The Storytel Reader device (aka Mofibo Reader in Denmark) is an Android based e-book reader from Swedish company Storytel AB - providers of the Storytel e-book and audiobook subscription service. Despite being based on Android, the device only allows one app to be run – the Storytel app.
Yeah, that's right, even if you paid €100 for it, you don't really own it – cancel that Storytel subscription and the device becomes useless.
This project is an effort to unlock this device, to turn it into a generic Android E-ink tablet and let you do whatever you want with it.
You paid for it, so you should own it for real.
- Determine which version of the device you have.
- Boot your device into maskrom mode.
- Install
rkflashtool. - Backup the
bootpartition:rkflashtool r boot > /some/safe/place/boot.img
Important
BACKUP YOUR boot PARTITION!!!
- Download and flash the patched boot image for your device version:
# Get patched boot image for 1st generation device curl -OL "https://github.com/ntherning/StorytelReaderMods/releases/latest/download/boot-gen1-patched.img.zip" # Extract (macOS/Linux) unzip boot-gen1-patched.img.zip # Extract (Windows) tar -xf boot-gen1-patched.img.zip # And flash it to the boot partition rkflashtool w boot < boot-gen1-patched.img # Get patched boot image for 2nd generation device curl -OL "https://github.com/ntherning/StorytelReaderMods/releases/latest/download/boot-gen2-patched.img.zip" # Extract (macOS/Linux) unzip boot-gen2-patched.img.zip # Extract (Windows) tar -xf boot-gen2-patched.img.zip # And flash it to the boot partition rkflashtool w boot < boot-gen2-patched.img
- Reboot the device:
rkflashtool b
- Install the Android SDK Platform Tools to get the ADB command which is needed to install new apps to the device. The package can be downloaded from https://developer.android.com/tools/releases/platform-tools. XDA has a great guide on how to install the SDK Platform Tools for Windows, macOS and Linux.
- Congratulations! If all worked you should now be able to connect to your device via ADB and install new apps and more. Have a look at the recipes below for instructions on how to install some useful apps.
1st generation Storytel Reader device running F-Droid

2nd generation Storytel Reader device running RelaunchX

There are two different versions of the Storytel Reader. Physically, from the outside, they look almost identical apart from the type of USB port they are equipped with – micro-USB port on the 1st generation device, USB-C on the 2nd generation device.
| 1st generation | 2nd generation | |
|---|---|---|
| SoC | Rockchip RK3026 | Rockchip RK3128 |
| CPU | Dual-Core ARM Cortex-A9, XXX GHz | Quad-Core ARM Cortex-A7, XXX GHz |
| GPU | ARM Mali-400MP | ARM Mali-400MP |
| RAM | 512 MB | 1 GB |
| Storage | 8 GB eMMC | 8 GB eMMC |
| Display | ||
| Connectivity | Wi-Fi | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth |
| OS | Android 4.2 | Android 6 |
Both generations of the device have been manufactured by the Chinese company ONYX and are most likely rebranded and slightly customized versions of devices in their ONYX BOOX line of products.
