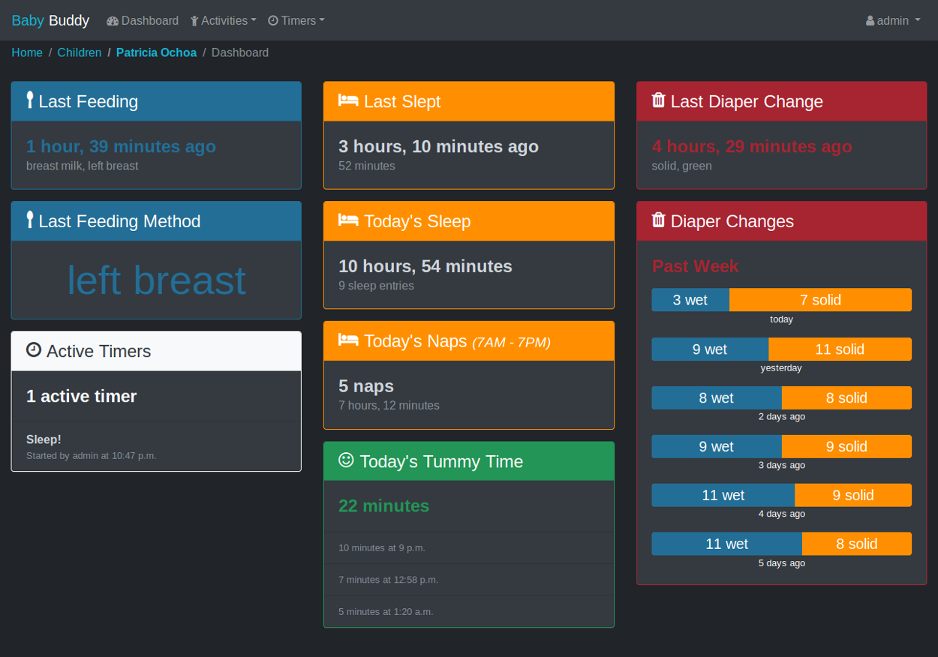
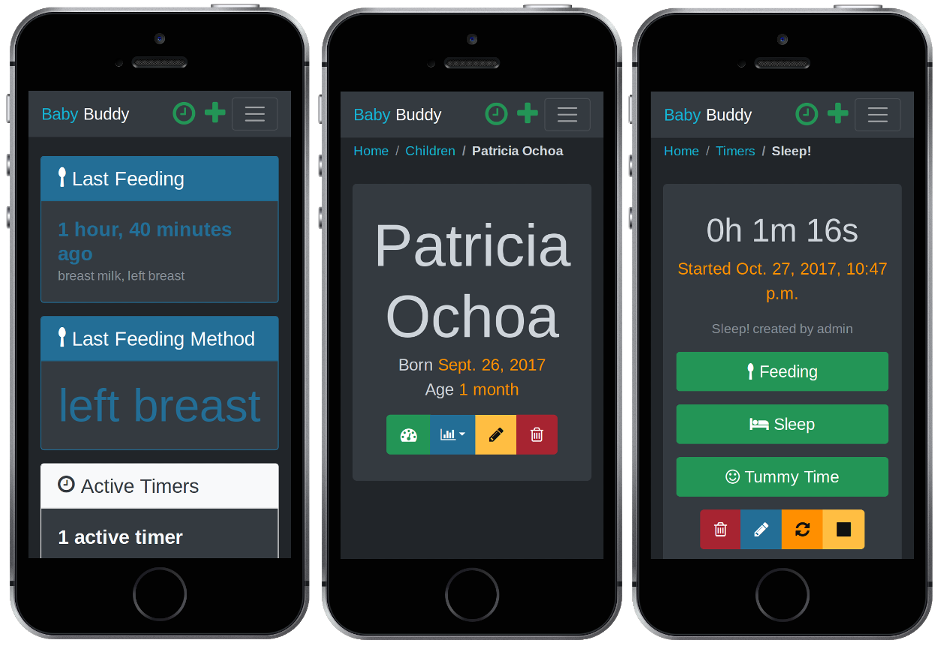
A buddy for babies! Helps caregivers track sleep, feedings, diaper changes, tummy time and more to learn about and predict baby's needs without (as much) guess work.
