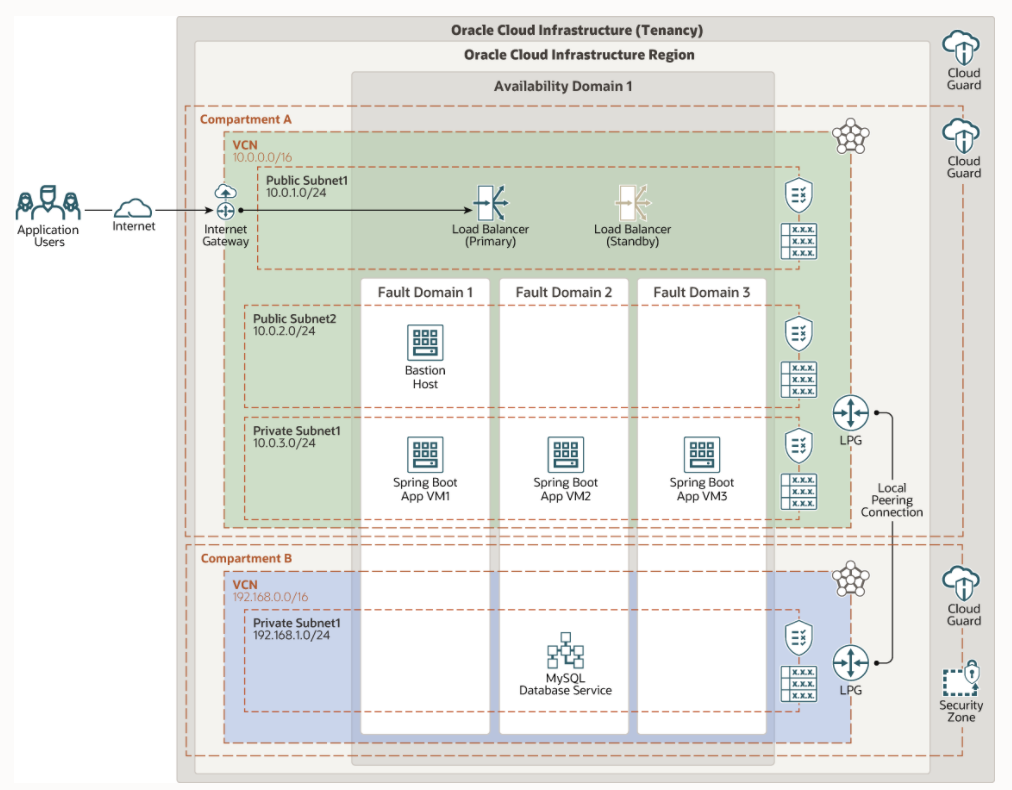
SpringBoot is an open source, Java-based framework that you can use to create production grade applications. SpringBoot simplifies the deployment of applications with minimal configuration and customization and includes third-party libraries to streamline the process.
MySQL Database service is a managed Database service on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. In this deployment we will deploy 3 node cluster(app server) along with a Load Balancer and MySQL Database service.
The OCI Terraform Provider is now available for automatic download through the Terraform Provider Registry. For more information on how to get started view the documentation and setup guide.
-
Permission to
managethe following types of resources in your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy:vcns,internet-gateways,route-tables,network-security-groups,subnets, andinstances. -
Quota to create the following resources: 2 VCN, 4 subnets, 1 Internet Gateway, 2 route rules, and 4 compute instance.
If you don't have the required permissions and quota, contact your tenancy administrator. See Policy Reference, Service Limits, Compartment Quotas
- OCID of compartments with Security Zone and without Security Zone enabled
If you aren't already signed in, when prompted, enter the tenancy and user credentials.
-
Review and accept the terms and conditions.
-
Select the region where you want to deploy the stack.
-
Follow the on-screen prompts and instructions to create the stack.
-
After creating the stack, click Terraform Actions, and select Plan.
-
Wait for the job to be completed, and review the plan.
To make any changes, return to the Stack Details page, click Edit Stack, and make the required changes. Then, run the Plan action again.
-
If no further changes are necessary, return to the Stack Details page, click Terraform Actions, and select Apply.
You'll want a local copy of this repo. You can make that with the commands:
git clone https://github.com/oracle-quickstart/oci-arch-spring-boot
cd oci-arch-spring-boot
ls
You'll need to do some pre-deploy setup. That's all detailed here.
Initialize them in terraform.tfvars file and populate with the following information:
# Authentication
tenancy_ocid = <"">
user_ocid = <"">
fingerprint = <"">
private_key_path = <"">
# SSH Keys
ssh_public_key = "id_rsa.pub"
ssh_private_key = "id_rsa"
# Region
region = "us-ashburn-1"
# Compartment
compartment_ocid = <""> (Compartment without Security Zones enabled)
compartment_SZ_ocid = <""> (Compartment with Security Zones enabled)
mysql_db_system_admin_password = <"">
NOTE: There are other variables that are assigned default value such as VCN CIDR and others. These can be changed in variables.tf file
Deploy:
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply
After the deployment is finished, you can test if your SpringBoot application has deployed correctly and can access picking up the value of the springboot_app_url:
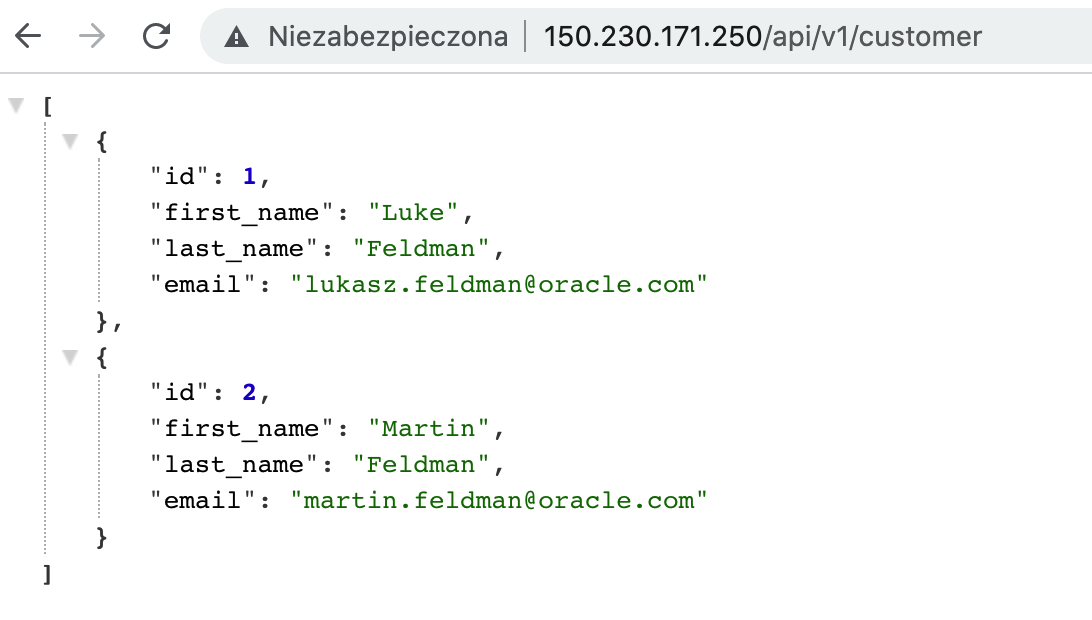
springboot_app_url = http://150.230.171.250/api/v1/customer
Then copy it into Web browser. Here is the example of the succesfull outcome:
When you no longer need the deployment, you can run this command to destroy it:
terraform destroy