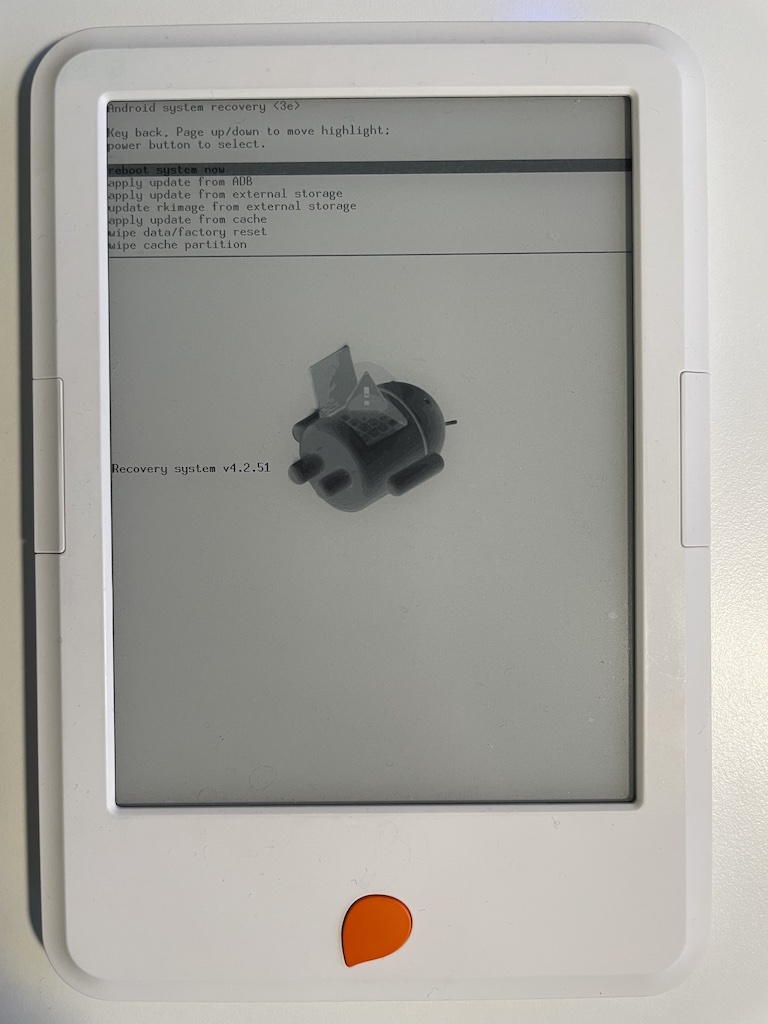
Both generations can be booted into recovery mode. Unfortunately not much can
be done from the recovery mode in terms of modding. The 1st gen device appears
to support sideloading updates via adb sideload but the update.zip likely
needs to be signed with a private key which we don't have access to.
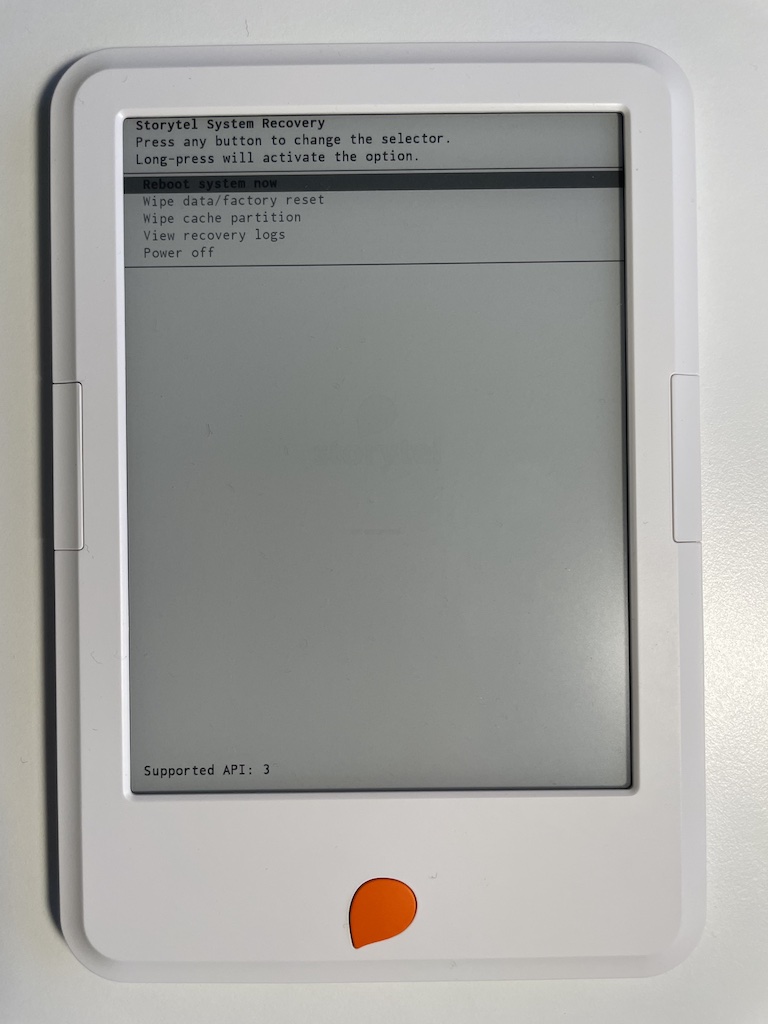
The 2nd gen device doesn't seem to support sideloading via recovery at all.
