Title: OpenAI functions streaming with Chainlit Tags: [openai-functions]
This directory contains an example of how to integrate OpenAI's powerful language model with Chainlit to create an interactive chat application that can call custom functions defined in your code. The example demonstrates a simple function that fetches the current weather for a specified location.
To get started with this example, follow these steps:
- Ensure you have Python installed on your system.
- Clone the repository and navigate to this directory.
- Install the required dependencies by running
pip install -r requirements.txt. - Set your OpenAI API key as an environment variable:
export OPENAI_API_KEY='your_api_key'. - Run the application with
python app.py.
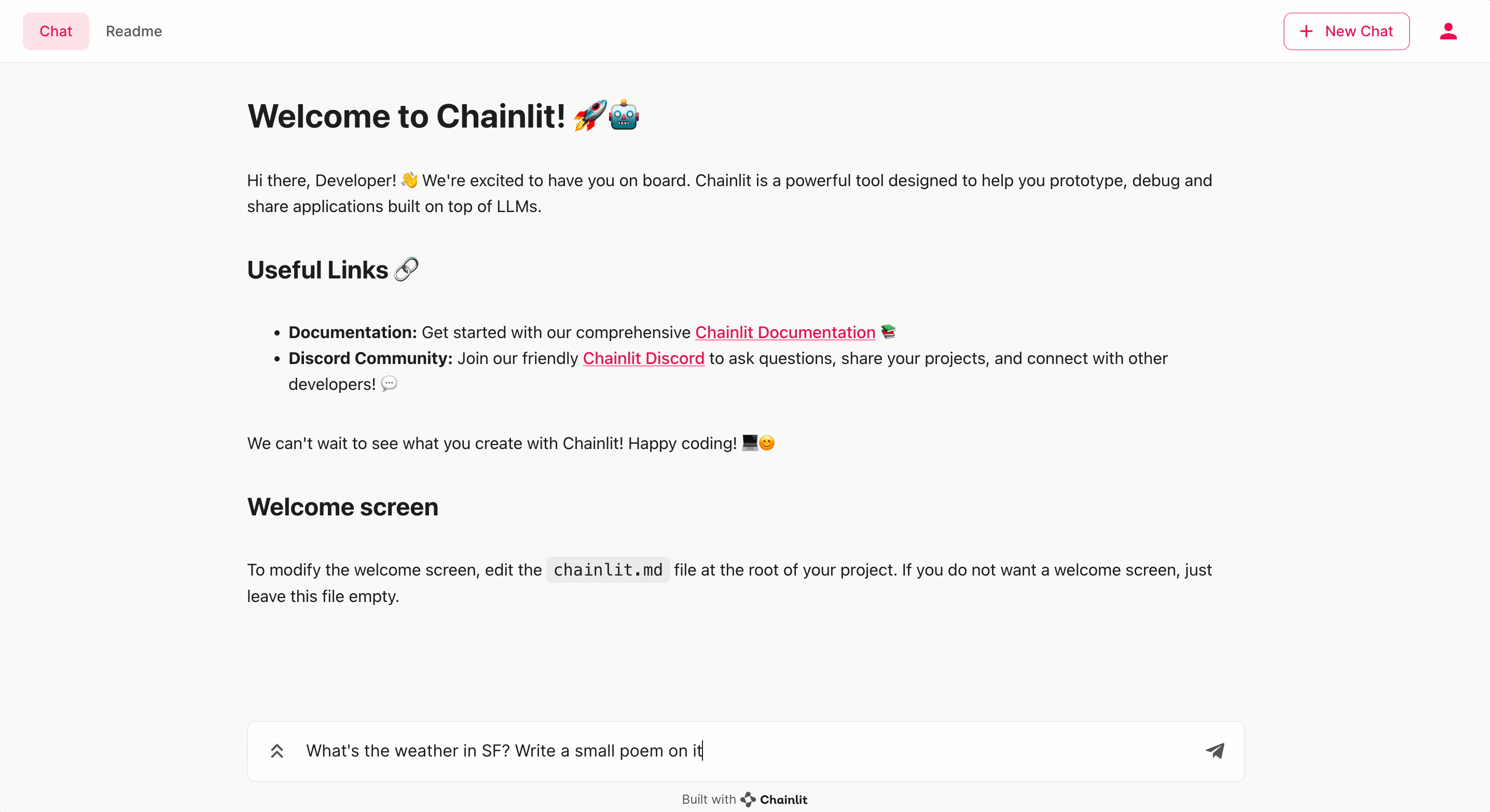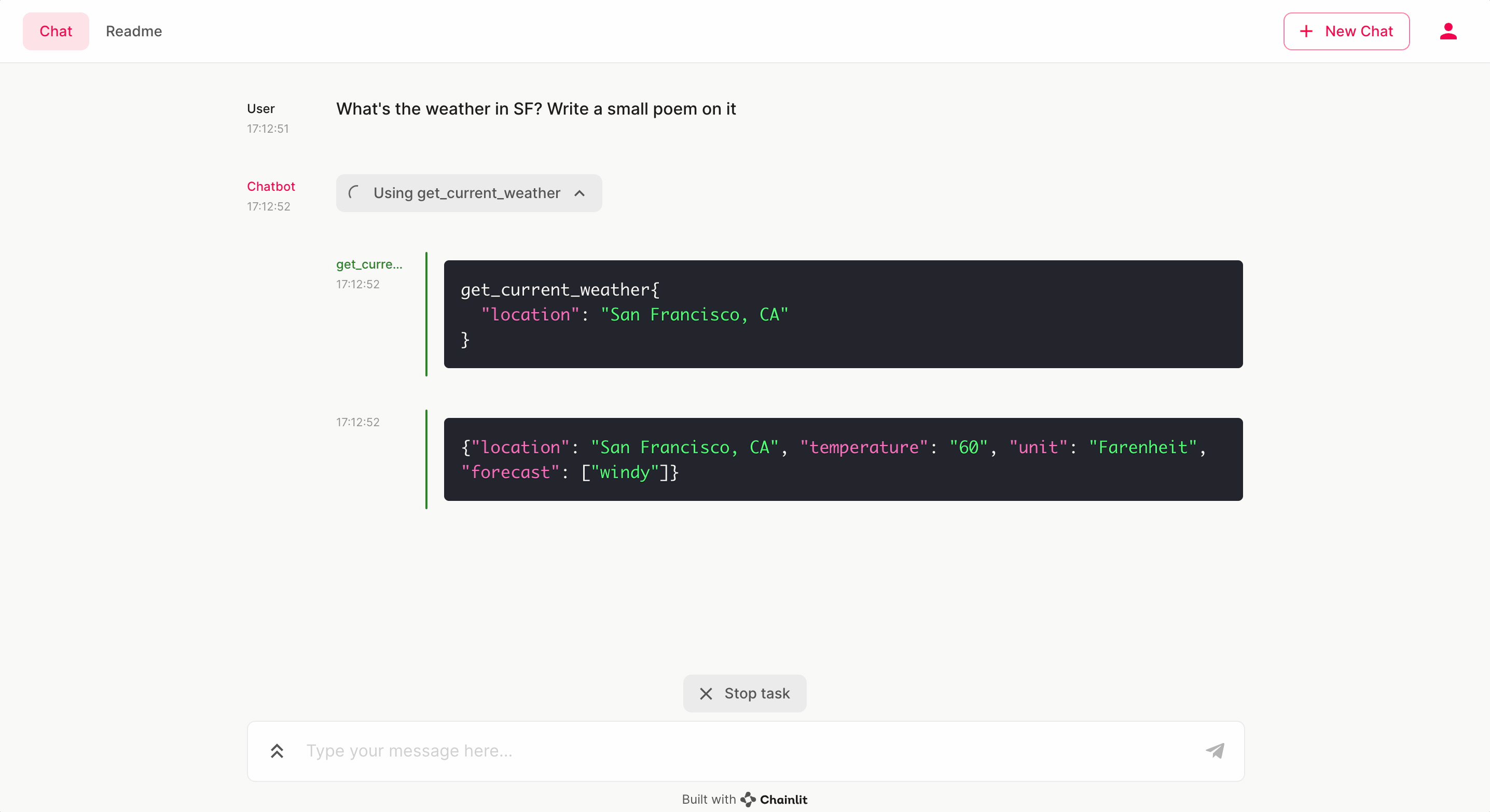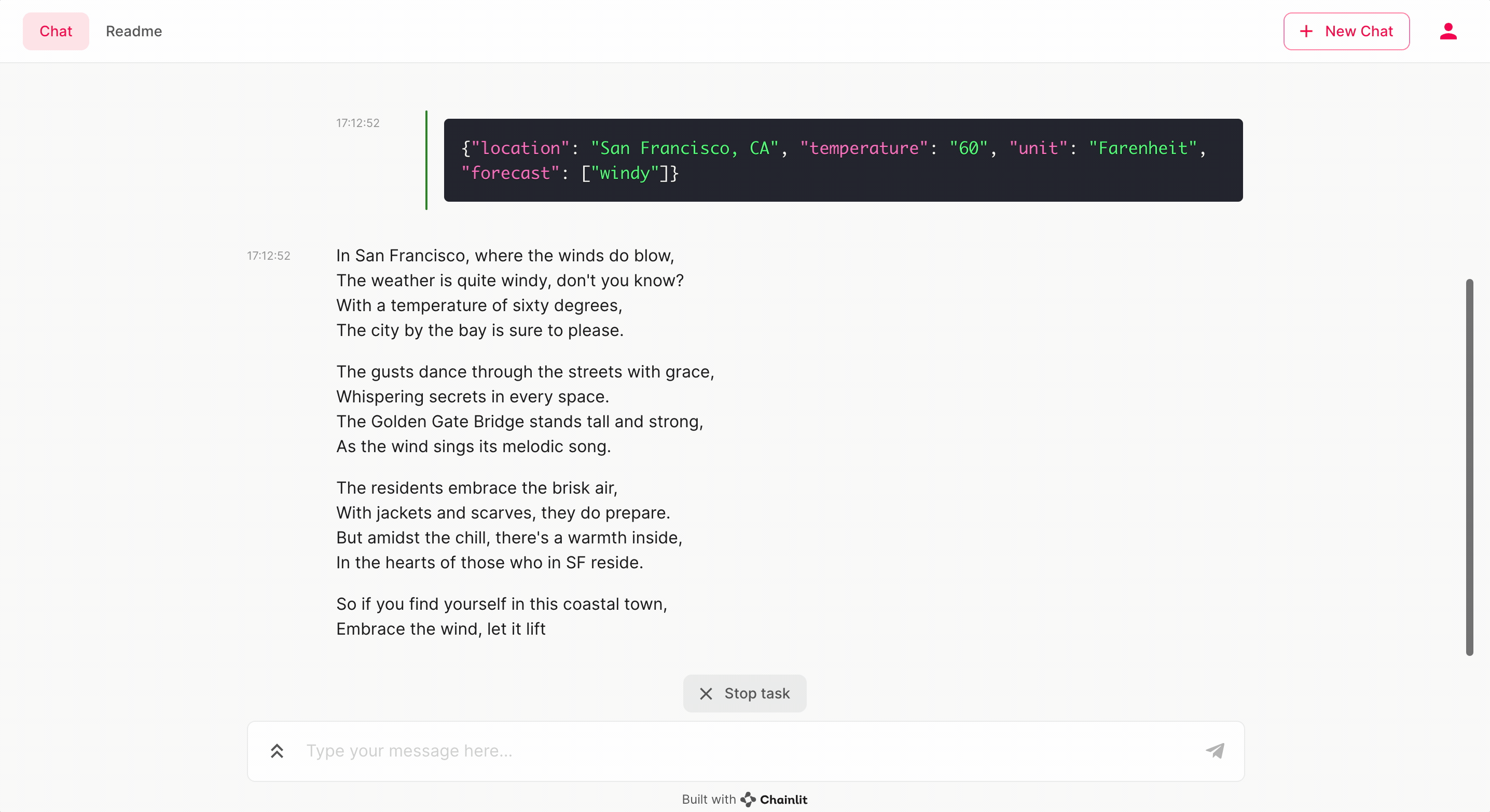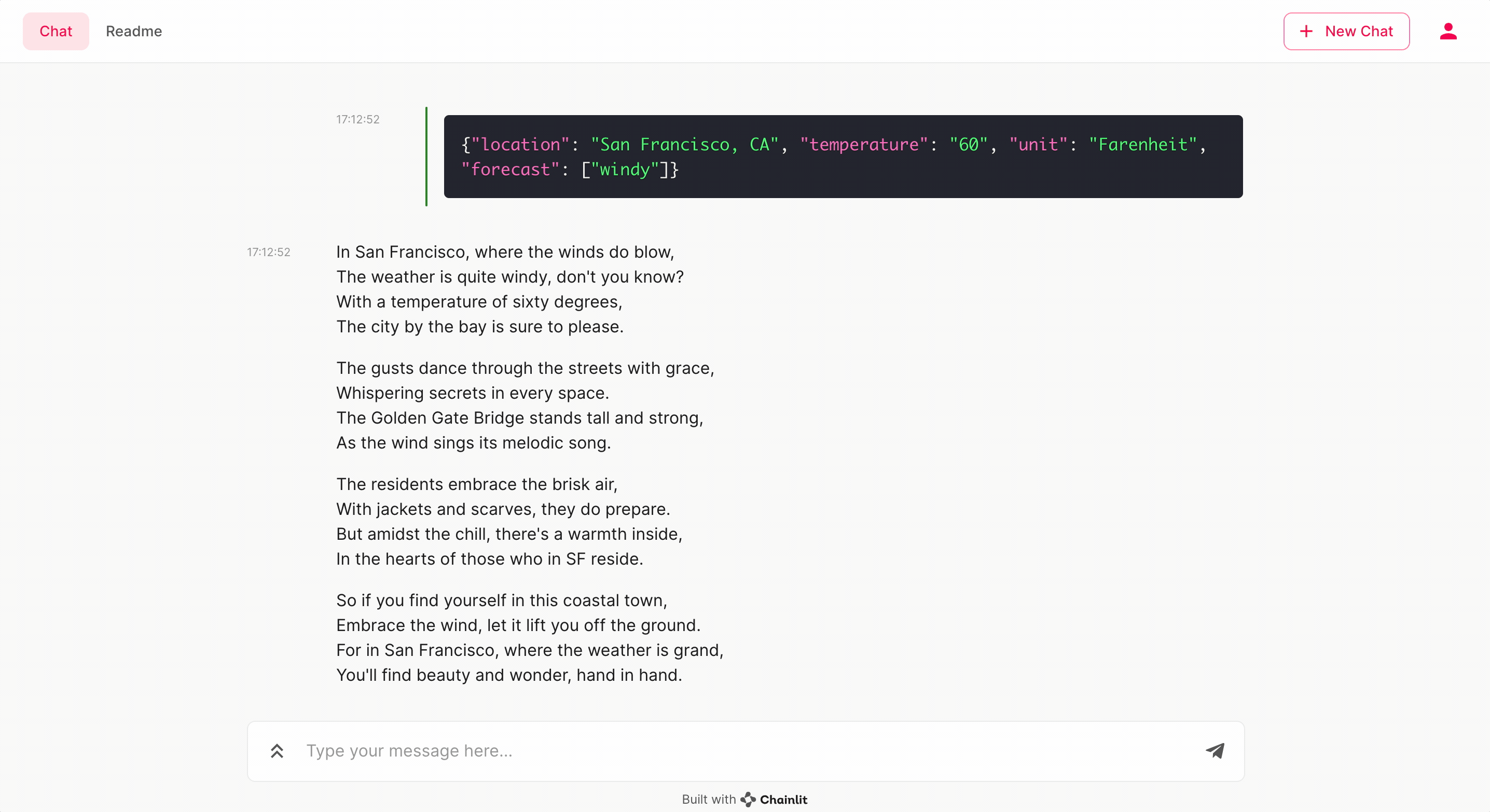
The core functionality is provided by the get_current_weather function defined in app.py. This function takes a location and a unit (Celsius or Fahrenheit) as arguments and returns a JSON string with the weather information.
def get_current_weather(location, unit):
unit = unit or "Fahrenheit"
weather_info = {
"location": location,
"temperature": "60", # Placeholder value
"unit": unit,
"forecast": ["windy"], # Placeholder forecast
}
return json.dumps(weather_info)The call_tool async function in app.py is designed to handle the invocation of get_current_weather from the chat interface. It processes the arguments, calls the function, and appends the result to the message history.
Once the application is running, you can interact with the chatbot through the Chainlit interface. The chatbot will use the OpenAI model to understand your requests and, when necessary, call the get_current_weather function to provide you with the weather information.
For detailed instructions and more information, refer to the main readme.
OpenAI functions enable GPT to use functions you defined in your code. To run the example, follow the instructions of the main readme.