Table of Contents
A demo of Baby Buddy is available on Heroku. The demo instance resets every hour. Login credentials are:
- Username:
admin - Password:
admin
The default user name and password for Baby Buddy is admin/admin. For any
deployment, log in and change the default admin password immediately.
Many of Baby Buddy's configuration settings can be controlled using environment variables - see Configuration for detailed information.
A basic Elastic Beanstalk
configuration is provided in .ebextensions/babybuddy.config. The steps
below are a rough guide to deployment. See Working with Python
for detailed information.
-
Clone/download the Baby Buddy repo
git clone https://github.com/babybuddy/babybuddy.git -
Enter the cloned/downloaded directory
cd babybuddy -
Set (at least) the
SECRET_KEYenvironment value in.ebextensions/babybuddy.config*See Configuration for other settings that can be controlled by environment variables.
-
Create an IAM user in AWS with EB, EC2, RDS and S3 privileges.
-
Initialize the Elastic Bean application (using the IAM user from the previous step)
eb init -p python-3.6 -
Create/deploy the environment! 🚀
eb create -db -db.engine postgres
The create command will also do an initial deployment. Run eb deploy to
redeploy the app (e.g. if there are errors or settings are changed).
A Docker deployment requires Docker Engine v18.06.0+ and Docker Compose v1.22.0+ to create two containers: one for the database and one for the application.
The example docker-compose.example.yml file provided in this repository is
intended for production deployments. Baby Buddy is deployed to Docker Hub as
babybuddy/babybuddy so this is
the only file needed for a Docker deployment with Docker Compose.
A secondary example file docker-compose.example.sqlite.yml is also available
for a simpler SQLite-based deployment (the default example users PostgreSQL).
-
Copy the raw content of either
docker-compose.example.ymlordocker-compose.example.sqlite.ymlinto a new file nameddocker-compose.ymlwget -O docker-compose.yml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/babybuddy/babybuddy/master/docker-compose.example.ymlor
wget -O docker-compose.yml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/babybuddy/babybuddy/master/docker-compose.example.sqlite.yml -
Within
docker-compose.yml, at the very least, set theALLOWED_HOSTSandSECRET_KEYvariables underservices:app:environment.See Configuration for other settings that can be controlled by environment variables.
-
Build/run the application
docker-compose up -d
The app should now be locally available at http://127.0.0.1:8000. See Docker's "Get Started" documentation for detailed information about deployment methods with Docker.
For manual deployments to Heroku without using the deploy button, make sure to create the following settings before pushing:
heroku config:set DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=babybuddy.settings.heroku
heroku config:set SECRET_KEY=<CHANGE TO SOMETHING RANDOM>
heroku config:set DISABLE_COLLECTSTATIC=1
heroku config:set TIME_ZONE=<DESIRED DEFAULT TIMEZONE>
See Configuration for other settings that can be controlled
by heroku config:set.
And after an initial push, execute the following commands:
heroku run python manage.py migrate
heroku run python manage.py createcachetable
There are many ways to deploy Baby Buddy manually to any server/VPS. The basic requirements are Python, a web server, an application server, and a database.
- Python 3.6+, pip, pipenv
- Web server (nginx, Apache, etc.)
- Application server (uwsgi, gunicorn, etc.)
- Database (sqlite, Postgres, MySQL, etc.)
This example assumes a 512MB VPS instance with Ubuntu 18.04. It uses Python 3.6+, nginx, uwsgi and sqlite and should be sufficient for a few users (e.g. two parents and 1+ child).