Both devices' recovery menus display options to wipe the data (effectively a
factory reset) and cache partitions.
To start the 1st generation Storytel Reader in recovery mode do the following:
- Make sure the device is powered off (blue LED is turned off) and unplugged from USB.
- Press and hold the orange button below the screen.
- Press and hold the power button next to the power LED at the top of the device.
- Keep pressing both buttons until "Recovery system ..." is printed on the screen. It usually takes about 15 seconds.
- Your device is now in recovery mode.
To start the 2nd generation Storytel Reader in recovery mode do the following:
- Make sure the device is powered off (blue power LED is off) and unplugged from USB.
- Press and hold the orange button below the screen.
- Connect the device to a wall plugged charger while still holding the button. NOTE: Do not connect the device to a PC. It will charge but depending on the type of cable the device might not enter recovery mode.
- Keep pressing the button until "Supported API: ..." is printed at the bottom of the screen. It may take 10-15 seconds.
- Your device is now in recovery mode and can be unplugged from the charger.
Maskrom mode is a special feature of the Rockchip SoCs in these devices. It gives us full control over the flash memory partitioning, lets us backup and reflash partitions and modify the kernel commandline and other boot parameters. The SoC will automatically enter maskrom mode if it is unable to find a partition to boot from. This is a very neat feature as it gives us a last resort if we accidentally brick the device.
