ESP-Skainet [中文]
ESP-Skainet is Espressif's intelligent voice assistant, which currently supports the Wake Word Engine and Speech Commands Recognition.
Overview
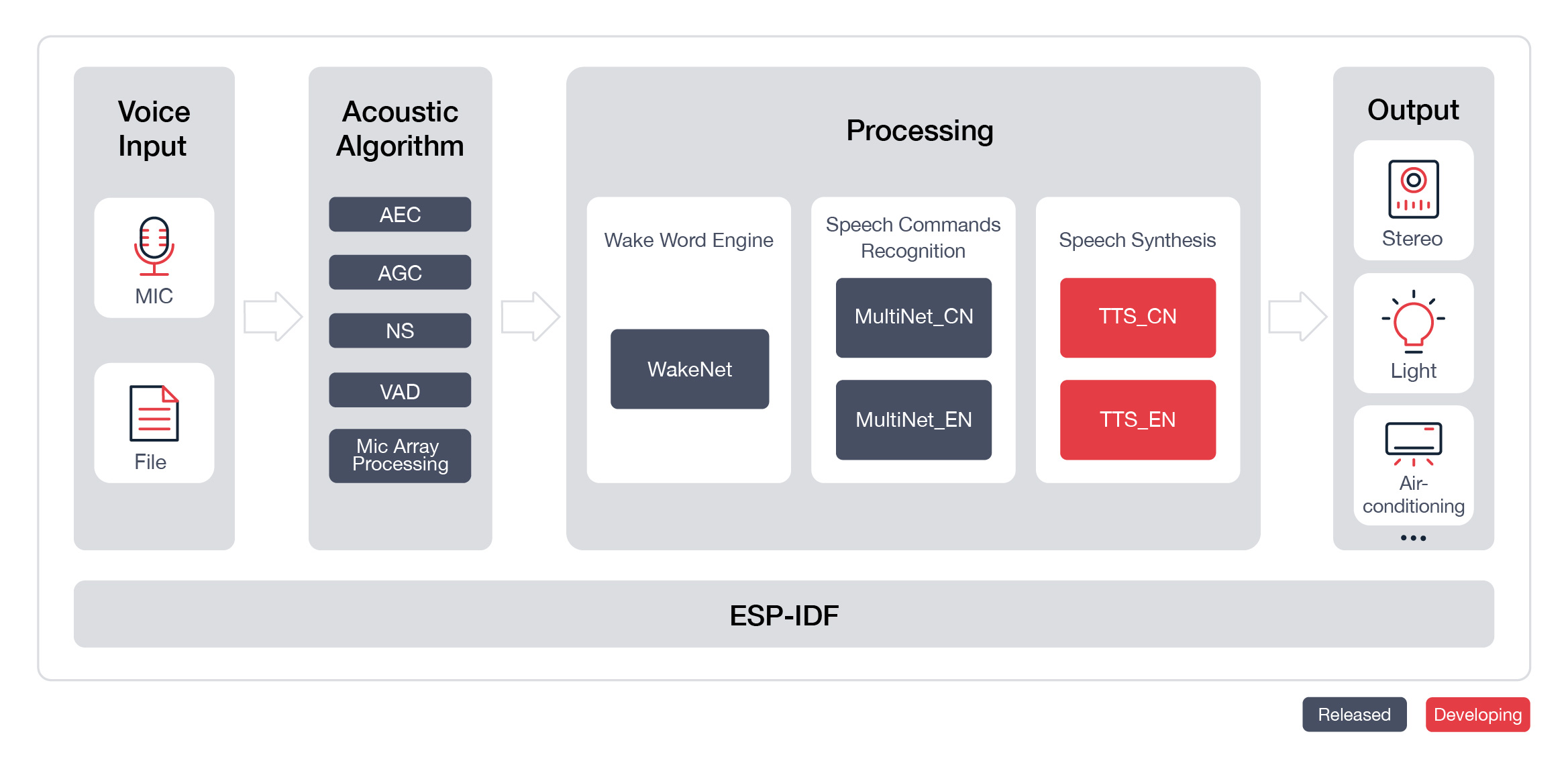
ESP-Skainet supports the development of wake word detection and speech commands recognition applications based around Espressif Systems' ESP32 chip in the most convenient way. With ESP-Skainet, you can easily build up wake word detection and speech command recognition applications.
In general, the ESP-Skainet features will be supported, as shown below:
Input Voice Stream
The input audio stream can come from any way of providing voice, such as MIC, wav/pcm files in flash/SD Card.
Wake Word Engine
Espressif wake word engine WakeNet is specially designed to provide a high performance and low memory footprint wake word detection algorithm for users, which enables devices always wait for wake words, such as "Alexa", “天猫精灵” (Tian Mao Jing Ling), and “小爱同学” (Xiao Ai Tong Xue).
Currently, Espressif has not only provided an official wake word "Hi, Lexin" to the public for free but also allows customized wake words. For details on how to customize your own wake words, please see Espressif Speech Wake Words Customization Process.
Speech Commands Recognition
Espressif's speech command recognition model MultiNet is specially designed to provide a flexible offline speech command recognition model. With this model, you can easily add your own speech commands, eliminating the need to train model again.
Currently, Espressif MultiNet supports up to 100 Chinese or English speech commands, such as “打开空调” (Turn on the air conditioner) and “打开卧室灯” (Turn on the bedroom light).
Acoustic Algorithm
Now, ESP-Skainet integrates AEC (Acoustic Echo Cancellation), AGC (automatic_gain_control), NS (Noise Suppression), VAD (Voice Activity Detection) and MASE (Mic Array Speech Enhancement).
Quick Start with ESP-Skainet
Hardware Preparation
To run ESP-Skainet, you need to have an ESP32 development board which integrates an audio input module . We use ESP32-LyraT-Mini or ESP32-Korvo V1.1 in examples.
On how to configure ESP32 module for your applications, please refer to the README.md of each example.
Software Preparation
ESP-Skainet
Make sure you have cloned this project with the --recursive option, shown as follows:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/espressif/esp-skainet.git
If you have cloned this project without the --recursive option, please go to the esp-skainet directory and run the git submodule update --init command before anything else.
ESP-IDF
In this case, we take ESP-IDF v3.3.1 as the test version. If you had already configured ESP-IDF before, and do not want to change your existing one, you can configure the IDF_PATH environment variable to the path to ESP-IDF. Now we have supported ESP-IDF v4.0.
NOTE: If you want to use ESP-IDF v3.2 or previous version, please refer to esp-skainet v0.2.0.
For details on how to set up the ESP-IDF, please refer to Getting Started Guide for the stable ESP-IDF version
Examples
The folder of examples contains sample applications demonstrating the API features of ESP-Skainet.
Please start with the get_started example.
- Navigate to one example folder `esp-skainet/examples/get_started).
cd esp-skainet/examples/get_started
- Compile and flash the project.
idf.py flash monitor
- Advanced users can add or modify speech commands by using the
idf.py menuconfigcommand.
For details, please read the README file in each example.
Resources
-
View the Issues section on GitHub if you find a bug or have a feature request, please check existing Issues before opening a new one.
-
If you are interested in contributing to ESP-Skainet, please check the Contributions Guide.