Author: Dr Jan Schindler (formerly Zörner) (mailto:schindlerj@landcareresearch.co.nz)
Published under GNU GPLv3
This fork of pycrown updates the package to run with the most recent versions of pandas, scipy, and geopandas. See the requirements.txt file for more information. To summarise, the python setup.py test completes with the following:
Python 3.10.10
- laspy 2.4.1
- numpy 1.23.5
- pandas 1.5.3
- geopandas 0.12.2
- GDAL 3.4.3
- rasterio 1.3.6
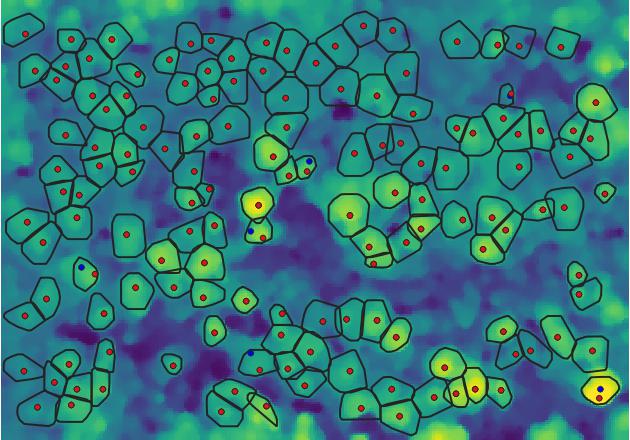
PyCrown is a Python package for identifying tree top positions in a canopy height model (CHM) and delineating individual tree crowns.
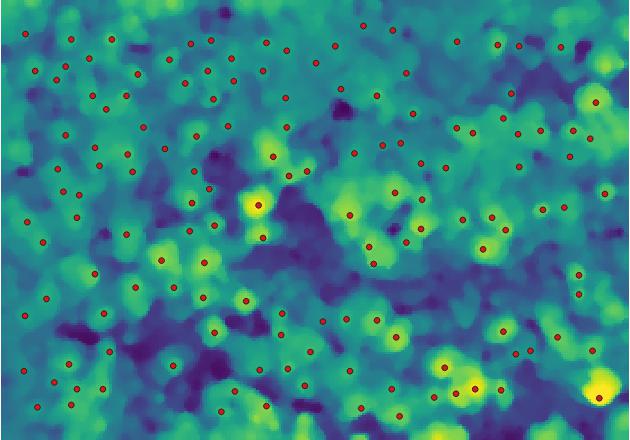
The tree top mapping and crown delineation method (optimized with Cython and Numba), uses local maxima in the canopy height model (CHM) as initial tree locations and identifies the correct tree top positions even in steep terrain by combining a raster-based tree crown delineation approach with information from the digital surface model (DSM) and terrain model (DTM).
Citation:
Zörner, J.; Dymond, J.; Shepherd J.; Jolly, B. PyCrown - Fast raster-based individual tree segmentation for LiDAR data. Landcare Research NZ Ltd. 2018, https://doi.org/10.7931/M0SR-DN55
Research Article:
Zörner, J., Dymond, J.R., Shepherd, J.D., Wiser, S.K., Bunting, P., Jolly, B. (2018) Lidar-based regional inventory of tall trees - Wellington, New Zealand. Forests 9, 702-71. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9110702
A number of open-source tools to identify tree top locations and delineate tree crowns already exist. The purpose of this package is to provide a fast and flexible Python-based implementation which builds on top of already well-established algorithms.
Tree tops are identified in the first iteration through local maxima in the smoothed CHM.
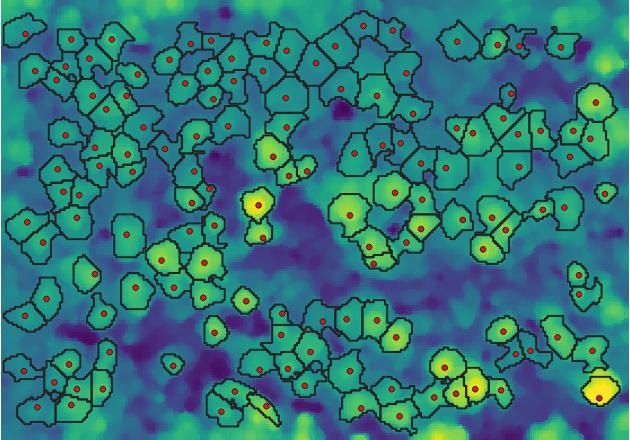
We re-implement the crown delineation algorithms from Dalponte and Coomes (2016) in Python. The original code was published as R-package itcSegment (https://cran.r-project.org/package=itcSegment) and was further optimized for speed in the lidR R-package (https://cran.r-project.org/package=lidR).
