The noasic CAN Controller is a professionally developed IP core implemenenting both medium access (MAC) and physical layer functions of the CAN bus protocol such as data encapsulation/decapsulation, frame coding (stuffing/destuffing), medium access management, error detection, error signaling, acknowledgment, serialization/deserialization, bit encoding/decoding, bit timing and synchronization.
- Implements the CAN protocol version 2.0A/B, ISO-11898-1
- Supports standard (11-bit) and extended (29-bit) identifiers
- Configurable data rate up to 1 Mbit/s
- Configurable timing parameters:
- Prescaler factor (1..256)
- Bit sampling time
- Built-in error handling & fault confinement
- Receive and transmit error counters
- Error active, error passive and bus-off states
- Interrupt request lines for bit error, stuff error, CRC error, form error, ACK error, arbitration loss and overload frame reception
- Parallel Tx and Rx message interface with simple valid/ready handshake
- Test modes
- Listen-only mode
- Loopback mode for self-testing purposes
The CAN Controller IP Core is provided under the terms of the Apache License Version 2.0. Please contact us if you require a commercial license or additional consulting services for your project.
- The controller does not generate overload frames on its own, but responds to overload flags on the bus
- The controller does not perform automatic bit-rate detection. Bit-rate detection, if needed, must be performed in software using the controller's listen-only mode.
- No built-in sleep mode/wake up functionality
- No automatic re-start after bus-off (core must be reset)
- No support for message abortion
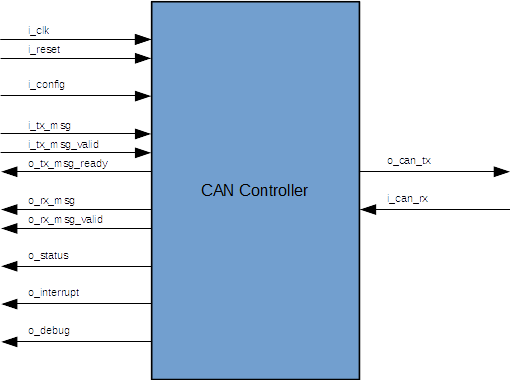
The following diagram shows the input and output interfaces of the CAN Controller Core.
| Name | Dir. | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
i_clk |
in | std_logic |
System clock, e.g. 100 MHz |
i_reset |
in | std_logic |
System reset (synchronous, active-high) |
| Name | Dir. | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
i_config.prescaler |
in | unsigned(7:0) |
Bitrate prescaler. Sets the length of a time quantum (TQ) in system clock cycles. The actual length is prescaler + 1. |
i_config.tseg1 |
in | unsigned(3:0) |
Time segment 1. Length of the first time segment in time quantums. The actual length is tseg1 + 1. The allowed range for tseg1 is 1 to 15 (actual length: 2..16 TQs). |
i_config.tseg2 |
in | unsigned(2:0) |
Time segment 2. Length of the second time segment in time quantums. The actual length is tseg2 + 1. The allowed range is 0 to 7 (actual length: 1..8 TQs) |
i_config.sjw |
in | unsigned(1:0) |
Synchronization jump width. The actual width is sjw + 1. The allowed range is 0 to 3 (actual jump width: 1..4 TQs) |
i_config.testmode |
in | unsigned(1:0) |
Test mode (0: normal operation, 1: listen-only mode, 2: loopback mode) |
| Name | Dir. | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
i_tx_msg.data |
in | std_logic_vector(63:0) |
Transmit message data ([63:56]: byte 0, [7:0]: byte 7) |
i_tx_msg.id |
in | std_logic_vector(28:0) |
Message identifier (use only bits [28:18] for standard-length identifiers). |
i_tx_msg.dlc |
in | unsigned(3:0) |
Data length code |
i_tx_msg.rtr |
in | std_logic |
Remote transmission request flag |
i_tx_msg.ide |
in | std_logic |
Extended identifier flag |
i_tx_msg_valid |
in | std_logic |
Signals that the TX-message is valid, and that it can be transmitted. |
o_tx_msg_ready |
out | std_logic |
Signals that the TX-message was transmitted successfully. |
| Name | Dir. | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
o_rx_msg.data |
out | std_logic_vector(63:0) |
Receive message data ([63:56]: byte 0, [7:0]: byte 7) |
o_rx_msg.id |
out | std_logic_vector(28:0) |
Message identifier (use only bits [28:18] for standard-length identifiers). |
o_rx_msg.dlc |
out | unsigned(3:0) |
Data length code |
o_rx_msg.rtr |
out | std_logic |
Remote transmission request flag |
o_rx_msg.ide |
out | std_logic |
Extended identifier flag |
o_rx_msg_valid |
out | std_logic |
Signals that the received message is valid (pulsed high for one clock cycle). |
| Name | Dir. | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
o_status.error_state |
out | unsigned(1:0) |
The CAN controller's error state (0: error active, 1: error passive, 2: bus off) |
o_status.rx_error_count |
out | unsigned(7:0) |
Current value of the receive error counter |
o_status.tx_error_count |
out | unsigned(8:0) |
Current value of the transmit error counter |
| Name | Dir. | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| bit_error | out | std_logic |
Bit error |
| stuff_error | out | std_logic |
Stuffing error |
| crc_error | out | std_logic |
CRC error |
| form_error | out | std_logic |
Form error |
| ack_error | out | std_logic |
Unacknowledged message |
| arb_loss | out | std_logic |
Arbitration lost while sending a |
| overload | out | std_logic |
Received an overload frame |
The debug interface provides information about the CAN Controller’s internal state.
