This repository provides ABBA, an algorithm for the adaptive symbolic aggregation of time series. The ABBA algorithm consists of two key parts: compression via an adaptive piecewise linear approximation, and digitization via mean-based clustering on the increments and lengths of each piece.
The algorithm uses a scaling parameter scl to control the weighting of
the increments and lengths during the clustering.
If scl = 0 or scl = np.inf, a one-dimensional clustering algorithm can be
used. We use a modified C++ implementation of CKmeans from Ckmeans.1d.dp R
package; see Prerequisites. If the C++ implementation is not available or a
different scaling parameter is used, then ABBA uses the Kmeans algorithm
from the Python package Scikit-learn.
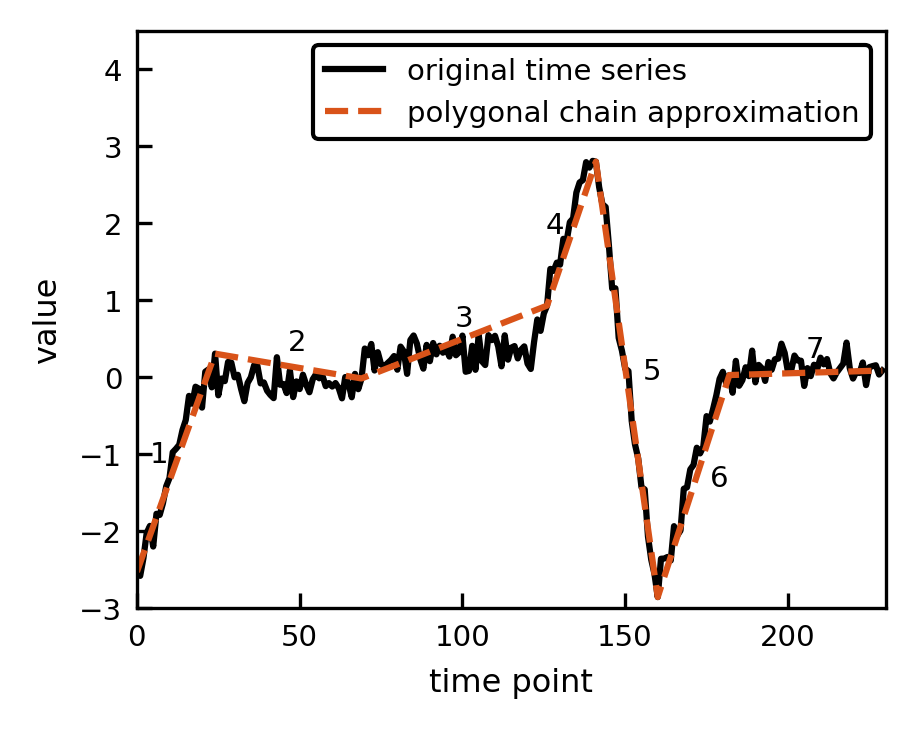
As an example, we consider a synthetic time series and apply ABBA's compression
method, which approximates the time series by a sequence of linear segments
stitched together. Each segment can be represented by its change in the
x-value (len) and change in y-direction (inc).
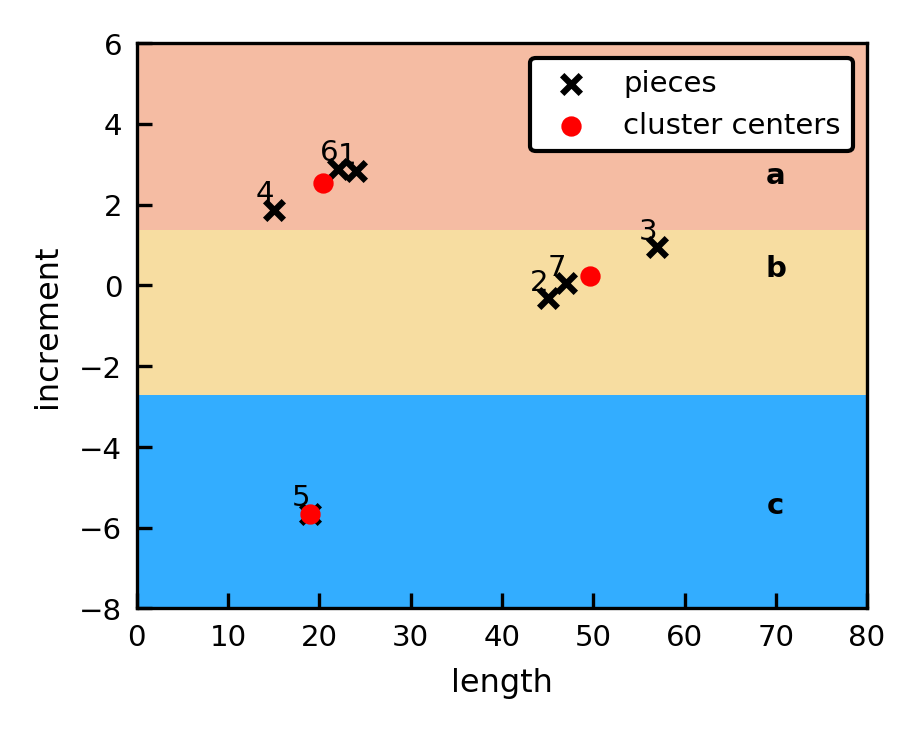
ABBA's digitization procedure clusters the tuples (len, inc),
assigning a unique symbol to each cluster.
The symbolic representation of the time series is 'abbacab'. For further information on ABBA, see [1].
Install python packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt
If scl = 0 or scl = np.inf, then ABBA will attempt to use a C++ implementation
of the CKmeans algorithm. For this we use SWIG, an open source Simplified
Wrapper and Interface Generator. SWIG generated a shared library and
corresponding python file which provides a wrapper for the C++ function. SWIG
can be installed via the following commands:
Linux (Ubuntu):
sudo apt-get install swig
Mac:
brew install swig
Once installed, the Python wrapper can be constructed using the makefile.
make
Run the unit tests by the following command:
python test_ABBA.py -v
>>> from ABBA import ABBA
>>> ts = [-1, 0.1, 1.3, 2, 1.9, 2.4, 1.8, 0.8, -0.5]
>>> abba = ABBA()
>>> string, centers = abba.transform(ts)
Compression rate: 77.77777777777779
Digitization: Using 4 symbols
>>> reconstructed_ts = abba.inverse_transform(string, centers, ts[0])
>>> print([round(i, 1) for i in reconstructed_ts])
[-1, 0.1, 1.3, 1.9, 1.5, 2.1, 1.8, 0.6, -0.5]- Make patches produce reconstruction that is the same length as original time series.
- Isolate clustering from digitization. This will allow us to convert time series using already constructed ABBA representation.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE.md file for details
- All contributors to Ckmeans.1d.dp R package (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/Ckmeans.1d.dp/index.html)
- All contributors to the UCR Time Series Classification Archive (https://www.cs.ucr.edu/~eamonn/time_series_data_2018/)
- Timothy D. Butters for help with C++ and SWIG
- Massimiliano Fasi for the performance profiling code
[1] S. Elsworth and S. Güttel. ABBA: Adaptive Brownian bridge-based symbolic aggregation of time series, MIMS Eprint 2019.11 (http://eprints.maths.manchester.ac.uk/2712/), Manchester Institute for Mathematical Sciences, The University of Manchester, UK, 2019.