The Office Booker was created to solve the problem of coordinating the safe return to offices once COVID-19 restrictions are lifted.
The Lab team of 4 developers put together this real-time booking app in just 10 days for proactively managing demand for office space by allowing you to book ahead of travelling to the office. Although originally created as a tactical solution within Telefónica UK but we decided to share this publicly as it might be a problem other companies are also facing - including some of our own customers.
Node.js, Yarn, Pulumi, Docker, AWS CLI
./install.sh- Restore packages./start.shstart API and client application
The default local auth setup allows you to enter any email address and code.
Note: Run ./make-env.sh [STACK] to use config from the deployed stack for local testing.
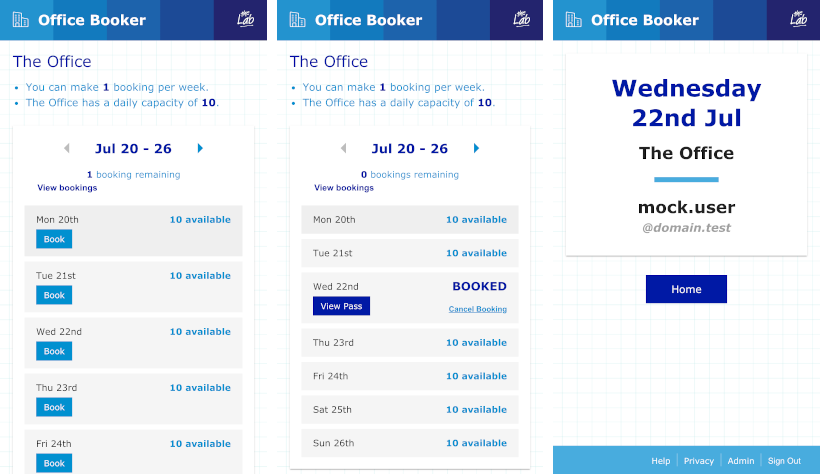
- Log in with email
- Pick office and day - showing which are available or not
- Click to reserve a space
- Can cancel reservation if needed
- Virtual pass shown in app or printable which security visually verifies
- Bookings are for the whole day
- Users can only make 1 booking per office, per day
- Default limit of 1 booking per week per user, can be adjusted by System Administrators
- Bookings for the today can only be cancelled by Administrators
- Users pick a single office (can be changed in help)
- Register domain
- Add Zone to Route53
- Change NS records to created Zone
./install.sh- restore all package dependencies./build.sh- audit, test and build infrastructure assetscd infrastructure- this is where deployment is coordinatedpulumi login- this is where the state of your deployment is storedpulumi stack init- create a new stack- Configure stack settings (see Pulumi Config Example below)
cd ..- Move back to the root of the project./deploy.sh [STACK]- deploy the stack created in step 5
- Add verified address
- Open Cognito Pools -> office-booker-booking-users-xxxxx -> FROM email address -> edit
- Do you want to send emails through your Amazon SES Configuration? - Yes - Use Amazon SES
- Fill required files
Note: the first smoke test might fail as DNS entries can take a while to propagate.
This is the same as for the first deploy, excluding creating and configuring the stack:
./install.sh./build.sh./deploy.sh [STACK]
Before running this application, you should review the privacy policy and adjust for your own situation.
We are following semantic versioning and maintain a changelog to indicate the impact of changes.
Each major release must be installed in order to make sure that migrations are completed. I.e. if you're running version 3 and want version 5, you must deploy version 4 first.
config:
aws:region: eu-west-1
office-booker:advance-booking-days: '14'
office-booker:default-weekly-quota: '1'
office-booker:dns-zone: my-company.example.
office-booker:domain-name: my-office-booker.my-company.example
office-booker:email-regex: ^(.*)@(my-company\.example)$
office-booker:office-quotas:
- name: Office Alpha
id: alpha
quota: 100
parkingQuota: 60
- name: Office Beta
id: beta
quota: 200
parkingQuota: 150
office-booker:registration-from-address: my-office-booker@my-company.example
office-booker:selftest-key:
secure: v1:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx==
office-booker:selftest-user: my-office-booker.selftest@my-company.example
office-booker:system-admin-emails:
- kaleb.hess@my-company.example
- catrin.vaughan@my-company.example
office-booker:reason-to-book-req: true
office-booker:notification-to-address: kaleb.hess@my-company.exampleNote:
The secure selftest-key can be generated and set by running:
pulumi config set --secret selftest-key `openssl rand -base64 30`If setting reason-to-book-req as true, you must also supply a notification-to-address.
