- Overview of AWS EC2 FPGA Development Kit
- Getting Started
- FPGA Developer AMI available on AWS Marketplace
- FPGA Hardware Development Kit (HDK)
- FPGA Software Development Kit (SDK)
- OpenCL Development Environment with Amazon EC2 F1 FPGA Instances to accelerate your C/C++ applications
- Developer Support
- Recommended Documentation
- Github tips and tricks
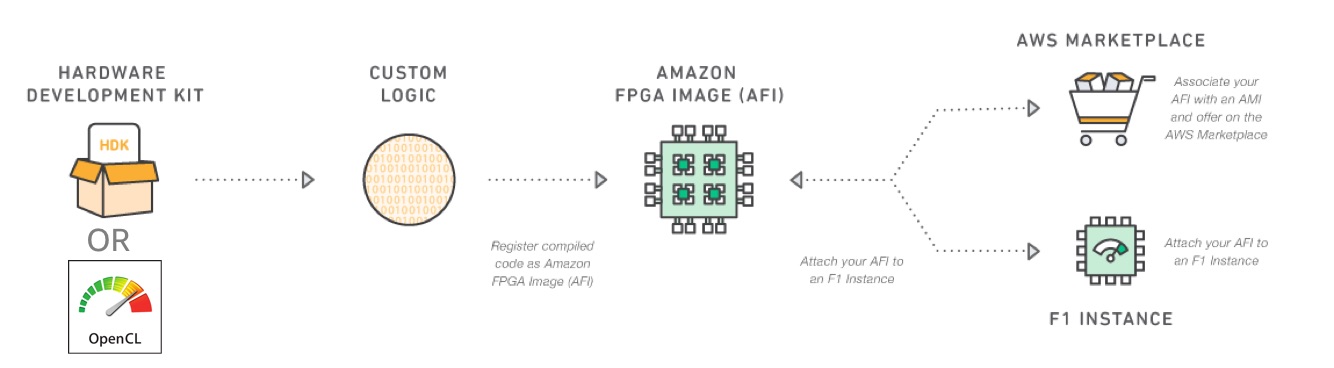
The AWS EC2 FPGA Development Kit is provided by AWS to support development and runtime on AWS FPGA instances. Amazon EC2 FPGA instances are high-performance compute instances with field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) that are programmed to create custom hardware accelerations in EC2. F1 instances are easy to program and AWS provides everything needed to develop, simulate, debug, compile and run hardware accelerated applications. Using the FPGA developer AMI, developers create an FPGA design. Once the FPGA design (also called CL - Custom logic) is complete, developers create the Amazon FPGA Image (AFI), and easily deploy it to the F1 instance. AFIs are reusable, shareable and can be deployed in a scalable and secure way.
| Development Environment | Description | Accelerator Language | Development Tool | Debug Options | Typical Developer / FPGA Experience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Software Defined Accelerator Development - SDAccel | Development experience leverages an optimized compiler to allow easy new accelerator development or migration of existing C/C++/openCL, Verilog/VHDL to AWS FPGA instances | C/C++/OpenCL, Verilog/VHDL (RTL) | SDx/Vivado (GUI or scipt) | SW/HW Emulation, Simulation, GDB, Virtual JTAG (Chipscope) | SW or HW Developer with zero FPGA experience |
| Hardware Accelerator Development - HDK | Fully custom hardware development experience provides hardware developers with the tools required for developing AFIs for AWS FPGA instances | Verilog/VHDL | Vivado | Simulation, Virtual JTAG | HW Developer with advanced FPGA experience |
| IP Integrator or High Level Synthesis (HLx) | Graphical interface development experience for integrating IP and high level synthesis development | Verilog/VHDL/C | Vivado (GUI) | Simulation, Virtual JTAG | HW Developer with intermediate FPGA experience |
| Runtime Environment | Hardware Interface | Host Code Language | FPGA Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| C/C++ Software Defined Accelerator Development | OpenCL APIs, XOCL Driver, HAL | C/C++ | SDK, SDx |
| Hardware Accelerator Development | XDMA Driver, peek/poke | C/C++ | SDK, Vivado |
| IP Integrator or High Level Synthesis (HLx) | XDMA Driver, peek/poke | C/C++ | SDK, Vivado |
| Tool | Development/Runtime | Tool location | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDx 2017.4 & 2018.2 | Development | FPGA developer AMI | Used for Software Defined Accelerator Development |
| Vivado 2017.4 & 2018.2 | Development | FPGA developer AMI | Used for Hardware Accelerator Development |
| FPGA AFI Management Tools | Runtime | SDK - fpga_mgmt_tools | Command-line tools used for FPGA management while running on the F1 instance |
| Virtual JTAG | Development (Debug) | FPGA developer AMI | Runtime debug waveform |
| wait_for_afi | Development | wait_for_afi.py | Helper script that notifies via email on AFI generation completion |
| notify_via_sns | Development | notify_via_sns.py | Notifies developer when design build process completes |
| AFI Administration | Development | Copy, Delete, Describe, Attributes | AWS CLI EC2 commands for managing your AFIs |
