Author: Nasanbayar Ulzii-Orshikh
Date: 01/06/2021
ABSTRACT:
Clustering nodes in a social network G = (V, E) based on their degree of information access is a tool with enormous potential to address the epistemic inequity, rooted from digital space (Beilinson et al. 2020). However, producing a network representation, called "information access signatures", that is appropriate for such clustering is computationally expensive, taking at least O(n^2) time, where |V| = n. Then, this project explores three representations of the 114th Congressional co-sponsorship network -- information access signatures, adjacency matrix, and representation with node2vec -- using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to find and experimentally validate a computationally less expensive pipeline of information access clustering. The full paper manuscript can be provided upon request from nulziiorsh@haverford.edu. Thank you! :)
PIPELINE:
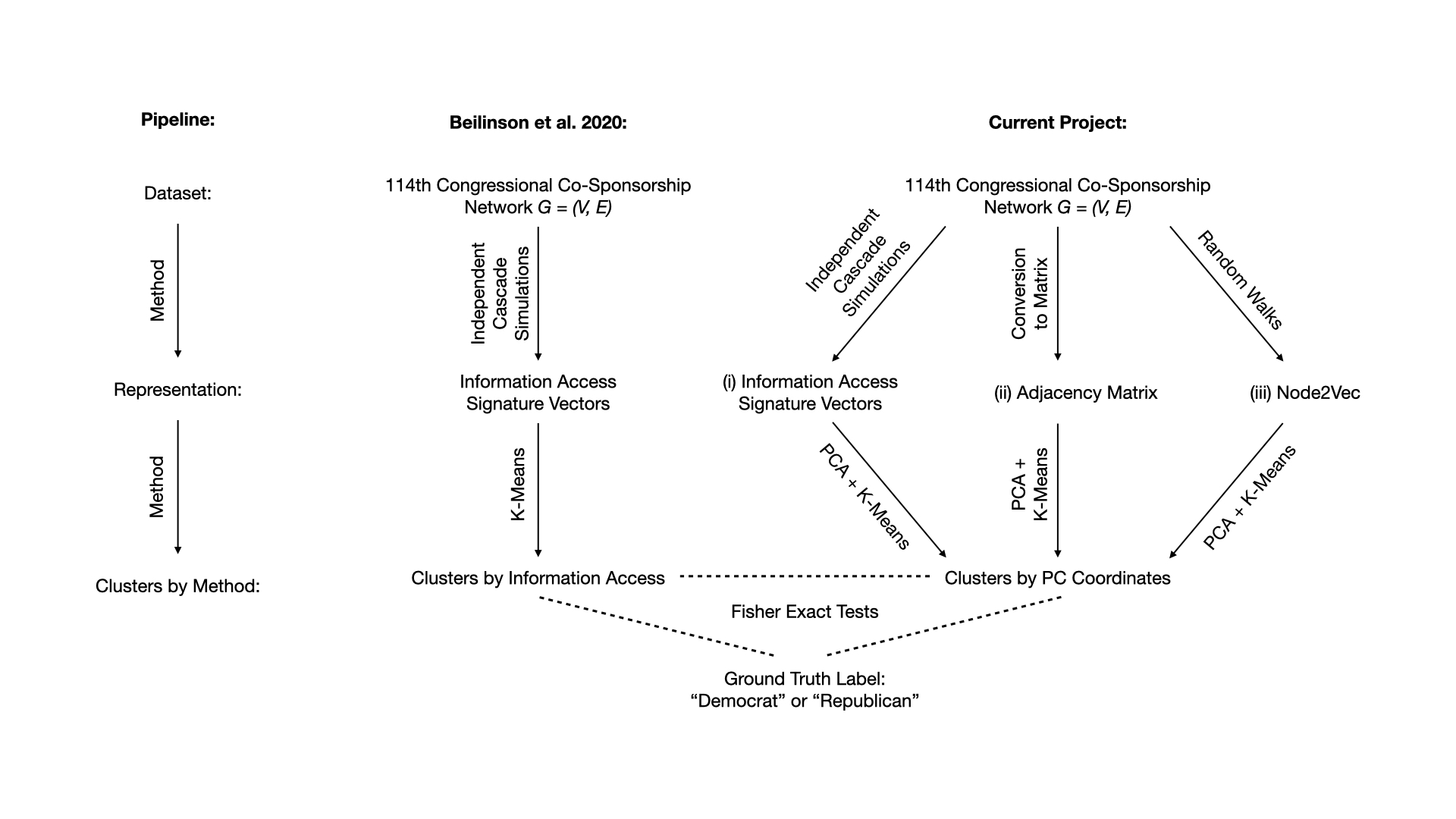 Figure 1. The project's pipeline and relation to Beilinson et al. 2020.
Figure 1. The project's pipeline and relation to Beilinson et al. 2020.
EXAMPLE INPUT:
python3 main_pipelines.py -m info_access -n 2
Arguments: -m is the mode from {info_access, adjacency, node2vec, all}, and -n is the number of PCs from [1,3].
RESULTS:
The results from Fisher Exact tests, used for hypothesis testing, were statistically significant and can be found in the qualitative_analysis folder. Relevant plots in the plots one.
CITATION:
Hannah C. Beilinson et al., "Clustering via Information Access in a Network", 2020.