The process to enter maskrom mode is the same on both generations of the Storytel Reader:
- Make sure the device is powered off (blue LED is turned off) and unplugged from USB.
- Connect a USB-A data cable to your Mac or PC. It has to be USB-A and the other side of the cable must be micro-USB for the 1st gen and USB-C for the 2nd gen. A USB-C to USB-C data cable does not seem to work for 2nd gen devices.
- Press and hold the orange button below the screen.
- While pressing the button connect the USB data cable to the device.
- The blue power LED will light up. Keep pressing the button for a few seconds.
Important
The display will not react and the device will appear to be powered off. Don't worry though, the device will still enter maskrom mode.
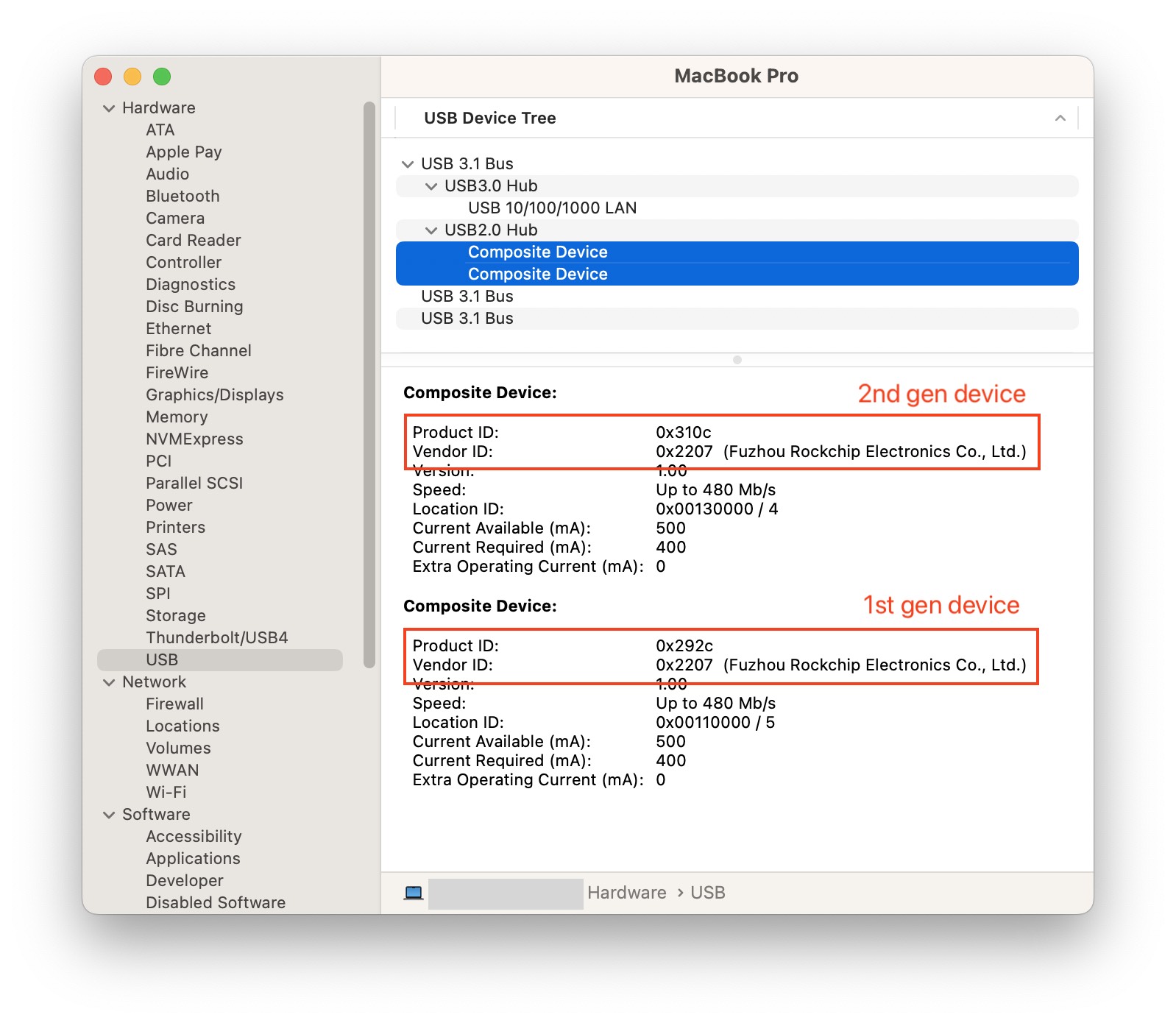
On macOS
use System Report.
Under Hardware -> USB you should see a device with a Vendor ID of 0x2207
and Product ID of either 0x292c (1st gen device) or 0x310c (2nd gen
device).
On Linux run lsusb in a terminal window:
lsusb
# ID 2207:292c -> 1st gen device
Bus 003 Device 002: ID 2207:292c Fuzhou Rockchip Electronics Company RK3026 in Mask ROM mode
# ID 2207:310c -> 2nd gen device
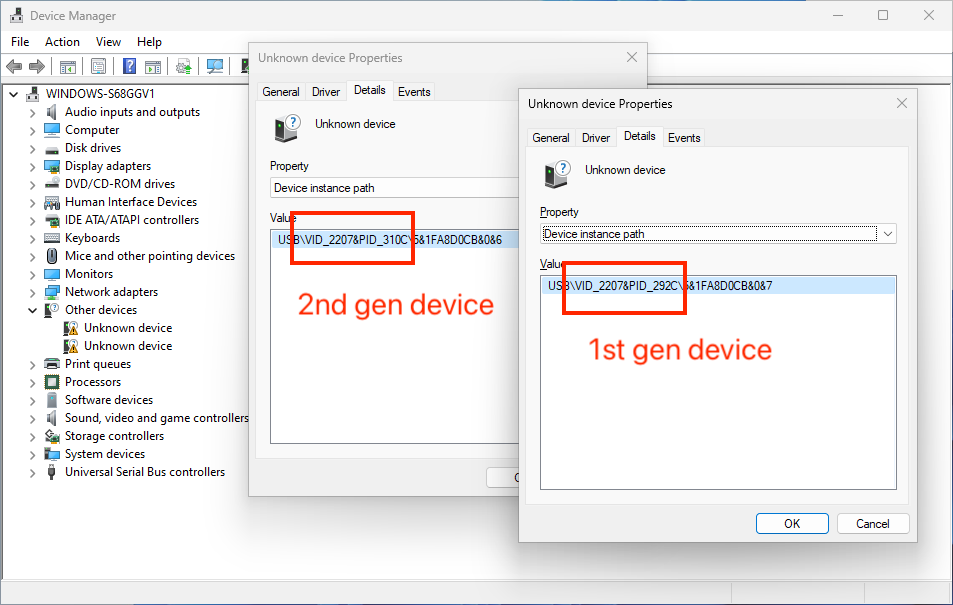
Bus 003 Device 003: ID 2207:310c Fuzhou Rockchip Electronics Company RK3126/RK3128 in Mask ROM modeOn Windows 10/11 launch Device Manager (Win+R shortcut, then type
devmgmt.msc). Double-click any Unknown device under Other devices and
check the Details tab. You should find a device with value
USB\VID_2207&PID_292c&... (1st gen device) or USB\VID_2207&PID_310c&...