| Name | Dir. | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
bsp_can_field |
out |
t_can_field |
the currently transmitted/received CAN message field |
bsp_can_field_slv |
out |
std_logic_vector(4:0) |
std_logic_vector version of 'bsp_can_field' |
bsp_transmitting |
out |
std_logic |
signals that the CAN controller is currently transmitting |
bsp_receiving |
out |
std_logic |
signals that the CAN controller is currently receiving |
bsp_stuff_bit |
out |
std_logic |
signals that the current transmitted/received bit is a stuff bit |
bsp_bit_idx_u5 |
out |
std_logic_vector(4:0) |
index of the current bit within the current field (unsigned integer) |
bsp_byte_idx_u3 |
out |
std_logic_vector(2:0) |
index of the current data field byte (unsigned integer) |
btl_tx_clk |
out |
std_logic |
the transmission clock-enable |
btl_rx_clk |
out |
std_logic |
the reception clock-enable |
btl_resync |
out |
std_logic |
signals a resynchronization event |
btl_phase_error_s6 |
out |
std_logic_vector(5:0) |
the measured phase error (signed integer) |
btl_hard_sync |
out |
std_logic |
signals a hard synchronization event |
quant_clk |
out |
std_logic |
the quantum clock (generated by the prescaler) |
can_rx |
out |
std_logic |
current level at the controller's CAN RX input |
can_tx |
out |
std_logic |
current level at the controller's CAN TX output |
| Name | Dir. | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
o_can_tx |
out | std_logic |
CAN TX signal (to PHY) |
i_can_rx |
in | std_logic |
CAN RX signal (from PHY) |
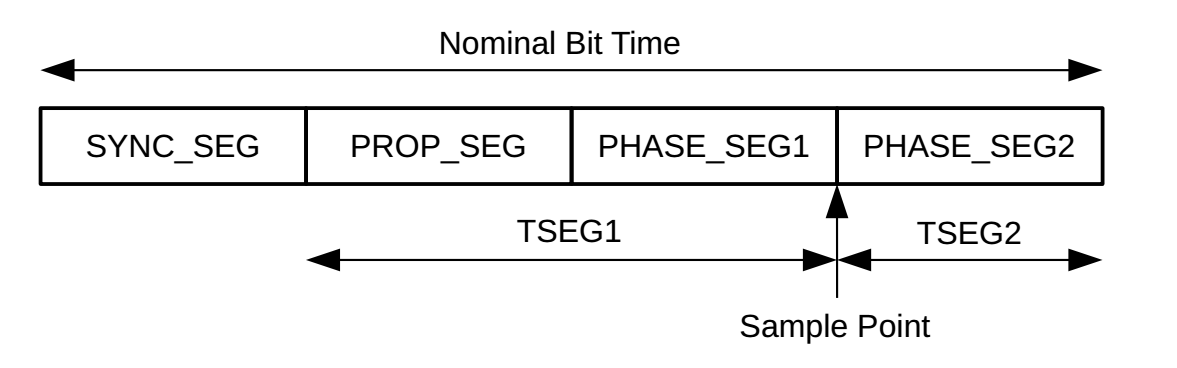
In accordance with the CAN standard, the nominal bit time is divided four separate, nonoverlapping time segments:
- The synchronization segment is used to synchronize the various nodes on the bus. An edge is expected to lie within this segment. The length of
SYNC_SEGis fixed to 1 TQ. - The propagation segment is used to compensate for the physical delay times within the network. The length of
PROP_SEGis 1..8 TQs. - The phase segments 1 and 2 are used to compensate for edge phase errors. These segments can be lengthened or shortened by resynchronization. The length of
PHASE_SEG1andPHASE_SEG2is 1..8 TQs.
The sample point is the point in time at which the bus level is read and interpreted as the value of that respective bit.
Within the CAN Controller Core, the bit timing can be set using the TSEG1 and TSEG2 parameters. The nominal bit time, is given by the following expression:
nominal bit time (in TQs) = 1 + TSEG1 + TSEG2
The length of a time quanta, in system clock cycles, is set using the PRESCALER configuration value:
TQ length (in system clock cycles) = 1 + PRESCALER
Note: for any given CAN bit rate, several bit-time settings can be used. You can use a CAN bit timing calculator such as http://www.bittiming.can-wiki.info to find the optimal settings for your application.
