OpenWhisk
OpenWhisk is a cloud-first distributed event-based programming service. It provides a programming model to upload event handlers to a cloud service, and register the handlers to respond to various events. Learn more at http://openwhisk.incubator.apache.org.
- Quick Start (Docker-Compose)
- Native development (Mac and Ubuntu)
- Kubernetes
- Vagrant
- Learn concepts and commands
- Issues
- Slack
Quick Start
The easiest way to start using OpenWhisk is to get Docker installed on on Mac, Windows or Linux. The Docker website has details instructions on getting the tools installed. This does not give you a production deployment but gives you enough of the pieces to start writing functions and seeing them run.
git clone https://github.com/apache/incubator-openwhisk-devtools.git
cd incubator-openwhisk-devtools/docker-compose
make quick-start
For more detailed instructions or if you encounter problems see the OpenWhisk-dev tools project.
Kubernetes Setup
Another path to quickly starting to use OpenWhisk is to install it on a Kubernetes cluster. On a Mac, you can use the Kubernetes support built into Docker 18.06 (or higher). You can also deploy OpenWhisk on Minikube, on a managed Kubernetes cluster provisioned from a public cloud provider, or on a Kubernetes cluster you manage yourself. To get started,
git clone https://github.com/apache/incubator-openwhisk-deploy-kube.git
Then follow the instructions in the OpenWhisk on Kubernetes README.md.
Vagrant Setup
A Vagrant machine is also available to run OpenWhisk on Mac, Windows PC or GNU/Linux but isn't used by as much of the dev team so sometimes lags behind. Download and install VirtualBox and Vagrant for your operating system and architecture.
Note: For Windows, you may need to install an ssh client in order to use the command vagrant ssh. Cygwin works well for this, and Git Bash comes with an ssh client you can point to. If you run the command and no ssh is installed, Vagrant will give you some options to try.
Follow these step to run your first OpenWhisk Action:
# Clone openwhisk
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/apache/incubator-openwhisk.git openwhisk
# Change directory to tools/vagrant
cd openwhisk/tools/vagrant
# Run script to create vm and run hello action
./hello
Wait for hello action output:
wsk action invoke /whisk.system/utils/echo -p message hello --result
{
"message": "hello"
}
These steps were tested on Mac OS X El Capitan, Ubuntu 14.04.3 LTS and Windows using Vagrant. For more information about using OpenWhisk on Vagrant see the tools/vagrant/README.md
During the Vagrant setup, the Oracle JDK 8 is used as the default Java environment. If you would like to use OpenJDK 8, please change the line "su vagrant -c 'source all.sh oracle'" into "su vagrant -c 'source all.sh'" in tools/vagrant/Vagrantfile.
Native development
Docker must be natively installed in order to build and deploy OpenWhisk. If you plan to make contributions to OpenWhisk, we recommend either a Mac or Ubuntu environment.
