Copy the folder in the vm:
scp -r dacota/ YOUR_VM:~
or connect to your vm and:
git clone https://github.com/ocots/dacota.git
Connect to your VM and install docker:
sudo bash dacota/install.sh
To start the containers, go to the folder dacota/ and do:
docker compose up
Make sure that you have the necessary environment files in their respective locations:
- One
.envfile inms-smith-python - One
.envfile inbackend_django - One
.envfile indb
The first time you launch application, you will have to populate the database, to do so, you will have to execute these commands in the folder where docker-compose.yml is located
docker compose exec backend_django python manage.py migrate
docker compose exec backend_django python manage.py load_component_data
You can now access the django app by using your vm address.
Remark. To clean everything and start again:
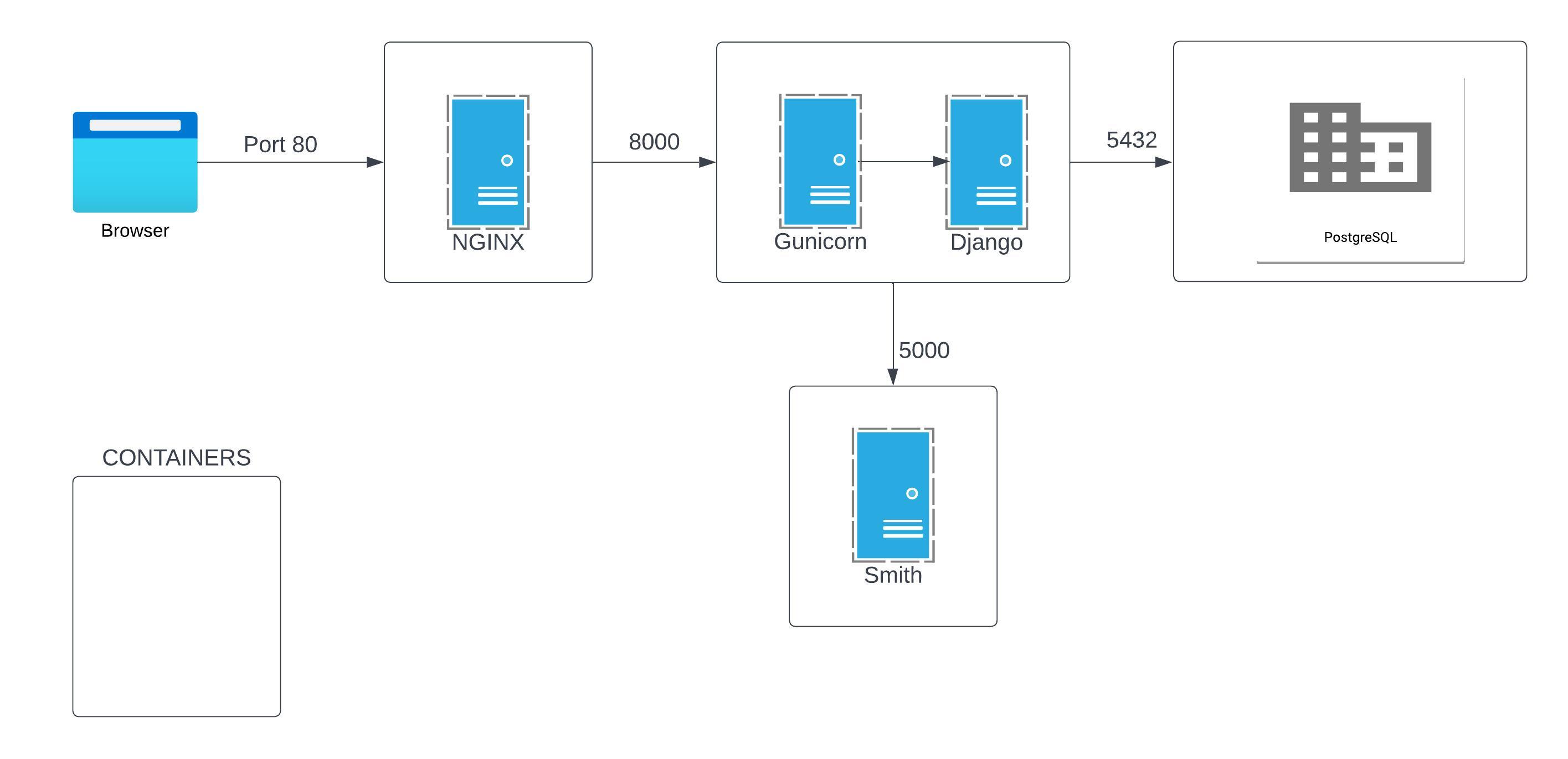
docker system prune --allThe application is composed of 4 containers:
nginxbackend_djangoms-smith-pythondb
Each container has its own Dockerfile that is used to build the container.
The docker-compose.yml file is used to define the containers and their dependencies.
The nginx container is used as a proxy for the backend_django container. It is used to serve static files and to redirect requests to the backend_django container.
The backend_django container is the django app. It serves the html pages and the api requests.
The ms-smith-python container is the python microservice that does the diagram calculation.
The nginx container is defined as follows:
nginx:
build:
context: ./nginx/
volumes:
- static:/app/static/
ports:
- 8080:80
depends_on:
- backend_django
networks:
- django_networkIt is built from the Dockerfile in the nginx folder.
It is exposed on port 80.
The backend_django container is defined as follows:
backend_django:
build:
context: ./backend_django/
command: gunicorn backend_django.wsgi:application --bind 0.0.0.0:8000
volumes:
- ./backend_django/:/app/
- static:/app/static/
expose:
- 8000
depends_on:
- db
networks:
- django_networkIt is built from the Dockerfile in the backend_django folder.
It is exposed internally in the django_network on port 8000.
It depends on the db container.
The ms-smith-python container is defined as follows:
ms-smith-python:
build:
context: ./ms-smith-python/
command: uvicorn app.main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 5000
expose:
- 5000
env_file:
- ./ms-smith-python/.env
networks:
- django_networkIt is built from the Dockerfile in the ms-smith-python folder.
It is exposed internally in the django_network on port 5000.
The db container is defined as follows:
db:
image: postgres
volumes:
- postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data/
env_file:
- ./db/.env
networks:
- django_networkIt is built from the postgres image.
It is exposed internally in the django_network on port 5432.
The networks section defines the networks used by the containers.
networks:
django_network:
name: django_networkThe volumes section defines the volumes used by the containers. The static volume is used by the nginx and backend_django containers. The postgres_data volume is used by the db container. This allows the data to persist between container restarts.
volumes:
static:
name: static
db_data:
name: db_dataTo switch the microservice from python to julia, you will have to use the julia image instead of the python image in the docker-compose.yml file.
This means that you have to uncomment the following lines:
ms-smith-julia:
build:
context: ./ms-smith-julia/
command: julia main.jl # le port est défini dans le fichier main.jl
expose:
- 5000
networks:
- django_networkand comment the following lines:
ms-smith-python:
build:
context: ./ms-smith-python/
command: uvicorn app.main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 5000
expose:
- 5000
env_file:
- ./ms-smith-python/.env
networks:
- django_networkYou will also have to change the following line in backend_django/.env from MS_ENDPOINT=ms-smith-python to MS_ENDPOINT=ms-smith-julia.