Authors: Niklas Risse, Christina Göpfert and Jan Philip Göpfert
Institution: Bielefeld University
- A python module to calculate robustness curves for arbitrary models and datasets
- The code to reproduce all experiments (with figures) from the paper, including the following:
- 2 experiments on inter class distances for different datasets and norms
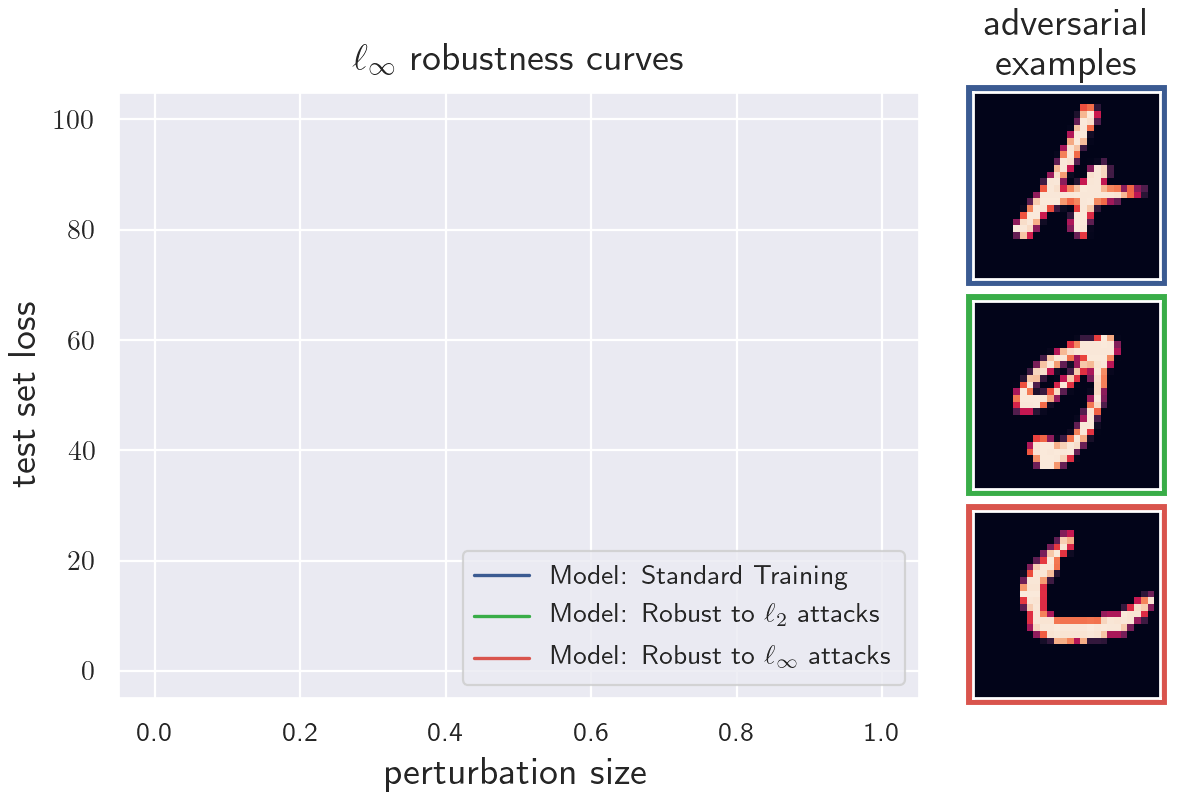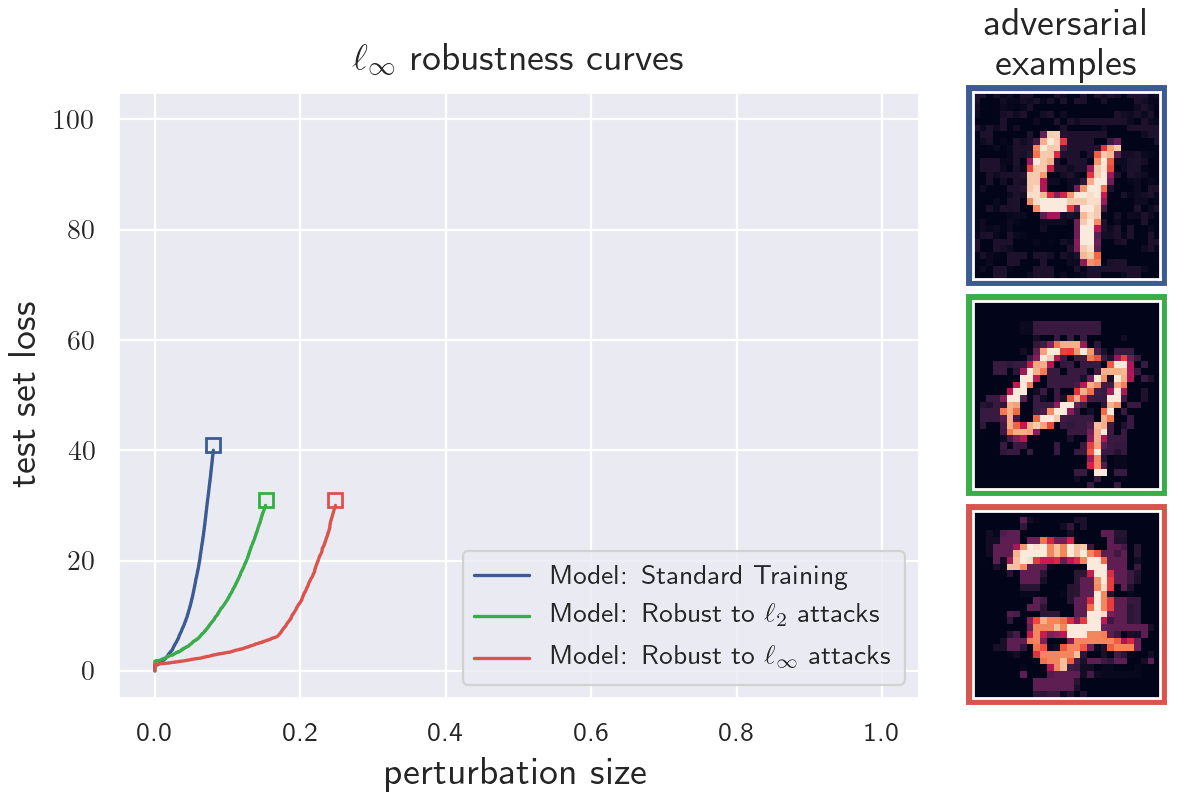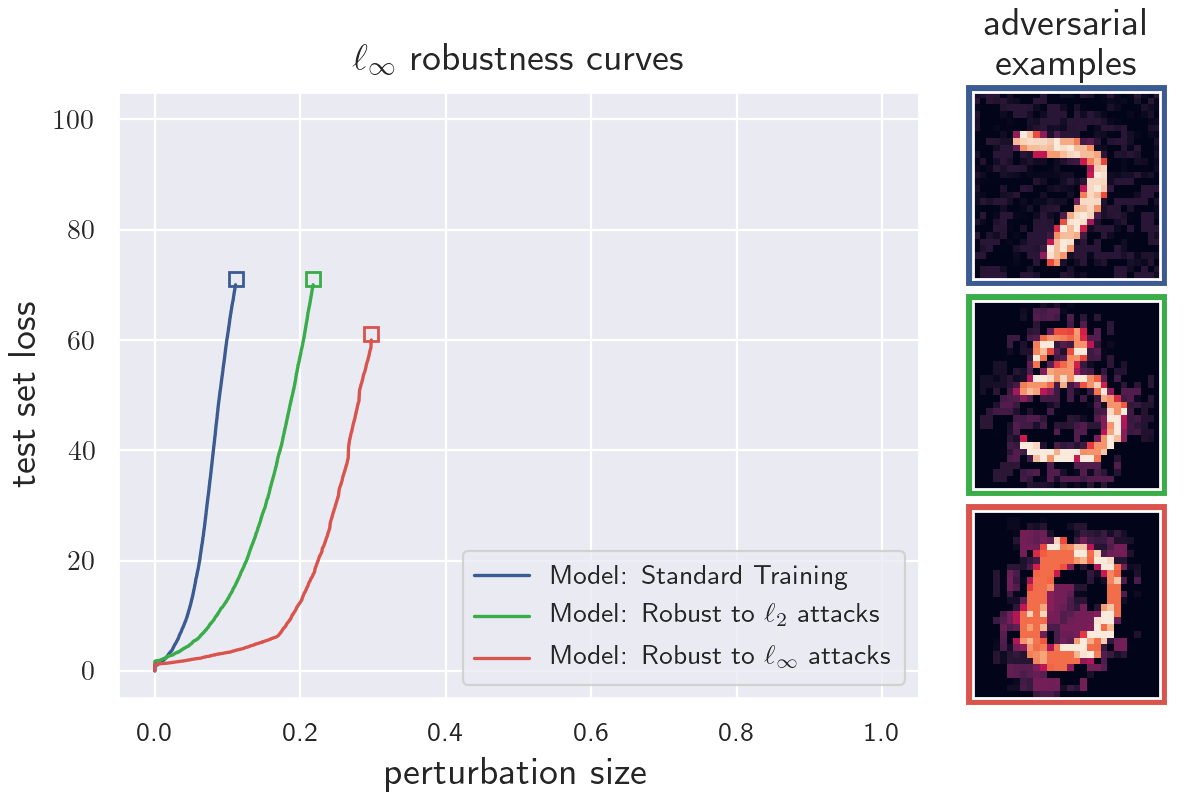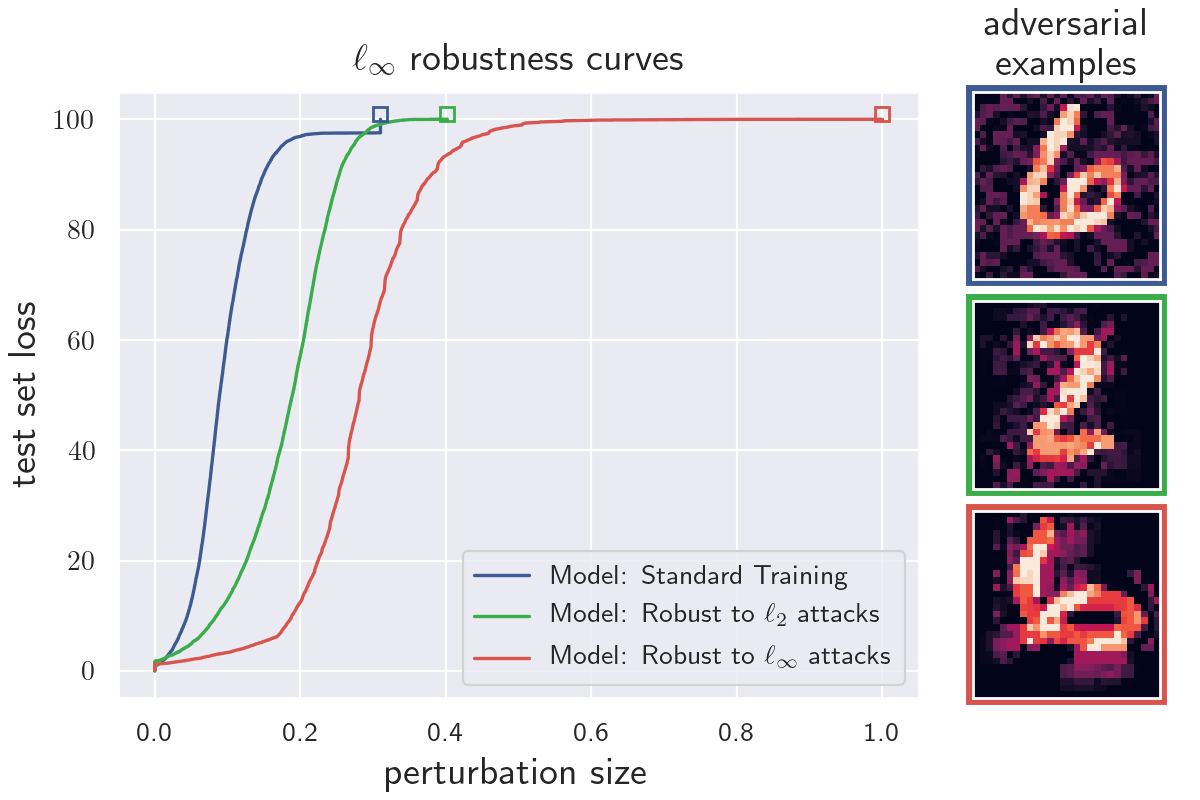
- 5 experiments on robustness curves for different models and datasets
The python module robustness_curves.py contains methods to calculate robustness curves. A tutorial on how to use the module can be found in the notebook how_to_generate_robustness_curves.ipynb. Most of the popular machine learning frameworks are supported (e.g. TensorFlow, PyTorch, JAX). Datasets need to be in numpy array format. The module can be used to generate robustness curves for the l_infty, l_2 and l_1 norms. Plotting and/or saving the generated data is optional.
We manage python dependencies with anaconda. You can find information on how to install anaconda at: https://docs.anaconda.com/anaconda/install/. After installing, create the environment with executing conda env create in the root directory of the repository. This automatically finds and uses the file environment.yml, which creates an environment called robustness with
everything needed to run our python files and notebooks. Activate the environment with conda activate robustness.
We use tensorflow-gpu 2.1 to calculate adversarial examples. To correctly set up tensorflow for your GPU, follow the instructions from: https://www.tensorflow.org/install/gpu.
The models and datasets for the experiments are hosted in Google Drive by Croce et al.. In order to reproduce the experiments, you need to download them and extract the folders models and datasets into the submodule directory provable_robustness_max_linear_regions.
If you have a problem or question regarding the code, please contact Niklas Risse.