(2nd gen device).
Now that the device is in mask rom mode we can use
rkflashtool to read and write partitions on the device's flash memory.
On macOS rkflashtool is available via Homebrew:
brew install rkflashtoolOn Ubuntu and Debian rkflashtool is available in the package
repository:
apt install -y rkflashtoolOn other Linux distributions rkflashtool can be built from the sources at
https://github.com/ntherning/rkflashtool.
On Windows 10/11 (64-bit) a prebuilt rkflashtool can be downloaded from
this project. Use this download link
or run curl from cmd.exe:
curl -O "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ntherning/StorytelReaderMods/main/tools/windows-x86_64/rkflashtool.exe"For the remainder of this doc it is assumed that rkflashtool.exe is in the
current directory or has been installed to a directory listed in the Windows
%PATH% environment variable.
Important
rkflashtool depends on libusb (which is
statically linked into the .exe downloaded above). To use libusb on Windows
a supported driver
must be installed. WinUSB is recommended and can be installed via
Zadig.
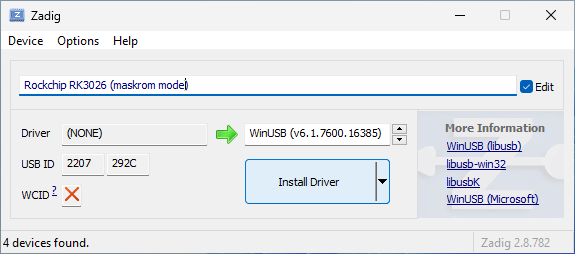
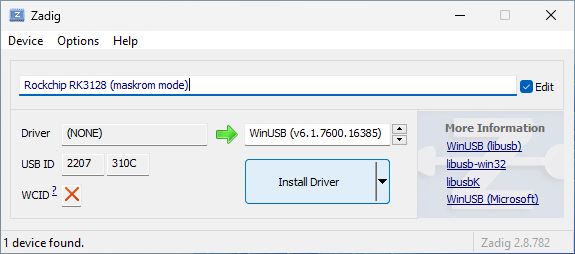
Here are screenshots of Zadig installing the WinUSB driver for 1st generation
device (USB ID is 2207:292C) and 2nd generation device (USB ID is
2207:310C). We have also given the devices nice descriptive names by checking
the Edit box and entering the new name in the text field. This name will be
shown in Device Manager.
