Johannes Brandstetter, Max Welling, Daniel Worrall
If you find our work and/or our code useful, please cite us via:
@article{brandstetter2022lie,
title={Lie Point Symmetry Data Augmentation for Neural PDE Solvers},
author={Brandstetter, Johannes and Welling, Max and Worrall, Daniel E},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.07643},
year={2022}
}source environment.sh
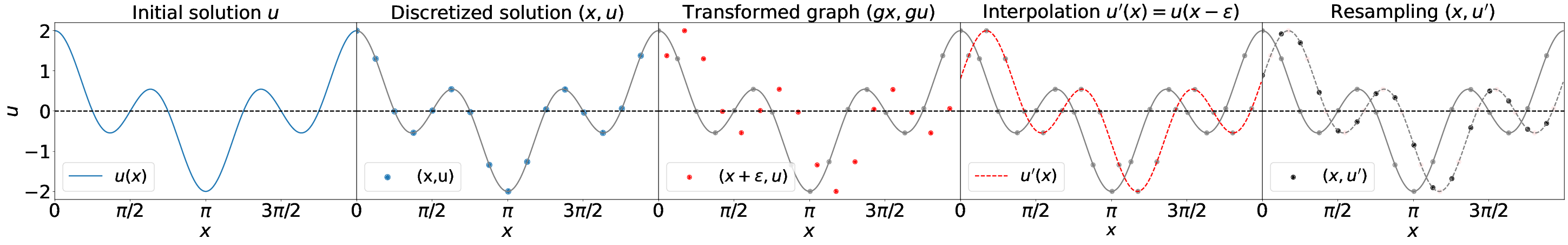
Have a look into our jupyter notebooks to get an idea how we do the data generation and how we apply Lie point symmetry data augmentation.
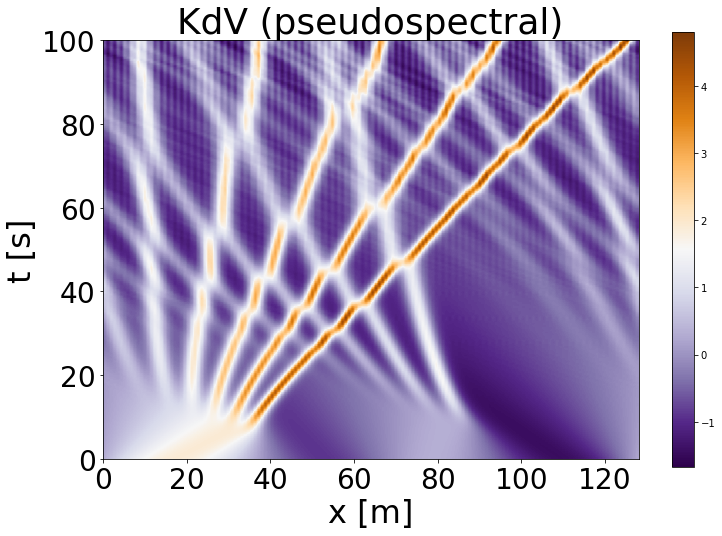
python generate/generate_data.py --experiment=KdV --train_samples=512 --valid_samples=512 --test_samples=512 --L=128
We used easier datasets for training the Resnet or the CNN model since these models do not have the same complexity as the FNO model and thus have a harder time fitting the default KdV equation.
python generate/generate_data.py --experiment=KdV --train_samples=512 --valid_samples=512 --test_samples=512 --L=128 --end_time=50. --suffix=easy
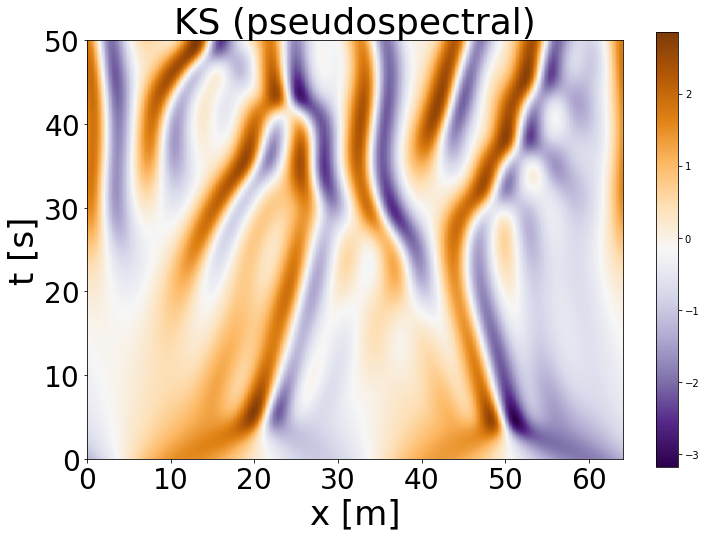
python generate/generate_data.py --experiment=KS --train_samples=512 --valid_samples=512 --test_samples=512 --L=64 --nt=500
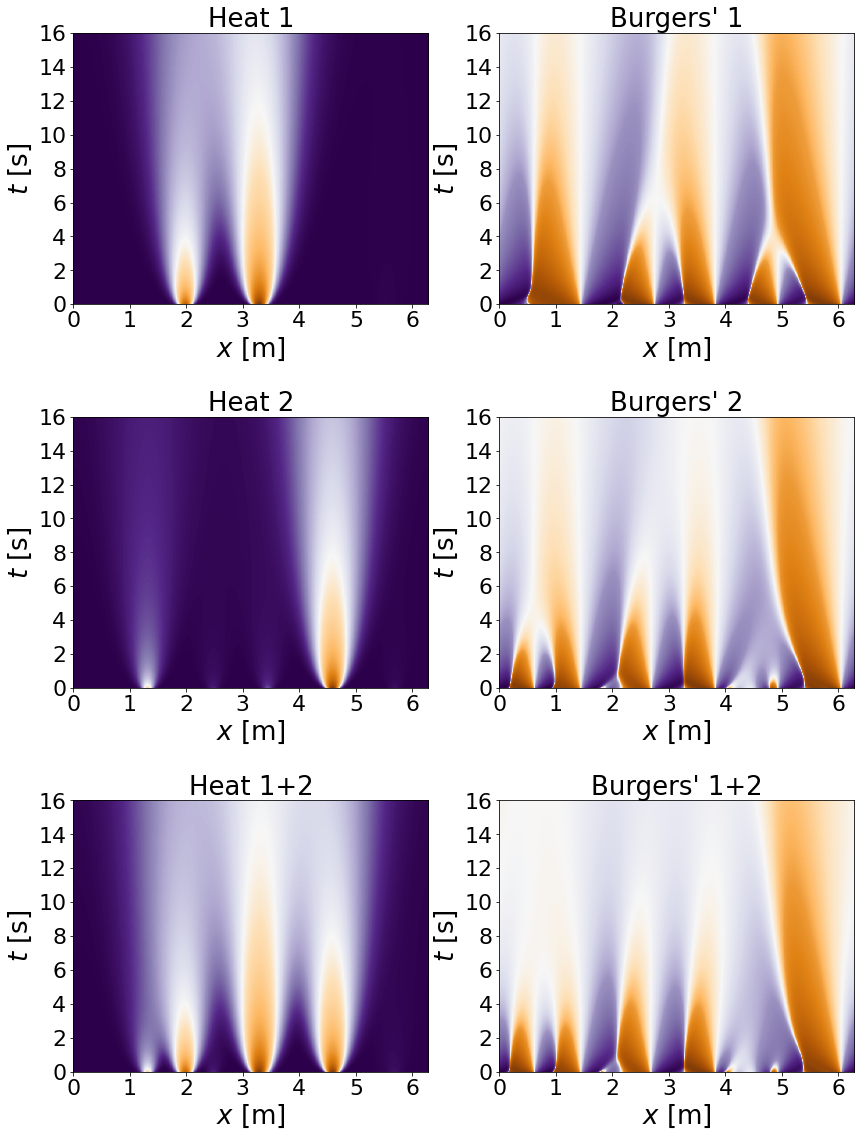
Trajectories are generated for the Heat equation and then transformed via the Cole-Hopf transformation into the Burgers' equation.
The L parameter is automatically set to 2*math.pi.