NOTE: For on-premises development, SDx/Vivado must have the correct license and use one of the supported versions of SDx/Vivado. The FPGA HDK+SDK Release Notes may contain additional information. The following links have more information on on-premises development: Vivado requirements and SDx requirements
| Accelerator Application | Example | Development Environment | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Custom hardware | cl_hello_world | HDK - RTL (Verilog) | Simple getting started example with minimal hardware |
| Custom hardware | cl_dram_dma | HDK - RTL (Verilog) | Demonstrates CL connectivity to the F1 shell and connectivity to/from all DDRs |
| Custom hardware IP integration example using a GUI | cl_dram_dma_hlx | HLx - Verilog | Demonstrates CL connectivity to the F1 shell and connectivity to/from DRAM using the Vivado IP Integrator GUI |
| Virtual Ethernet Application | Example Application | HDK SDE Example | The Virtual Ethernet framework facilitates streaming Ethernet frames from a network interface (or any source) into the FPGA for processing and back out to some destination. Possible use cases for this include deep packet inspection, software defined networking, stream encryption or compression, and more. |
| Pipelined Workload Applications | cl_dram_dma_data_retention | HDK SDAccel | Demonstrates how to preserve data in DRAMs while swapping out accelerators. Applications that use a temporal accelerator pipeline can take advantage of this feature to reduce latency between FPGA image swaps |
| Digital Up-Converter using High Level Synthesis | cl_hls_dds_hlx | HLx - C-to-RTL | Demonstrates an example application written in C that is synthesized to RTL (Verilog) |
| Security | AES, RSA, SHA1 | SDAccel - C/C++/OpenCL | Developed using software defined acceleration, this example demonstrates methods of using hardware acceleration to speed up security software algorithms |
| Computer Vision | Affine, Convolve, Huffman, IDCT | SDAccel - C/C++/OpenCL | Developed using software defined acceleration, this example demonstrates methods of using hardware acceleration to speed up image detection algorithms |
| Misc Algorithms | Kmeans, SmithWaterman, MatrixMult | SDAccel - C/C++/OpenCL | Developed using software defined acceleration, this example demonstrates methods of applying hardware acceleration to a variety of sorting and search algorithms |
| Financial | Blacksholes, Heston | SDAccel - C/C++/OpenCL | Developed using software defined acceleration, this example demonstrates methods of using hardware acceleration on Monte Carlo financial models |
| Custom Hardware with Software Defined Acceleration | RTL Kernels | SDAccel - RTL (Verilog) + C/C++/OpenCL | Developed using software defined acceleration, this example demonstrates a quick method for developing new or migrating existing hardware designs (RTL) |
| File Compression | GZip | SDAccel - C/C++/OpenCL | Developed using software defined acceleration, this example demonstrates methods of using hardware acceleration to speed up GZIP compression on an FPGA |
| WebP Image Compression | WebP | SDAccel - C/C++/OpenCL | Developed using software defined acceleration, this example demonstrates methods of using hardware acceleration to speed up WebP encoder application on an FPGA |
If you have never used AWS before, we recommend you start with AWS getting started training, and focus on the basics of the AWS EC2 and AWS S3 services. Understanding the fundamentals of these services will make it easier to work with AWS FPGAs.
