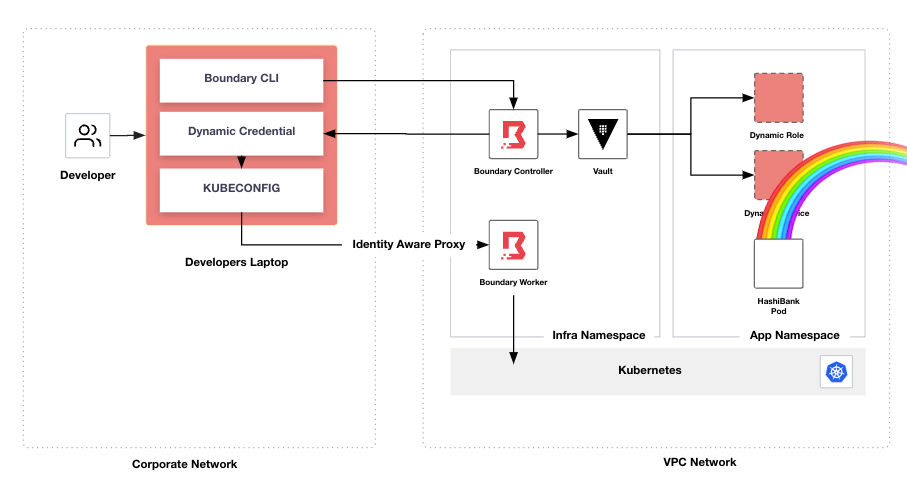
This repo deploys Boundary and Vault into a GKE Kubernetes cluster and configures them to demonstrate an example workflow where by a developer uses Boundary to request Just-In-Time access to their application namespace.
A Youtube video of me presenting this demo is available here.
| Requirement | Version |
|---|---|
| GKE Cluster | 1.26.5 |
| gcloud CLI | 422.0.0 |
| Boundary Desktop Client | 1.6.0 |
| Boundary CLI | 0.13.0+ent |
| Terraform CLI | 1.5.1 |
| Helm CLI | 3.9.0 |
| Vault CLI | 1.12.0 |
| Boundary Enterprise Licence | - |
Although the code in this repo was written to work with the above requirements and version, there's no reason with a small amount of customization it wouldn't work on any Kubernetes distribution. The main change that you'd have to would be the ingress objects.
Before you start, you need to be authenticated to the Kubernetes API. Confirm so by running this command.
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
gke-cluster-1-my-node-pool-f34728b6-9275 Ready <none> 15m v1.26.5-gke.1200
If the above command doesn't work, see Authenticating to the Kubernetes API server.
Step 1 - Deploy Namespaces
Deploy 2 namespaces.
- app - Used by the example web app.
- infra - Used by Vault and Boundary.
sh demo.sh namespacesStep 2 - Deploy Ingress
Deploy Services for HashiBank and Vault. In GKE, we deploy Kubernetes Services of type: LoadBalancer which then provisions a Cloud Loadbalancer mapped to the Service.
Why do we create the service ingress objects separately here and not together with each app? Because requesting a public IP from Google takes a few minutes, setting them up early makes sure that they have a public IP associated by the time we need them.
sh demo.sh ingressStep 3 - Deploy Vault
Using the official Helm chart, deploy a single node of Vault, running in dev mode.
sh demo.sh vault
Step 4 - Deploy Postgres
Using the Bitnami Helm chart, deploy a single instance of Postgresql.
sh demo.sh postgres
Step 5 - Deploy Boundary License
Your Boundary license file needs to be exported in the environment variable BOUNDARY_LICENSE. If the env var is not set, the script will exit with an error.
export BOUNDARY_LICENSE=02MVENNEWU...
sh demo.sh boundary-license
Step 6 - Deploy Boundary Controller
Deploy the Boundary Enterprise Controller.
sh demo.sh boundary-controller
Step 7 - Save Boundary Worker Public IP Address
Store the public IP address from the Boundary worker's external service into a ConfigMap. We set this value as an env var in the worker container because the worker needs to know it's public IP address for establishing sessions. This command will fail if the external loadbalancer hasn't been assigned an IP address yet.
sh demo.sh boundary-worker-addr
Step 8 - Deploy Boundary Worker
Deploy a single instance of Boundary PKI Worker with auth persistence, session recording storage cache and encryption.
sh demo.sh boundary-worker
Step 9 - Register the Boundary Worker with the Boundary Controller
Register the Boundary Worker to the Boundary controller using the worker-led registration method.
sh demo.sh boundary-worker-register
Step 10 - Configure Vault
Use Terraform to manage all of Vault's configuration as code.
sh demo.sh vault-config-init
sh demo.sh vault-config-plan
sh demo.sh vault-config-apply
Step 11 - Configure Boundary
Use Terraform to manage all of Boundary's configuration as code.
sh demo.sh boundary-config-init
sh demo.sh boundary-config-plan
sh demo.sh boundary-config-apply
Accessing Vault and Boundarys UI
kubectl -n infra get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
boundary-controller-external LoadBalancer 10.244.5.138 <external-ip> 80:30126/TCP 44m
boundary-worker-external LoadBalancer 10.244.15.157 <external-ip> 80:30668/TCP 44m
vault-external LoadBalancer 10.244.13.132 <external-ip> 80:31234/TCP 44m
Default Usernames and Passwords
| Component | Username | Password | Token |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boundary | admin-user | password123 | - |
| Vault | - | - | Hash!123 |
Authenticate to Boundary
Output env vars to auth the Boundary CLI.
sh demo.sh boundary-auth
Authenticate to Vault
Output env vars to auth the Vault CLI.
sh demo.sh vault-auth
Developer logging in to Kubernetes via Boundary
Authenticate to Boundary.
sh demo.sh boundary-auth
BOUNDARY_ADDR set to http://x.x.x.x.x
BOUNDARY_AUTH_METHOD set to ampw_msTnsE7nJ2
Authentication information:
Account ID: acctpw_roAzBnLRBY
Auth Method ID: ampw_msTnsE7nJ2
Expiration Time: Wed, 02 Aug 2023 17:59:36 AEST
User ID: u_5pFXn6rNSj
The token was successfully stored in the chosen keyring and is not displayed here.
Run the following command to use the Boundary CLI locally
export BOUNDARY_ADDR=http://x.x.x.x
Copy and paste the export command to your CLI,.
export BOUNDARY_ADDR=http://x.x.x.x
Find the target ID for our Kubernetes cluster.
boundary targets list -recursive
Target information:
ID: ttcp_gshPlGwsct <-- HERE
Scope ID: p_BWY9lDC7R4
Version: 3
Type: tcp
Name: Kubernetes Production
Description: Kubernetes Production Cluster
Authorized Actions:
no-op
read
update
delete
add-host-sources
set-host-sources
remove-host-sources
add-credential-sources
set-credential-sources
remove-credential-sources
authorize-session
Run the connect.sh helper script to establish a session with Boundary and generate our KUBECONFIG.
sh deploy/kubeconfig/connect.sh ttcp_gshPlGwsct
Connecting to cluster My-Kubernetes-Cluster via Boundary Proxy 0:55578
You are now successfully authenticated as a developer using a dynamic service account that Vault has created on our behalf.
Let's deploy an application with our newly created access.
kubectl apply -f deploy/hashibank
Confirm that our HashiBank application has deployed sucessfully by browsing to the external IP on the service.
kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
hashibank-external LoadBalancer 10.244.7.230 y.y.y.y 80:30566/TCP 129m
Browse to http://y.y.y.y in your web browser.