Distrod is a systemd-based meta-distro for WSL2 that allows you to install Ubuntu, Arch Linux, Gentoo and many other distros with systemd in a minute, or make your current distro run systemd.
Distrod also provides built-in auto-start feature and port forwarding service.
This allows you to start systemd-managed services, such as ssh, on Windows startup and make it accessible from outside Windows.
With Distrod, you can
-
Run systemd in WSL 2
You can do the both of the following- Install a new distro with systemd running
- Make your current WSL 2 distro run systemd
-
Install any image available from linuxcontainers.org as a WSL 2 distro in 1 minute1.
- The following distros are continuously tested
- Other distros may or may not work
* linuxcontainers.org is a vendor-neutral project that offers distro images for containers, which is unrelated to Distrod. LXC/LXD is one of its projects. Systemd runs in the installed distro, so you can also try LXC/LXD in WSL!
-
Start WSL on Windows Startup.
This means that you can manage your ssh server and other services with systemd and start them automatically without any hassle!- Distrod also provides a port proxy service managed by systemd, allowing you to expose your Linux server to the outside world of Windows easily.
Feature under development
- Make your dual-booted physical Linux distro on a separate disk run as a WSL instance.
-
Make sure that your default WSL version is 2.
> wsl --set-default-version 2 -
Download and unzip the latest
distrod_wsl_launcher-x86_64.zipfrom release, and double-click the extracted.exefile. -
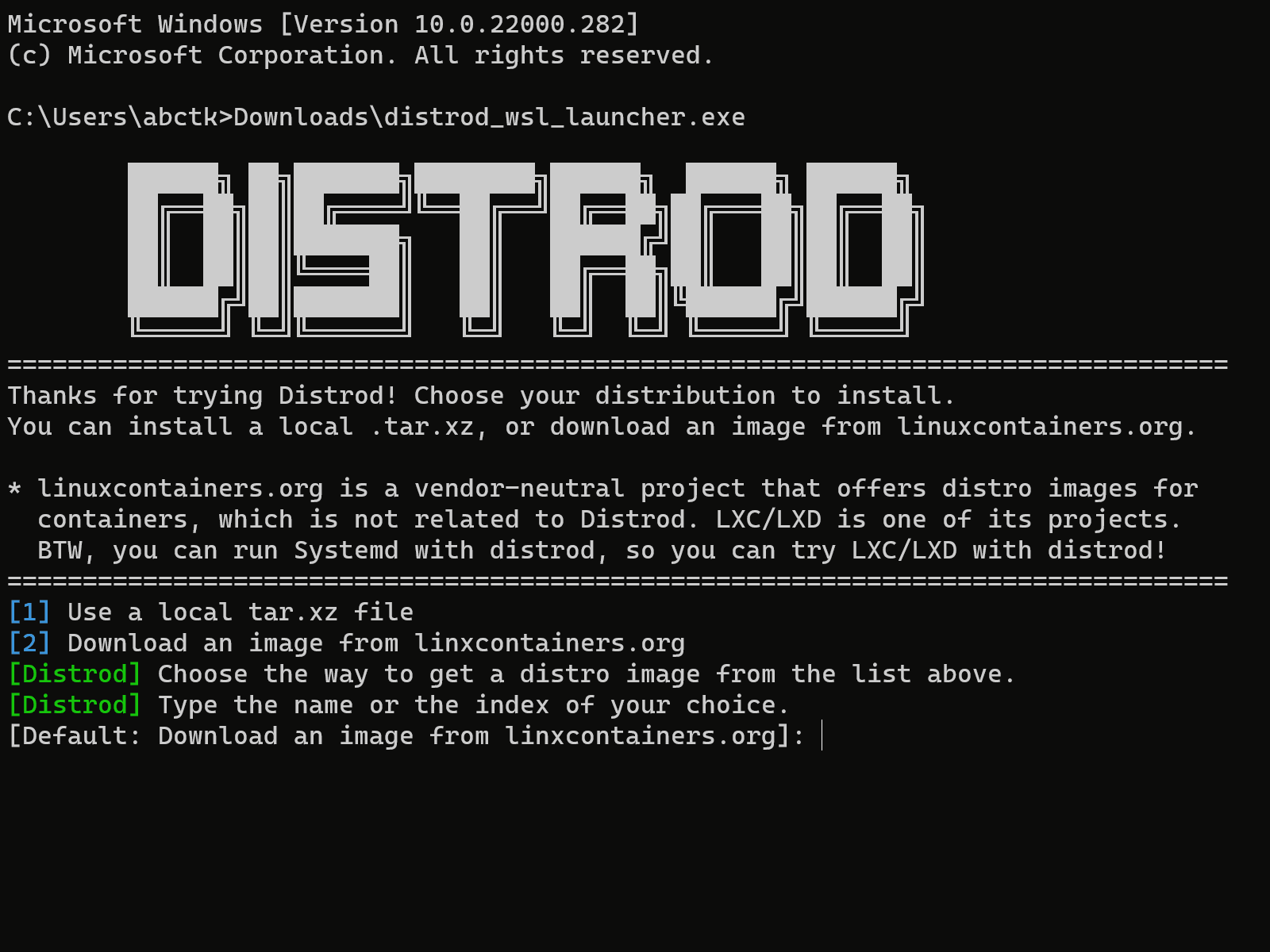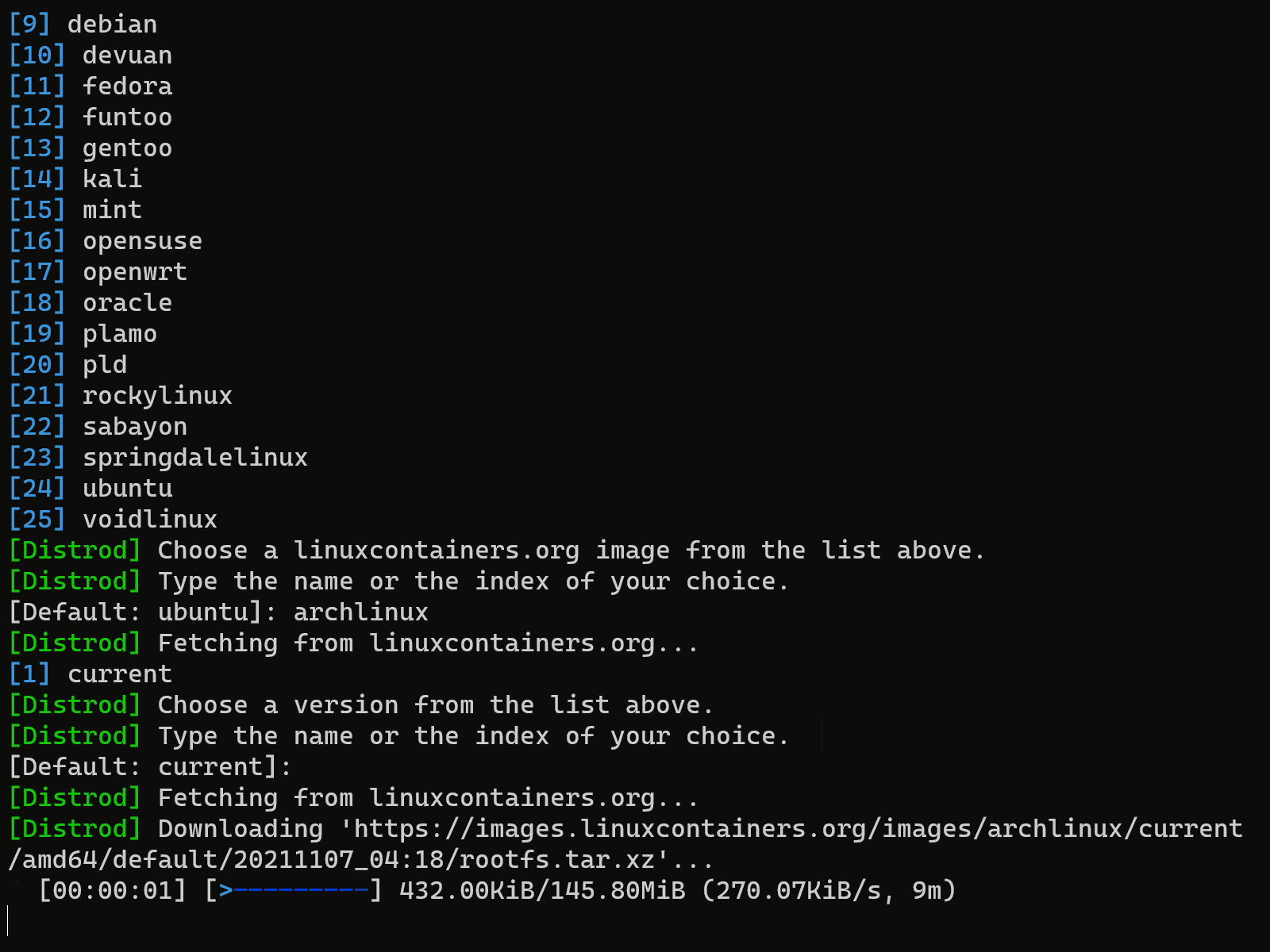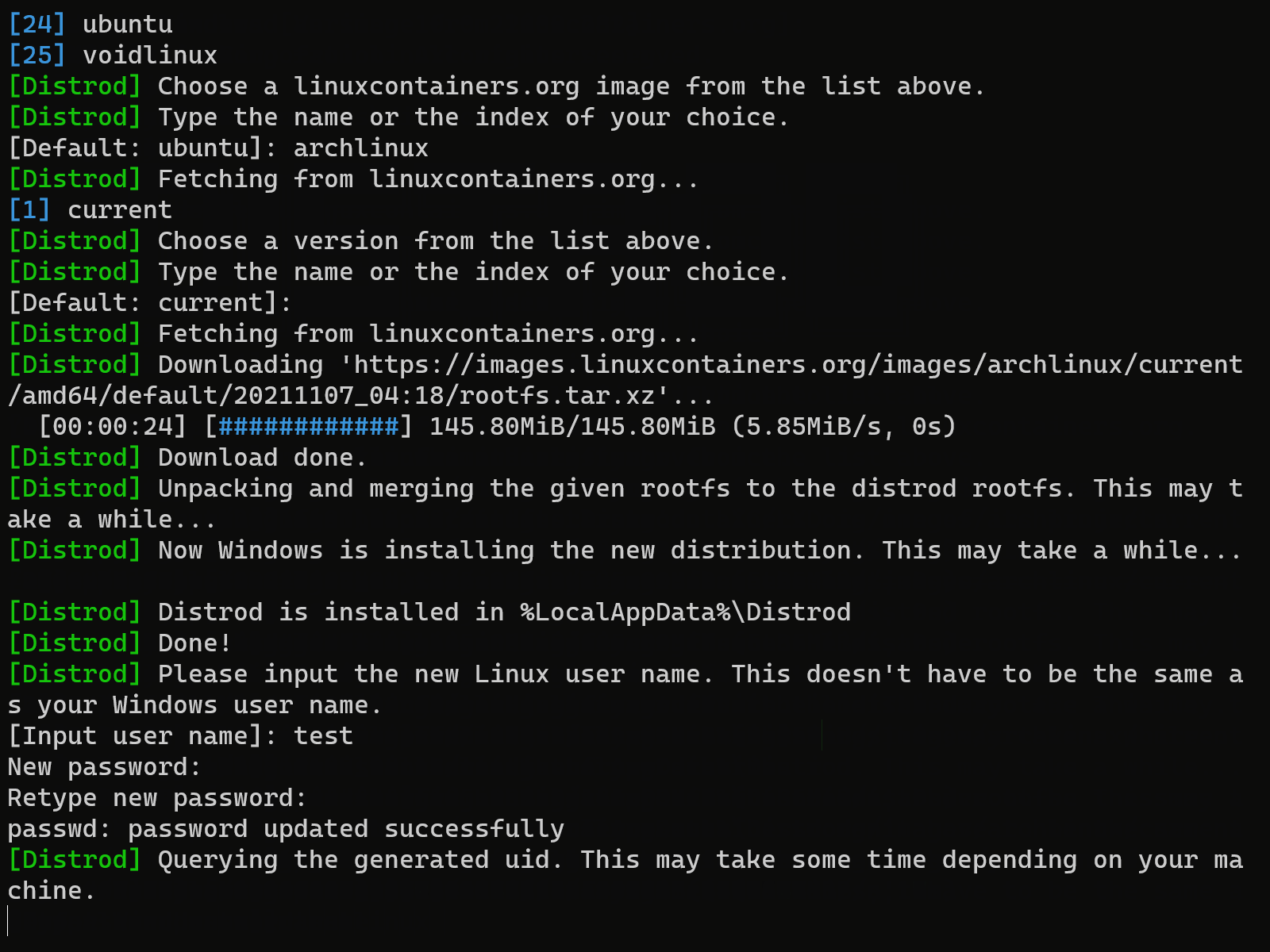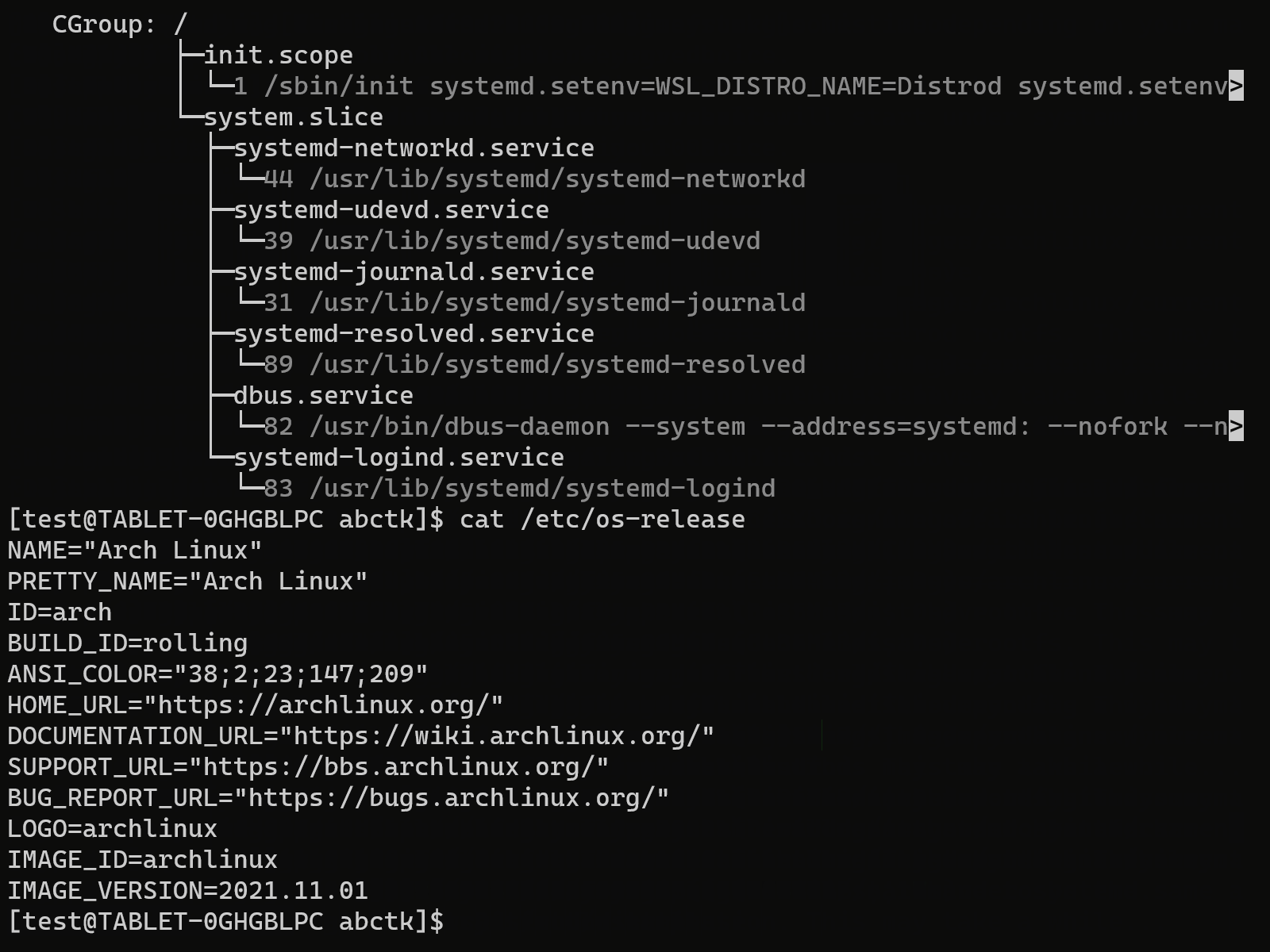
Follow the wizard to install a new distro.