-
Install system packages
sudo apt-get install python3 python3-pip nginx uwsgi uwsgi-plugin-python3 git libopenjp2-7-dev -
Default python3 to python for this session
alias python=python3 -
Install pipenv
sudo -H pip3 install pipenv -
Set up directories and files
sudo mkdir /var/www/babybuddy sudo chown $USER:$(id -gn $USER) /var/www/babybuddy mkdir -p /var/www/babybuddy/data/media git clone https://github.com/babybuddy/babybuddy.git /var/www/babybuddy/public -
Move in to the application folder
cd /var/www/babybuddy/public -
Set pipenv to install locally.
export PIPENV_VENV_IN_PROJECT=1 -
Initiate and enter the Python environment
pipenv install --three pipenv shell -
Create a production settings file and set the
SECRET_KEYandALLOWED_HOSTSvaluescp babybuddy/settings/production.example.py babybuddy/settings/production.py editor babybuddy/settings/production.py -
Initiate the application
export DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=babybuddy.settings.production python manage.py migrate python manage.py createcachetable -
Set appropriate permissions on the database and data folder
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/babybuddy/data sudo chmod 640 /var/www/babybuddy/data/db.sqlite3 sudo chmod 750 /var/www/babybuddy/data -
Create and configure the uwsgi app
sudo editor /etc/uwsgi/apps-available/babybuddy.iniExample config:
[uwsgi] plugins = python3 project = babybuddy base_dir = /var/www/babybuddy chdir = %(base_dir)/public virtualenv = %(chdir)/.venv module = %(project).wsgi:application env = DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=%(project).settings.production master = True vacuum = TrueSee the uWSGI documentation for more advanced configuration details.
-
Symlink config and restart uWSGI:
sudo ln -s /etc/uwsgi/apps-available/babybuddy.ini /etc/uwsgi/apps-enabled/babybuddy.ini sudo service uwsgi restart -
Create and configure the nginx server
sudo editor /etc/nginx/sites-available/babybuddyExample config:
upstream babybuddy { server unix:///var/run/uwsgi/app/babybuddy/socket; } server { listen 80; server_name babybuddy.example.com; location / { uwsgi_pass babybuddy; include uwsgi_params; } location /media { alias /var/www/babybuddy/data/media; } }See the nginx documentation for more advanced configuration details.
-
Symlink config and restart NGINX:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/babybuddy /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/babybuddy sudo service nginx restart -
That's it (hopefully)! 🎉
Environment variables can be used to define a number of configuration settings.
Baby Buddy will check the application directory structure for an .env file or
take these variables from the system environment. System environment variables
take precedence over the contents of an .env file.
ALLOWED_HOSTSALLOW_UPLOADSAWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAMEDEBUGNAP_START_MAXNAP_START_MINDB_ENGINEDB_HOST- 'DB_NAME'
DB_PASSWORDDB_PORTDB_USERSECRET_KEYTIME_ZONEUSE_24_HOUR_TIME_FORMAT
Default: * (any)
This option may be set to a single host or comma-separated list of hosts (without spaces). This should always be set to a specific host or hosts in production deployments.
See also: Django's documentation on the ALLOWED_HOSTS setting
Default: True
Whether or not to allow uploads (e.g. of Child photos). For some deployments (AWS, Heroku) this setting will default to False due to the lack of available persistent storage.
Default: None
Required to access your AWS S3 bucket, should be uniquely generated per bucket for security.
See also: AWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAME
Default: None
Required to access your AWS S3 bucket, should be uniquely generated per bucket for security.
See also: AWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAME
Default: None
If you would like to use AWS S3 for storage on ephemeral storage platforms like Heroku you will need to create a bucket and add it's name. See django-storages' Amazon S3 documentation.
Default: False
When in debug mode, Baby Buddy will print much more detailed error information for exceptions. This setting should be False in production deployments.
See also Django's documentation on the DEBUG setting.
Default: 18:00
The maximum start time (in the instance's time zone) before which a sleep entry is consider a nap. Expects the 24-hour format %H:%M.
Default: 06:00
The minimum start time (in the instance's time zone) after which a sleep entry is considered a nap. Expects the 24-hour format %H:%M.
Default: django.db.backends.postgresql
The database engine utilized for the deployment.
See also Django's documentation on the ENGINE setting .
Default: db
The name of the database host for the deployment.
Default: postgres
The name of the database table utilized for the deployment.
No Default
The password for the database user for the deployment. In the default example, this is the root PostgreSQL password.