Once rkflashtool has been installed properly and
rkflashtool is in the $PATH and a Storytel Reader device is connected in
maskrom mode you should be able to run rkflashtool p and get
output similar to:
# 1st generation device
rkflashtool p
rkflashtool: info: rkflashtool v6.1
rkflashtool: info: Detected RK3026...
rkflashtool: info: interface claimed
rkflashtool: info: reading parameters at offset 0x00000000
rkflashtool: info: size: 0x000002b1
FIRMWARE_VER:4.2.2
MACHINE_MODEL:rk30sdk
MACHINE_ID:007
MANUFACTURER:RK30SDK
MAGIC: 0x5041524B
ATAG: 0x60000800
MACHINE: 3066
CHECK_MASK: 0x80
KERNEL_IMG: 0x60408000
WAV_ADDR:0x7ff00000
RECOVER_KEY: 1,3,30,60,0
PWR_HLD:0,1,A,1,1
CMDLINE:console=ttyFIQ0 androidboot.console=ttyFIQ0 waveform_addr=0x7ff00000 init=/init initrd=0x62000000,0x00800000 mtdparts=rk29xxnand:0x00002000@0x00002000(misc),0x00004000@0x00004000(kernel),0x00008000@0x00008000(boot),0x00010000@0x00010000(recovery),0x00100000@0x00020000(backup),0x000c8000@0x00120000(cache),0x00190000@0x001e8000(userdata),0x00002000@0x00378000(kpanic),0x00100000@0x0037a000(system),-@0x0047a000(user) pcb_ver=2 onyx_emmc=1# 2nd generation device
rkflashtool p
rkflashtool: info: rkflashtool v6.1
rkflashtool: info: Detected RK312X...
rkflashtool: info: interface claimed
rkflashtool: info: reading parameters at offset 0x00000000
rkflashtool: info: size: 0x00000335
FIRMWARE_VER:6.0.0
MACHINE_MODEL:rk312x
MACHINE_ID:007
MANUFACTURER:RK30SDK
MAGIC: 0x5041524B
ATAG: 0x60000800
MACHINE: 312x
CHECK_MASK: 0x80
KERNEL_IMG: 0x60408000
#RECOVER_KEY: 1,1,0,20,0
CMDLINE:console=ttyFIQ0 androidboot.baseband=N/A androidboot.selinux=permissive androidboot.hardware=rk30board androidboot.console=ttyFIQ0 init=/init initrd=0x62000000,0x00800000 mtdparts=rk29xxnand:0x00002000@0x00002000(uboot),0x00002000@0x00004000(misc),0x00008000@0x00006000(resource),0x00008000@0x0000e000(kernel),0x00010000@0x00016000(boot),0x00010000@0x00026000(recovery),0x0001a000@0x00036000(backup),0x000A0000@0x00050000(cache),0x00002000@0x000F0000(kpanic),0x00300000@0x000F2000(system),0x00008000@0x003F2000(metadata),0x00020000@0x00400000(radical_update),0x00008000@0x00420000(vendor),-@0x00428000(userdata)The CMDLINE parameter we get from rkflashtool p is the command line used to
initialize the Linux kernel. The mtdparts kernel command line parameter
reveals how the device's flash is partitioned. After mtdparts=rk29xxnand:
each partition is specified on the format size@offset(partition_name) where
size is the size of the partition in 512 byte sectors and offset is the
offset of the partition from the start of the flash memory, again in 512 byte
sectors.
The 1st generation partition string 0x00100000@0x0037a000(system) specifies
that there is a partition named system at sector 0x0037a000 and with a size
of 0x00100000 sectors, i.e. 512 MB.
The last partition can look like -@offset(partition_name) where the - size
means that the partition takes up the rest of the space on the flash memory.