Our Cython and Numba implementations of the original algorithm provide a significant speed-up compared to itcSegment and a moderate improvement over the version available in the lidR package.
We also adapted the crown algorithm slightly to grow in circular fashion around the tree top which gives crown a smoother, more natural looking shape.
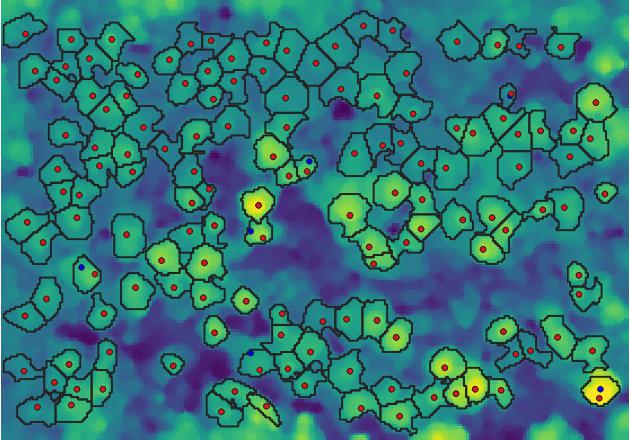
We add an additional step to correct for erroneous tree top locations on steep slopes by taking either the high point from the surface model or the centre of mass of the tree crown as new tree top.
Reference:
Dalponte, M. and Coomes, D.A. (2016) Tree-centric mapping of forest carbon density from airborne laser scanning and hyperspectral data. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 1236-1245.
- Tree top locations (stored as 3D ESRI .shp-file)
- Tree crowns (stored as 2D ESRI .shp-file)
- Individual tree classification of the 3D point cloud (stored as .las-file)
- Dr Jan Zörner (Manaaki Whenua - Landcare Research, Lincoln, New Zealand)
- Dr John Dymond (Manaaki Whenua - Landcare Research, Palmerston North, New Zealand)
- Dr James Shepherd (Manaaki Whenua - Landcare Research, Palmerston North, New Zealand)
- Dr Ben Jolly (Manaaki Whenua - Landcare Research, Palmerston North, New Zealand)
It is assumed that you generated a canopy height model (CHM), digital surface model (DSM) and digital terrain model (DTM) from the LiDAR dataset before running PyCrown. If you want to classify individual trees in the point cloud, it is recommended to normalize heights to height above ground elevation (also done externally).
For processing laser scanning data we recommend the open-source software SPDLib (http://www.spdlib.org).
Python 3.6 is required.
Tested on: Windows 10, Debian 9 (Stretch), Fedora 28, Ubuntu 18.04 & 16.04
conda env create
Windows: activate pycrown-env
Linux: source activate pycrown-env
python -m venv pycrown-env
Linux: source pycrown-env/bin/activate
Windows: pycrown-env\Scripts\activate.bat
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
There are only some rudimentary tests provided at the moment, but it is advised to check that everything works:
python setup.py test
Build and install the PyCrown module with:
python setup.py install
On some platforms (e.g. Ubuntu 16.04) the installation of laspy does not include laszip/laszip-cli. See the issue report on github for more infos.
In this case, please follow these steps:
wget http://lastools.org/download/LAStools.zipunzip LAStools.zip && cd LAStools && makecp bin/laszip /home/USERNAME/miniconda3/envs/pycrown-env/bin/
If you encounter this error under Windows, please download LAStools.zip, extract the archive and copy the file "laszip.exe" from the "bin"-directory to the conda environment, e.g. C:\Users<username>\AppData\Local\Continuum\miniconda3\envs\pycrown-env\Scripts\ or C:\Users<username>\Miniconda3\envs\pycrown-env\Scripts
Building the Cython module requires C++ build tools which may need to be installed on your system.
The Windows error message on Windows provides instructions:
error: Microsoft Visual C++ 14.0 is required. Get it with "Build Tools for Visual Studio": https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/downloads/
During the setup process, please select 'C++ Build Tools'.
There seems to be an incompatibility between laspy and numpy in recent versions. The combination numpy==1.16.4 and laspy==1.5.1 works for me.
I suggest either not using .laz files for the time being or downgrading to the appropiate package versions.
Please also refer to this github issue: laspy/laspy#112
You can find an IPython Notebook demonstrating each step of the tree segmentation approach in the example folder.
You can also run the example python script directly. Results are stored in the example/result folder.
cd example
python example.py