Default: 5432
The listening port for the database. The default port is 5432 for PostgreSQL.
Default: postgres
The database username utilized for the deployment.
Default: None
A random, unique string must be set as the "secret key" before Baby Buddy can be deployed and run.
See also Django's documentation on the SECRET_KEY setting.
Default: Etc/UTC
The default time zone to use for the instance. See List of tz database time zones for all possible values. This value can be overridden per use from the user settings form.
Default: False
Whether to force 24-hour time format for locales that do not ordinarily use it
(e.g. en). Support for this feature must implemented on a per-locale basis.
See format files under babybuddy/formats for supported
locales.
Note: This value for this setting is interpreted as a boolean from a string
using Python's built-in strtobool
tool. Only certain strings are supported (e.g. "True" for True and "False" for
False), other unrecognized strings will cause a ValueError and prevent Baby
Buddy from loading.
Baby Buddy includes translation support as of v1.2.2. Language can be set on a
per-user basis from the user settings page (/user/settings/). See
CONTRIBUTING.md for information about how to
create/update translations.
🇺🇸 English (U.S.) (base)
🇳🇱 Dutch
🇫🇮 Finnish
🇫🇷 French
🇩🇪 German
🇮🇹 Italian
🇲🇽 🇪🇸 Spanish
🇸🇪 Swedish
🇹🇷 Turkish
Baby Buddy uses the django-import-export application to provide import and export functionality.
Export actions are accessible from Baby Buddy's "Database Admin" area (the Django admin interface). For example, to export all diaper change entries from Baby Buddy as an Excel file:
-
Log in as a user with "staff" access.
-
From the user menu, click "Database Admin" under the "Site" heading.
-
Click "Diaper Changes" in the list of data types.
-
Click the "Export" button above the filters list on the right side of the screen.
-
Select the "xlxs" format and click "Submit"
Note: any applied filters will also filter the exported entries. Alternatively, on the Diaper Change list screen (step 3 above), it is possible to select one or many individual records and select "Export selected Diaper Changes" from the "Actions" list.
Import actions are accessible from Baby Buddy's "Database Admin" area (the Django admin interface). From the list of entry types in the Database Admin, select the type to import and click the "Import" button on the list page. The import screen for a particular type will list the fields generally expected to be present for an import. Multiple file types -- including csv, xlsx, etc. -- are supported for the import.
The import pages do not provide detailed information about the required data and formats. When an import is attempted, all rows will be checked for errors and any issues will be reported on screen and will need to be resolved before the import can be performed.
See the example import files used for tests to get an idea of the expected data format.
Baby Buddy uses the Django REST Framework (DRF) to provide a REST API.
The only requirement for (most) requests is that the Authorization header is
set as described in the Authentication section. The one
exception is the /api endpoint, which lists all available endpoints.
Currently, the following endpoints are available for GET, OPTIONS, and
POST requests:
/api/children//api/changes/(Diaper Changes)/api/feedings//api/notes//api/sleep//api/temperature//api/timers//api/tummy-times//api/weight/
By default, the TokenAuthentication and SessionAuthentication classes are enabled. Session authentication covers local API requests made by the application itself. Token authentication allows external requests to be made.
❗ In a production environment, token authentication should only
be used for API calls to an https endpoint. ❗
Each user is automatically assigned an API key that can be used for token
authentication. This key can be found on the User Settings page for the logged
in the user. To use a key for an API request, set the request Authorization
header to Token <user-key>. E.g.
Authorization: Token 2h23807gd72h7hop382p98hd823dw3g665g56
If the Authorization header is not set or the key is not valid, the API will
return 403 Forbidden with additional details in the response body.
API schema information in the OpenAPI format
can be found in the openapi-schema.yml file in the project root. A live
version is also available at the /api/scehma path of a running instance.
The limit and offset request parameters can be used to limit
and offset the results set respectively. For example, the following request
will return five diaper changes starting from the 10th diaper change entry:
curl -X GET 'https://[...]/api/changes/?limit=5&offset=10' -H 'Authorization: Token [...]'
{
"count": <int>,
"next": "https://[...]/api/changes/?limit=5&offset=15",
"previous": "https://[...]/api/changes/?limit=5&offset=5",
"results": [...]