python generate/generate_data.py --experiment=Burgers --train_samples=512 --valid_samples=512 --test_samples=512 --end_time=18. --nt=180
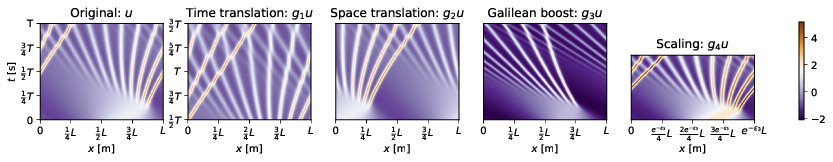
KdV augmentation is controlled via [time translation (bool), space translation (max_x_shift), Galilean translation (max_velocity), scale (max_scaling)] Setting any of these values to zero corresponds to switching off the augmentation.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python experiments/train.py --device=cuda:0 --experiment=KdV --KdV_augmentation=1,1.0,0.4,0.1 --train_samples=512
KS augmentation is controlled via [time translation (bool), space translation (max_x_shift), Galilean translation (max_velocity)] Setting any of these values to zero corresponds to switching off the augmentation.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python experiments/train.py --device=cuda:0 --experiment=Burgers --KS_augmentation=1,1.0,0.4 --train_samples=512
Burgers augmentation is controlled via [time translation (bool), space translation (max_x_shift), mixing parameter] Setting any of these values to zero corresponds to switching off the augmentation. The mixing parameter determines to which extend different trajectories are mixed to generate a new trajectory.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python experiments/train.py --device=cuda:0 --experiment=KS --Burgers_augmentation=1,1.0,0.5 --train_samples=512