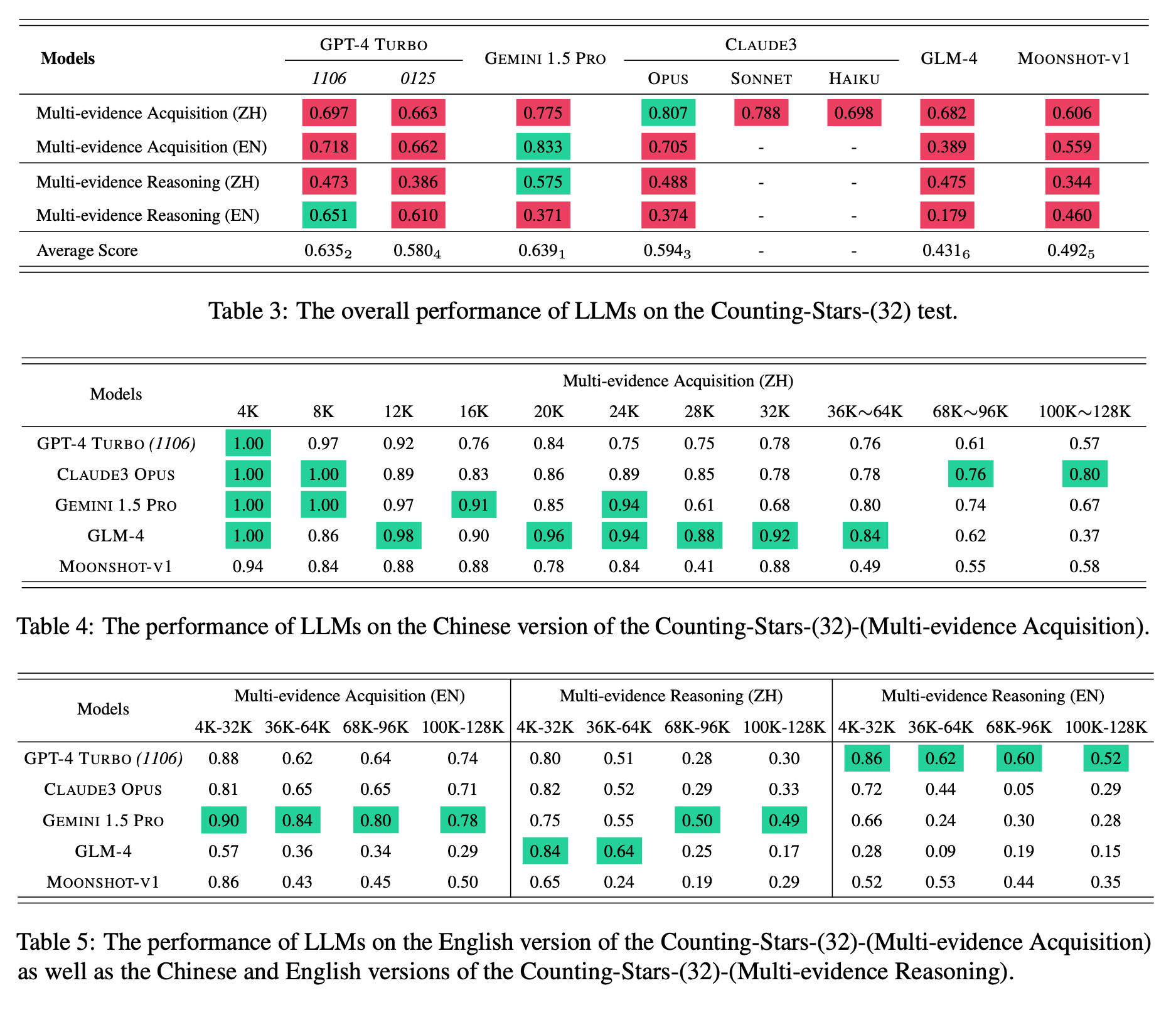
Based on the Counting-Stars test, we conduct experiments to evaluate long-context LLMs (i.e., GPT-4 Turbo, Gemini 1.5 Pro, Claude3 Opus, GLM-4, and Moonshot-v1). Experimental results demonstrate that Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves the best overall results, while the performance of GPT-4 Turbo is the most stable across various tasks. Furthermore, our analysis of these LLMs, which are extended to handle long-context scenarios, indicates that there is potential for improvement as the length of the input context and the intricacy of the tasks are increasing.
Please find more details of this work in the paper.
We'd like to encourage you to test the Counting-Stars using
- Me-Acq. (EN) means the English version of Multi-evidence Acquisition in the Counting-Stars.
Counting_Stars_EN_acquisition_128000_32_32.jsonl
- Me-Acq. (ZH) means the Chinese version of Multi-evidence Acquisition in the Counting-Stars.
Counting_Stars_ZH_acquisition_128000_32_32.jsonl
- Me-Rea. (EN) means the English version of Multi-evidence Reasoning in the Counting-Stars.
Counting_Stars_EN_reasoning_128000_32_32.jsonl
- Me-Rea. (ZH) means the Chinese version of Multi-evidence Reasoning in the Counting-Stars.
Counting_Stars_ZH_reasoning_128000_32_32.jsonl
, the 128K English and Chinese versions of the Counting-Stars.
| Rank | Models | Claimed Length | Me-Acq.(ZH) | Me-Acq.(EN) | Me-Rea.(ZH) | Me-Rea.(EN) | Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gemini 1.5 Pro | 1M | 0.775 | 0.833 | 0.575 | 0.371 | 0.639 |
| 2 | GPT-4 Turbo (1106) | 128K | 0.697 | 0.718 | 0.473 | 0.651 | 0.635 |
| 3 | Claude3 Opus | 200K | 0.807 | 0.705 | 0.488 | 0.374 | 0.594 |
| 4 | GPT-4 Turbo (0125) | 128K | 0.663 | 0.662 | 0.386 | 0.610 | 0.580 |
| 5 | Moonshot-v1 | 200K | 0.606 | 0.559 | 0.344 | 0.460 | 0.492 |
| 6 | GLM-4 | 128K | 0.682 | 0.389 | 0.475 | 0.179 | 0.431 |
| - | Claude3 Sonnet | 200K | 0.788 | - | - | - | - |
| - | Claude3 Haiku | 200K | 0.698 | - | - | - | - |
| - | Baichuan3-Turbo | 128K | 0.759 | 0.490 | - | - | - |
Visualization of the results on the Chinese version of the Counting-Stars-32-(Multi-evidence Acquisition).
Visualization of the results on the Chinese version of the Counting-Stars-32-(Multi-evidence Reasoning).
If you use this benchmark, please cite this paper
@misc{song2024countingstars,
title={Counting-Stars: A Multi-evidence, Position-aware, and Scalable Benchmark for Evaluating Long-Context Large Language Models},
author={Mingyang Song and Mao Zheng and Xuan Luo},
year={2024},
eprint={2403.11802},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}
For any questions, feel free to create an issue, and we will try our best to solve it.
If the problem is more urgent, you can email me simultaneously (I check email almost daily).
NAME: Mingyang Song
EMAIL: nickmysong@tencent.com
Our visualization code is built on the source code from NeedleInAHaystack. Thanks for their work.