{% if False %}
The goal of this project is to provide minimalistic django project template that everyone can use, which just works out of the box and has the basic setup you can expand on.
Template is written with django 1.11 and python 3 in mind.
-
Separated dev and production settings
-
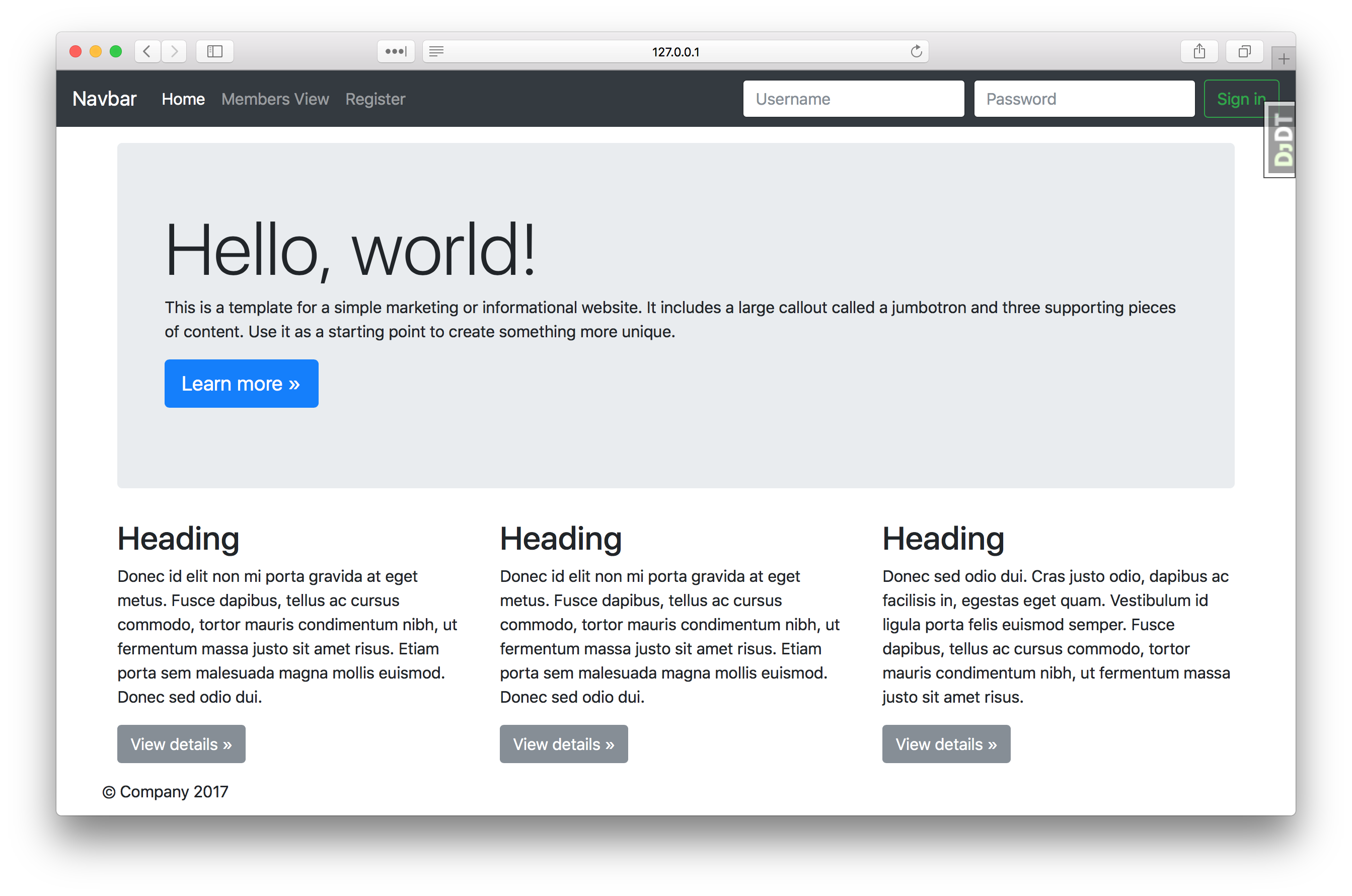
Example app with custom user model
-
Bootstrap static files included
-
User registration and logging in as demo
-
Procfile for easy deployments
-
Separated requirements files
-
SQLite by default if no env variable is set
To use this template to start your own project:
If your project is already in an existing python3 virtualenv first install django by running
$ pip install django
And then run the django-admin.py command to start the new project:
$ django-admin.py startproject \
--template=https://github.com/nikola-k/django-template/zipball/master \
--extension=py,md \
<project_name>
This assumes that python3 is linked to valid installation of python 3 and that pip is installed and pip3is valid
for installing python 3 packages.
Installing inside virtualenv is recommended, however you can start your project without virtualenv too.
If you don't have django installed for python 3 then run:
$ pip3 install django
And then:
$ python3 -m django startproject \
--template=https://github.com/nikola-k/django-template/zipball/master \
--extension=py,md \
<project_name>
After that just install the local dependencies, run migrations, and start the server.
{% endif %}
First clone the repository from Github and switch to the new directory:
$ git clone git@github.com/USERNAME/{{ project_name }}.git
$ cd {{ project_name }}
Activate the virtualenv for your project.
Install project dependencies:
$ pip install -r requirements/local.txt
Then simply apply the migrations:
$ python manage.py migrate
You can now run the development server:
$ python manage.py runserver