-
[Optional] To make your distro start on Windows startup, run the following command.
sudo /opt/distrod/bin/distrod enable --start-on-windows-bootYou also might want to forward ports of services such as
sshto the outside of Windows. In that case, you can enable the built-in port proxy service provided by Distrod.NOTE: On Windows 11,
portproxy.servicedoesn't work on Windows startup, which should be fixed soon. See Known bus.echo 22 | sudo tee /opt/distrod/conf/tcp4_ports # update the portproxy.service's configuration sudo systemctl enable --now portproxy.service # enable and start it
For more detailed instruction, see Forward Ports to outside of Windows.
- Launch WSL 2 on Windows Startup
- Forward Ports to outside of Windows
- Troubleshoot WSL Network Down
- Install and Run Multiple Distros at the same time
By this installation, systemd is enabled in your WSL 2 distro.
-
Download and run the latest installer script.
curl -L -O "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nullpo-head/wsl-distrod/main/install.sh" chmod +x install.sh sudo ./install.sh installThis script installs distrod, but doesn't enable it yet.
-
Enable distrod in your distro
You have two options. If you want to automatically start your distro on Windows startup, enable distrod by the following command
/opt/distrod/bin/distrod enable --start-on-windows-bootOtherwise,
/opt/distrod/bin/distrod enableYou can run
enablewith--start-on-windows-bootagain if you want to enable autostart later. -
Restart your distro
Close your WSL's terminal. Open a new Command Prompt window, and run the following command.
wsl --terminate DistrodAfter re-opening a new WSL window, your shell runs in a systemd session.
- Launch WSL 2 on Windows Startup
- Forward Ports to outside of Windows
- Troubleshoot WSL Network Down
- Open a Shell Session outside the Container for Systemd
- Disable Systemd / Distrod
If you are using Windows Terminal, Windows Terminal will automatically find and register Distrod for you. Just open the tab named "Distrod".
If you are using other terminals, please update your terminal settings to launch the Distrod. For reference, the following command launches a distro by name in WSL
> wsl --distribution Distrod-
Inside a Distrod session, download and run the latest installer script.
curl -L -O "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nullpo-head/wsl-distrod/main/install.sh" chmod +x install.sh sudo ./install.sh update
In a nutshell, Distrod is a binary that creates a simple container that runs systemd as an init process, and starts your WSL sessions within that container. To realize that, Distrod does the following things.
- Modify the rootfs of the concrete distro you chose so that it is compatible with both WSL and systemd.
- Modify systemd services so that they are compatible with WSL
- Configure networks for WSL
- Put
/opt/distrod/bin/distrodand other resources in the rootfs. - Register the Distrod's binary as the login shell
- When Distrod is launched by WSL's init as a login shell, Distrod
- Starts systemd in a simple container
- Launches your actual shell within that container
- Bridges between the systemd sessions and the WSL interop environment.
-
Does WSLg works on Distrod?
Yes! Distrod doesn't prevent anything about WSLg. Distrod sets up sockets for X11 and environment variables properly.
However, WSLg itself has some quirks even on non-Distrod WSL2 distros. Try many things until a GUI app runs. For example, to run
xeyeswithout failure, I had to run it three times on the non-Distrod official Ubuntu 20.04.
Footnotes
-
as long as your network connection is fast enough :) ↩