To transmit a message, the user must apply valid message contents on the i_tx_msg port
and assert the i_tx_msg_valid port. Both signals must remain constant until the message
transmission is acknowledged by the core using the o_tx_msg_ready port.
The reception of a message is signalled by the o_rx_msg_valid port going high for one clock
cycle. It is the responsibility of the user to register the received message upon assertion of
the o_rx_msg_valid signal.
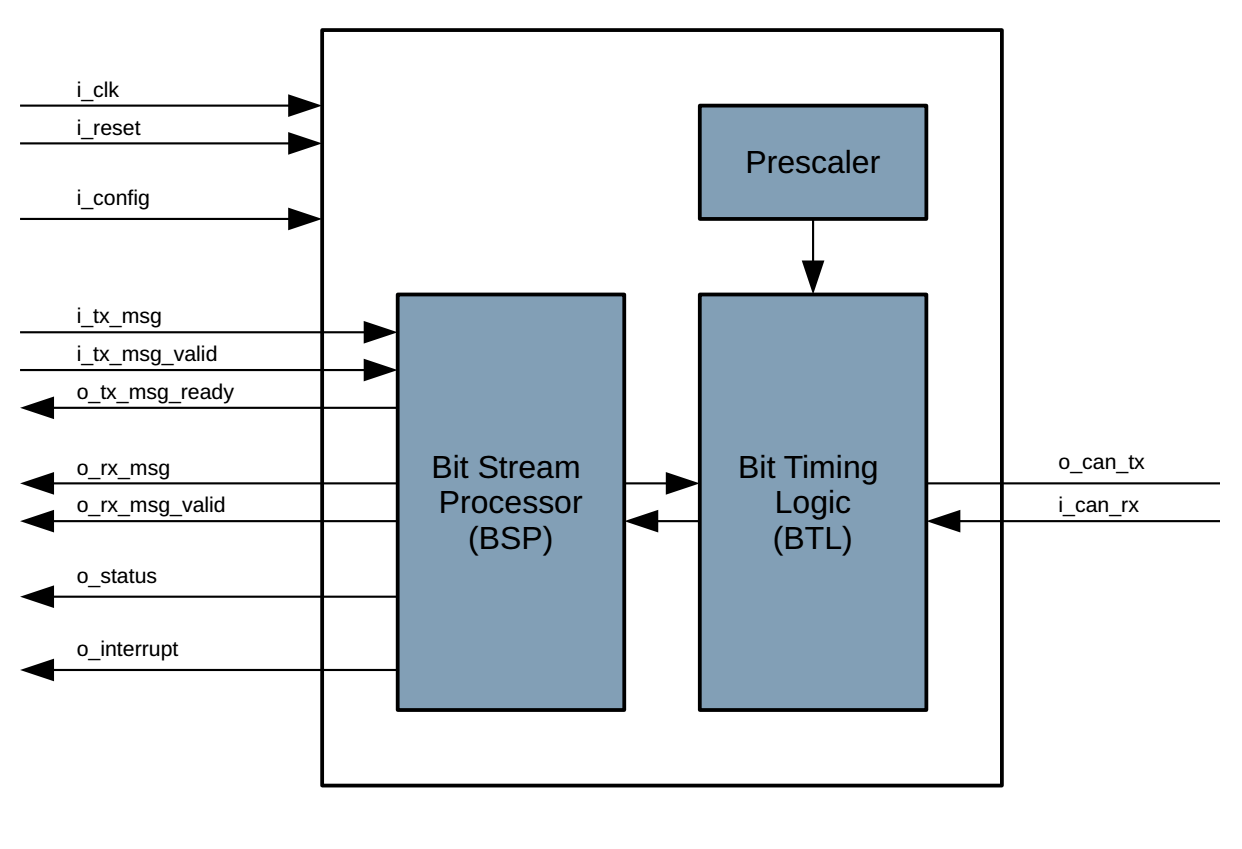
The CAN Controller Core consists of a number of sub-modules:
- The Prescaler divides the system clock by a programmable factor to match the adapt for the bus data rate
- The Bit Timing Logic (BTL) handles the transmission and reception of single bits on the bus
- The Bit Stream Processor (BSP) implements the medium access controller (MAC) tasks such as data encapsulation/decapsulation, arbitration, error detection, retry on lost arbitration. It also manages the error state of the controller (error-active, errorpassive, bus-off) as well as the error counters and generates the interrupt signals.
TODO
The following table shows implementation results for the CAN Controller Core on selected devices.
| Device | LUT | FF | BRAM | DSP48 | Fmax | Toolchain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virtex-6 | XC6VLX130T-1 |
1112 | 409 | 0 | 0 | 120 MHz |
Thanks to Sigasi for providing a Sigasi Studio XPRT license, which was of great help for developing the core.