AWS FPGA generation and EC2 F1 instances are supported in the us-east-1 (N. Virginia), us-west-2 (Oregon), eu-west-1 (Ireland) and us-gov-west-1 (GovCloud US) regions.
The developer kit is supported for Linux operating systems only. You have the choice to develop on AWS EC2 using the FPGA developer AMI or on-premises. Within a linux environment, you can execute git clone https://github.com/aws/aws-fpga.git to download the latest release to your EC2 Instance or local server. Help on cloning from github is available here. When using a SSH connection, execute git clone git@github.com:aws/aws-fpga.git. To get help with connecting to Github via SSH.
Before you start your first AWS FPGA design, we recommend that you go through one of the step-by-step guides. The guides will walk through development steps for hello world examples. Based on the tables above, pick the development environment that best fits your needs and use the guide to get started:
- For fastest way to get started on FPGA accelerator development, start with the software defined development environment. The guide starts with the SW Hello World example.
- Next use the same guide to develop using the C/C++/openCL/RTL based 80+ examples on github.
- For custom hardware development (HDK) environment, start with the HDK Hello World example.
- Next use the same guide to develop using the cl_dram_dma.
Once you have completed your hello world examples, we recommend diving deeper into a training workshop or application notes
- Software-defined re:Invent 2017 Workshop demonstrates a video encoder acceleration and how to debug and optimize your accelerator.
- Custom hardware developers need to learn about how the hardware accelerator interfaces to the F1 Shell
- Shell Interface
- Shell Address Map
- Programmer view of the FPGA
- Virtual JTAG
- Application for methods of interfacing the host application to the Hardware accelerator
The FPGA developer AMI is available on the AWS marketplace without a software charge and includes free tools and drivers needed for FPGA development on EC2 instances. FPGA development runs on several EC2 instance types. Given the large size of the FPGA used inside the AWS FPGA instances, the implementation tools require 32GiB Memory (ex: z1d.xlarge, z1d.2xlarge, c5.4xlarge, m5.2xlarge, r5.xlarge, t2.2xlarge). z1d.xlarge/c5.4xlarge and z1d.2xlarge/c5.8xlarge would provide the fastest execution time with 30GiB+ and 60GiB+ of memory respectively. Developers who want to save on cost, could start coding and run simulations on low-cost instances, like t2.2xlarge, and move to the aforementioned larger instances to run the synthesis of their acceleration code.
Currently, AWS marketplace includes multiple versions of the FPGA developer AMI, supporting Xilinx SDx 2017.4 and 2018.2 toolchain versions. The following compatibility table describes the mapping of currently supported developer kit versions to AMI versions:
| Developer Kit Version | Tool Version Supported | Compatible FPGA developer AMI Version |
|---|---|---|
| 1.3.7-1.3.X | 2017.4 | v1.4.0-v1.4.X (Xilinx Vivado/SDx 2017.4) |
| 1.4.X | 2017.4 | v1.4.0-v1.4.X (Xilinx Vivado/SDx 2017.4) |
| 1.4.3+ | 2018.2 | v1.5.0-v1.5.X (Xilinx Vivado/SDx 2018.2) |
Developer kit versions prior to v1.3.7 and Developer AMI prior to v1.4 (2017.1) reached end-of-life. See AWS forum announcement for additional details.
If developing using SDAccel environment please refer to this Runtime Compatibility Table
The HDK directory contains useful information, examples, and scripts for developers wanting to start building Amazon FPGA Images (AFI). It includes the development environment, simulation, build and AFI creation scripts. The HDK can be installed on any on-premises server or an EC2 instance. The developer kit is not required if you plan to use a pre-built AFI shared from another developer.
The software-defined development environment allows customers to compile their C/C++/OpenCL code into the FPGA as kernels, and use OpenCL APIs to pass data to the FPGA. Software developers with no FPGA experience will find a familiar development experience that supercharges cloud applications.