Learn concepts and commands
Browse the documentation to learn more. Here are some topics you may be interested in:
- System overview
- Getting Started
- Create and invoke actions
- Create triggers and rules
- Use and create packages
- Browse and use the catalog
- Using the OpenWhisk mobile SDK
- OpenWhisk system details
- Implementing feeds
Repository Structure
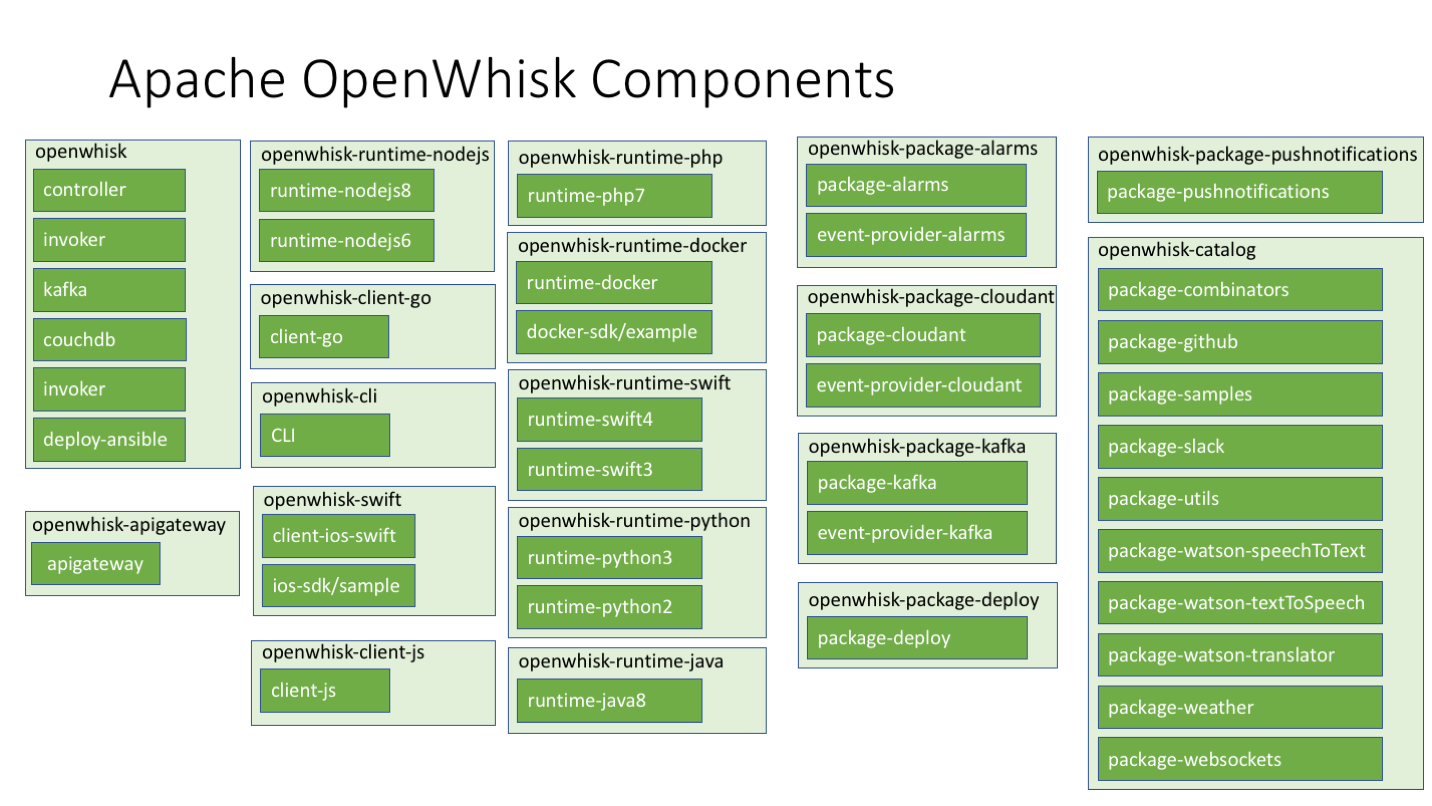
The OpenWhisk system is built from a number of components. The picture below groups the components by their GitHub repos. Please open issues for a component against the appropriate repo (if in doubt just open against the main openwhisk repo).
Issues
Report bugs, ask questions and request features here on GitHub.
Slack
You can also join the OpenWhisk Team on Slack https://openwhisk-team.slack.com and chat with developers. To get access to our public slack team, request an invite https://openwhisk.incubator.apache.org/slack.html.
Disclaimer
Apache OpenWhisk is an effort undergoing incubation at The Apache Software Foundation (ASF), sponsored by the Apache Incubator. Incubation is required of all newly accepted projects until a further review indicates that the infrastructure, communications, and decision making process have stabilized in a manner consistent with other successful ASF projects. While incubation status is not necessarily a reflection of the completeness or stability of the code, it does indicate that the project has yet to be fully endorsed by the ASF.