Quotas are applied to all users regardless of role.
- Default: Any user with a valid email address gets this role.
- Can manage their own bookings only.
- System Admin: Must be configured in Pulumi
- Can manage all bookings in the system
- Can manage other users
- Office Admin: Must be assigned by a System Admin
- Can manage bookings for their assigned offices
- Can view other users (but can't make changes)
General meanings of log levels:
- ERROR: something broke in the server which should have worked fine
- INFO: everything worked as expected, but the user might have been shown an error
All changes to the database are audit-logged for trouble-shooting purposes.
- Email OTAC login, limited by configured regular expression
- Online administration dashboard for booking and user management
- Designed for use on mobiles but has desktop support too
- Linear cost scaling based on usage
- All storage is encrypted-at-rest
- No remote terminal access or system patching required
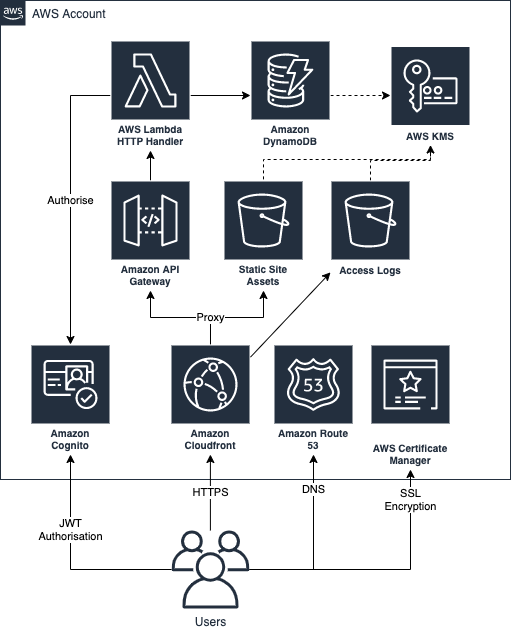
The client application is a React.js single page application (SPA). We uses AWS Cognito for authentication. The API is written on NodeJS running on AWS Lambda via API Gateway with dynamic data stored in DynamoDB (encrypted via AWS KMS).
All logged errors are centrally monitored by the alerts lambda. Add your own code to alerts/src/lambda.ts in the postNotification function to send notifications to somewhere like a slack channel or email account.
- Disable the CloudFront CDN to stop all traffic
- Empty the S3
api-cdn-logsandapi-static-sitebuckets - Run
pulumi destroy
Due to the serverless architecture of the application, all costs scale linearly based on:
- The number of monthly active users
- The number of requests to the application
If no requests are made to the system, it should cost $0.00 USD per month.
Here's a detailed example of estimated cost based on the following generous approximations:
- 10,000 users
- 1,000 API requests per user, per day (extremely heavy usage)
- 100 milliseconds to process each request
- 1KB API response size
- London AWS region
Upper-bound estimated cost per month, excluding free tier: $494.38 USD
Breakdown by service:
- Lambda: $310.00
- Requests (300,000,000): $60.00
- Compute Time (30,000,000 seconds): $250.00
- S3: $0.07
- Standard Storage (1GB): $0.02
- GET Requests (100,000): $0.04
- Cognito (10,000 Monthly Active Users): $55.00
- API Gateway (300,000,000 API Calls): $105.00
- DynamoDB: $0.00
- CloudFront (286 GB out): $24.31
Estimated cost, including free tier is $428.51 USD:
- Lambda:
- 1,000,000 free requests per month
- 400,000 GB-seconds of compute time per month
- Cognito: First 50,000 users are always free
- S3 - free for first year:
- 5 GB of Standard Storage
- 20,000 Get Requests
- 2,000 Put Requests
- API Gateway: 1,000,000 API Calls Received per month for first year
- CloudFront: 50 GB out free for first year