}
Field-based filters for specific endpoints can be found the in the filters
field of the OPTIONS response for specific endpoints.
Single entries can also be retrieved by adding the ID (or in the case of a Child entry, the slug) of a particular entry:
curl -X GET https://[...]/api/children/gregory-hill/ -H 'Authorization: Token [...]'
{
"id":3,
"first_name":"Gregory",
"last_name":"Hill",
"birth_date":"2020-02-11",
"slug":"gregory-hill",
"picture":null
}
curl -X GET https://[...]/api/sleep/1/ -H 'Authorization: Token [...]'
{
"id":480,
"child":3,
"start":"2020-03-12T21:25:28.916016-07:00",
"end":"2020-03-13T01:34:28.916016-07:00",
"duration":"04:09:00",
"nap":false
}
Returns JSON data in the response body in the following format:
{
"count":<int>,
"next":<url>,
"previous":<url>,
"results":[{...}]
}
count: Total number of records (in the database, not just the response).next: URL for the next set of results.previous: URL for the previous set of results.results: An array of the results of the request.
For single entries, returns JSON data in the response body keyed by model field names. This will vary between models.
All endpoints will respond to an OPTIONS request with detailed information
about the endpoint's purpose, parameters, filters, etc.
Returns JSON data in the response body describing the endpoint, available
options for POST requests, and available filters for GET requests. The
following example describes the /api/children endpoint:
{
"name": "Child List",
"renders": [
"application/json",
"text/html"
],
"parses": [
"application/json",
"application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
"multipart/form-data"
],
"actions": {
"POST": {
"id": {
"type": "integer",
"required": false,
"read_only": true,
"label": "ID"
},
[...]
}
},
"filters": [
"first_name",
"last_name",
"slug"
]
}
To add new entries for a particular endpoint, send a POST request with the
entry data in JSON format in the request body. The Content-Type header for
POST request must be set to application/json.
Regular sanity checks will be performed on relevant data. See the OPTIONS
response for a particular endpoint for details on required fields and data
formats.
The "timer" field is a special field available for POST operations to model
endpoints supporting duration (Feeding, Sleep, Tummy Time). When the "timer"
field is set in the request, the start and end fields will be filled in
automatically using the start and end values from the Timer (the Timer
will be stopped if it is currently running).
Additionally, if the Timer has a Child relationship, the child field will be
filled in automatically use the child value from the Timer.
If the "timer" field is set, it's values will always override the relevant
fields in the request. E.g. if a POST request is sent with both the timer
and end fields, the value for the end field will be ignored and replaced by
the Timer's end value. The same applies for start and child. These fields
can all be left out of the request when the Timer is provided, otherwise they
are required fields.
Returns JSON data in the response body describing the added/updated instance or
error details if errors exist. Errors are keyed by either the field in error or
the general string non_field_errors (usually when validation involves
multiple fields).
To update existing entries, send a PATCH request to the single entry endpoint
for the entry to be updated. The Content-Type header for PATCH request must
be set to application/json. For example, to update a Diaper Change entry with
ID 947 to indicate a "wet" diaper only:
curl -X PATCH \
-H 'Authorization: Token [...]' \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"wet":1, "solid":0}' \
https://[...]/api/changes/947/
Regular sanity checks will be performed on relevant data. See the OPTIONS
response for a particular endpoint for details on required fields and data
formats.
Returns JSON data in the response body describing the added/updated instance or
error details if errors exist. Errors are keyed by either the field in error or
the general string non_field_errors (usually when validation involves
multiple fields).
To delete an existing entry, send a DELETE request to the single entry
endpoint to be deleted. For example, to delete a Diaper Change entry with ID
947:
curl -X DELETE https://[...]/api/changes/947/ -H 'Authorization: Token [...]'
Returns an empty response with HTTP status code 204 on success, or a JSON
encoded error detail if an error occurred (e.g. {"detail":"Not found."} if
the requested ID does not exist).
Contributions are welcome! See CONTRIBUTING.md for detailed information about how to contribute to Baby Buddy.