In addition, this development environment (also called SDAccel) allows the mix of C/C++ and RTL accelerator designs into a C/C++ software based development environment. This method enables faster prototyping using C/C++ while supporting manual optimization of critical blocks within RTL. This approach is similar to optimizing time critical functions using software compiler optimization methods.
This developer kit has 80+ examples to help you get started on FPGA acceleration. To get started, review the Software-defined development environment readme.
The SDK directory includes the runtime environment required to run on EC2 FPGA instances. It includes the drivers and tools to manage the AFIs that are loaded on the FPGA instance. The SDK isn't required during the AFI development process; it is only required once an AFI is loaded onto an EC2 FPGA instance. The following sdk resources are provided:
- Linux Kernel Drivers - The developer kit includes three drivers:
- XDMA Driver - DMA interface to/from HDK accelerators.
- XOCL Driver - DMA interface with software defined accelerators (also called hardware kernels).
- EDMA Driver - Legacy DMA interface to/from HDK accelerators.
- FPGA Libraries - APIs used by C/C++ host applications.
- FPGA Management Tools - AFI management APIs for runtime loading/clearing FPGA image, gathering metrics and debug interface on the F1 instance.
The Amazon FPGA Development User Forum is the first place to go to post questions, learn from other users and read announcements from the EC2 FPGA team.
- Click the "Watch" button in GitHub upper right corner to get regular updates.
- We recommend you will join the AWS forum to engage with the FPGA developer community and get help when needed (both AWS and Xilinx engineers monitor this forum).
- In case you can't see "Your Stuff" details, you will need to logout using the logout button on the forums page and log back in again.
The documentation is located throughout this developer kit, therefore, to help developers find information quicker the table below consolidates a list of key documents:
| Topic | Document Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Developer Kit Features | RELEASE_NOTES, Errata | Release notes and Errata for all developer kit features, excluding the shell |
| Frequently asked questions | FAQ, Errata | Q/A are added based on developer feedback and common AWS forum questions |
| F1 Shell (HDK) | AWS_Shell_RELEASE_NOTES, AWS_Shell_ERRATA | Release notes and Errata for F1 shell |
| F1 Shell (HDK) | AWS_Shell_Interface_Specification | Shell-CL interface specification for HDK developers building AFI |
| AWS setup | Setup_AWS_CLI_and_S3_Bucket | Setup instructions for preparing for AFI creation |
| SDx graphical interface (SDAccel) | README_GUI | Instructions using the SDx GUI for software defined acceleration development and debug |
| Software defined acceleration using RTL (SDAccel) | Debug_RTL_Kernel | Instructions on debugging RTL Kernel |
| Software defined acceleration Run time (SDAccel) | Create_Runtime_AMI | Instructions on creating a runtime AMI |
| Host Application (HDK) | Programmer_View | Host application to CL interface specification |
| CL Debug (HDK) | Virtual_JTAG_XVC | Debugging CL using Virtual JTAG (Chipscope) |
| CL/Shell Simulation (HDK) | RTL_Simulating_CL_Designs | Shell-CL simulation specification |
| Driver (HDK) | README | Describes the DMA driver (XDMA) used by HDK examples and includes a link to an installation guide |
| Shell Timeout and AXI Protocol Protection | HOWTO_detect_shell_timeout | The shell will terminate transactions after a time period or on an illegal transaction. This describes how to detect and gather data to help debug CL issues caused by timeouts. |
| AFI Power | afi_power | Helps developers with understanding AFI power and preventing power violations on the F1 instance |
| AFI Management | README | CLI documentation for managing AFI on the F1 instance |
| AFI Administration | copy_fpga_image, delete_fpga_image, describe_fpga_images, fpga_image_attributes | CLI documentation for administering AFIs |
| AFI Creation Error Codes | create_fpga_image_error_codes | CLI documentation for managing AFIs |
| Developing on-premises | HDK: on_premise_licensing_help, SDAccel: On_Premises_Development_Steps | Guidance for developer wanting to develop AFIs from on-premises instead of using the FPGA developer AMI running on AWS EC2 |
- Cloning the repository
- Forking the repository
- Searching code and advanced search syntax
- Finding files
- Simply replace github.com with gitprint.com to generate a printable PDF