| Size | Offset | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00002000 | 0x00002000 | misc |
| 0x00004000 | 0x00004000 | kernel |
| 0x00008000 | 0x00008000 | boot |
| 0x00010000 | 0x00010000 | recovery |
| 0x00100000 | 0x00020000 | backup |
| 0x000c8000 | 0x00120000 | cache |
| 0x00190000 | 0x001e8000 | userdata |
| 0x00002000 | 0x00378000 | kpanic |
| 0x00100000 | 0x0037a000 | system |
| - | 0x0047a000 | user |
| Size | Offset | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00002000 | 0x00002000 | uboot |
| 0x00002000 | 0x00004000 | misc |
| 0x00008000 | 0x00006000 | resource |
| 0x00008000 | 0x0000e000 | kernel |
| 0x00010000 | 0x00016000 | boot |
| 0x00010000 | 0x00026000 | recovery |
| 0x0001a000 | 0x00036000 | backup |
| 0x000A0000 | 0x00050000 | cache |
| 0x00002000 | 0x000F0000 | kpanic |
| 0x00300000 | 0x000F2000 | system |
| 0x00008000 | 0x003F2000 | metadata |
| 0x00020000 | 0x00400000 | radical_update |
| 0x00008000 | 0x00420000 | vendor |
| - | 0x00428000 | userdata |
In order to make modifications, such as installing custom apps, we need to
enable Android Debug Bridge (ADB)
support on the device. Out of the box the Storytel Reader comes with ADB
disabled via certain properties in the /system/build.prop file on the system
partition.
One approach to enable ADB would be to use rkflashtool to dump the
system partition to a file, mount it locally, edit build.prop to set
the required properties and then write the modified system partition file back
to the flash memory. This is easy enough on Linux as the system partition is
formatted using the ext4 filesystem, native to Linux. On Windows and macOS
ext4 filesystems are not that easy to mount in writable mode. Furthermore, on
the 2nd generation device which runs Android 6, we also have to make changes to
other partitions in order to circumvent ADB client device authentication (for
some unknown reason the Allow USB debugging dialog is never displayed –
there is no way to allow the ADB client to connect).
The approach we will take here is to modify the Linux kernel ramdisk in the
boot partition. We will modify the init.rc and set the properties which
enable ADB after the /system/build.prop file is loaded. On 2nd generation
devices we will also patch the ramdisk with
magisk to gain full root permission and
be able to use su via ADB.
We need Git and Python 3 to run the scripts to patch the boot partition.
On macOS you get Git and Python 3 by installing the Xcode command line developer tools:
xcode-select --installOr alternatively one can use Homebrew:
brew install git python3On Linux Git and Python 3 should be available in your distribution's package repository. E.g. on Ubuntu and Debian:
apt install -y git python3On Windows 10/11 download and install Git and
Python 3. Both are available via
winget.
Make sure git.exe and python3.exe is in your PATH.
Clone this repository using git:
git clone https://github.com/ntherning/StorytelReaderMods.git
cd StorytelReaderMods/
git submodule init
git submodule updateRun tools/repack.py to patch the boot partition from a 1st generation
device:
cd StorytelReaderMods/
mkdir tmp
rkflashtool r boot > tmp/boot.img
python3 tools/repack.py --boot_img tmp/boot.img --out_img tmp/boot-gen1-patched.img --mods_dir mods/gen1/Run tools/repack.py to patch the boot partition from a 2nd generation
device:
cd StorytelReaderMods/
mkdir tmp
rkflashtool r boot > tmp/boot.img
python3 tools/repack.py --boot_img tmp/boot.img --out_img tmp/boot-gen2-patched.img --mods_dir mods/gen2/Here are instructions for installing some nice to have apps on your Storytel Reader.
F-Droid is an alternative to Google Play Store for installing FOSS (Free and Open Source Software) apps. Unfortunately the latest version is not compatible with the 1st generation Storytel Reader as it runs Android 4.2.2 – instead we have to use the last version compatible version.
1st generation:
curl -O "https://f-droid.org/F-Droid.apk"
adb install F-Droid.apk
# Launch F-Droid
adb shell monkey -p org.fdroid.fdroid -v 12nd generation:
curl -O "https://f-droid.org/archive/org.fdroid.fdroid_1012051.apk"
adb install org.fdroid.fdroid_1012051.apk
# Launch F-Droid
adb shell monkey -p org.fdroid.fdroid -v 1Once F-Droid is installed you can use it to install RelaunchX – a launcher targeted at devices with E-Ink displays.
Warning
After installing RelaunchX it is recommended to reboot your device. It has been reported that, without a reboot, no apps will show up in RelaunchX.
KOReader is an Ebook reader with support for many formats like PDF, DjVu, EPUB, FB2, CBZ. It is available via F-Droid.