This lab is part of the foundations trainings at OCTO Technology Australia.
In this lab we'll need to create a serverless application using AWS Lambda service which will react on events from S3 service. It will also respond to HTTP requests from AWS API Gateway
That will cover the following topics:
- Working with AWS Lambda service via AWS console
- Creating a simple lambda function with S3 event trigger
This lab will take approximately 60 minutes
AWS provides a set of managed services which do not require infrastructure setup and management. Such services are usually referenced as serverless. These include:
- Lambda functions - pieces of code which are run on demand in containers hidden from lambda's owner
- S3 - serverless blob storage
- API Gateway - handles API calls from internet and directs them to other services, e.g. Lambda, S3, EC2
Now let's dive into the world of serverless technology :)
In this exercise we're going to create a simple application which will react on uploading events in S3 bucket and write a object's key into index.lst file in the same bucket
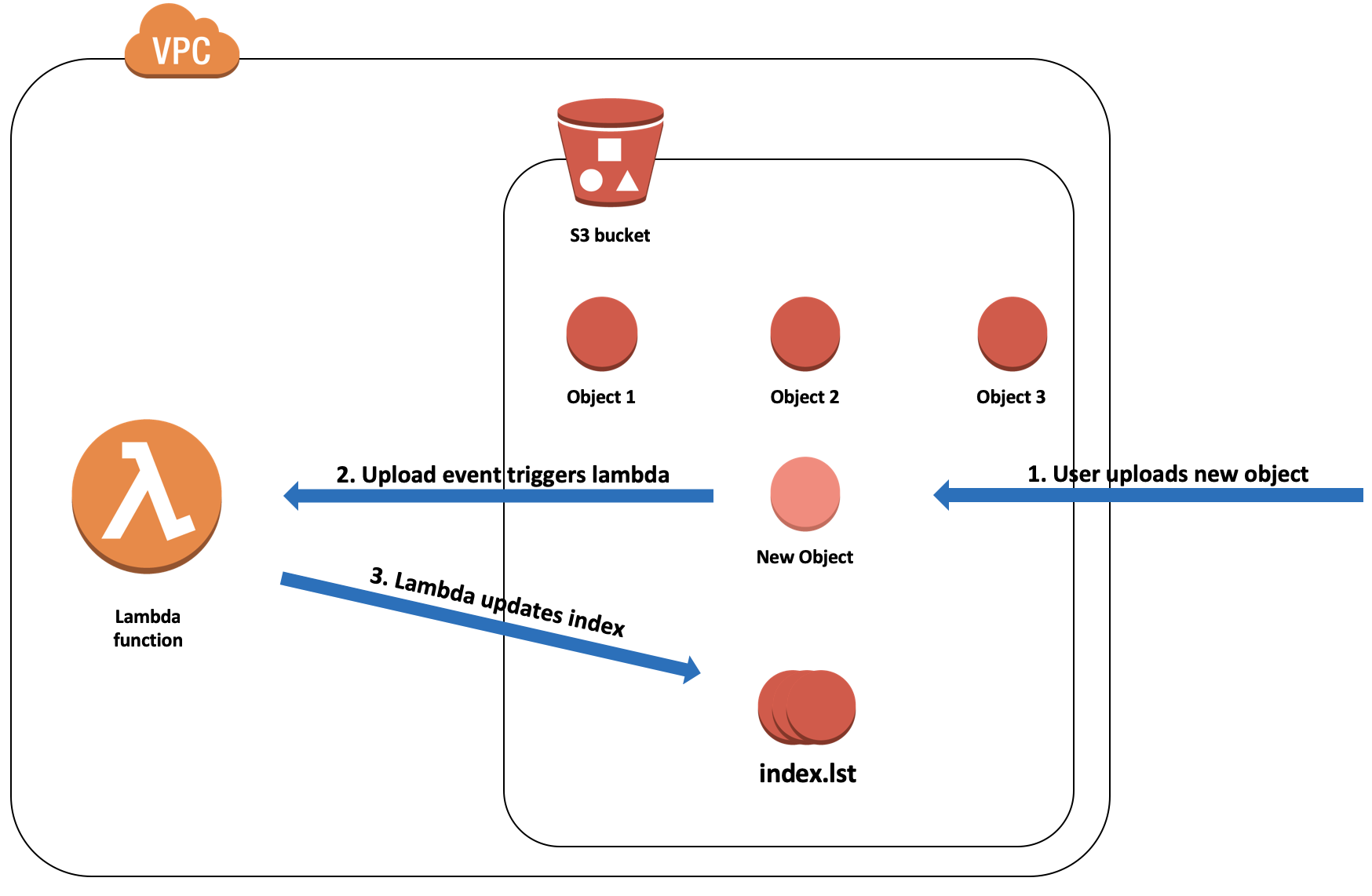 Few things to mention:
Few things to mention:
- logic of the app is a basic one, no complex cases
- we want to ignore events for the
index.lstfile to avoid indefinite loop
- In AWS Console, go to
S3service, then clickCreate bucket - Type
foundation-labs-lambda-<your_name>in theBucket namefield (don't forget to replace <your_name> with your name ;) ) - Leave all other parameters as default and create the bucket
- In AWS Console, go to
Lambdaservice, then clickCreate function - Select
Author from scratch - Set
Nameasfoundation-labs-lambda-<your_name> - Set
RuntimeasNode.js 8.10 - Set
RoletoCreate a new role from one or more templates. - Set
Role nameasfoundation-labs-lambda-role-<your_name> - Choose
Amazon S3 object read-only permissionsinPolicy templates - Click
Create function
We'll need to add write permissions to our lambda's role to allow it create/modify objects in our bucket
- In AWS Console, go to
IAMservice, then clickRoleson the left panel - Find your
foundation-labs-lambda-role-<your_name>role in the list, then click on it - Click
Add inline policy. Then inJSONtab put following code (replace <your_name>):
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "GetAndPut",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:*
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::foundation-labs-lambda-<your_name>*"
}
]
}
- Click
Review policy, then typefoundation-labs-lambda-s3-policy-<your_name>in thenamefield - Click
Save changes
Now let's create a trigger for our lambda function. That will be a reaction to object uploads into our bucket.
For the sake of simplicity, we'll not distinguish between new objects and new versions of existing objects
- On our lambda function screen, find
Designersection and on the left side of it click onS3inAdd triggersmenu. That should add a S3 configuration block:

- Click on that block and scroll down to
Configure triggerssection - Set
bucketfield asfoundation-labs-lambda-<your_name> - Set
Event typeasObject Created (All) - Make sure that
Enable triggeris ticked - Click
Add, then clickSamein the top right corner. That should save all changes:

It's time to write some code! Our function will need to S3 put object event, sample of which could be found in AWS Documentation (see Event samples). For simplicity, here is a stripped version of the sample with only fields which we'll need in our exercise:
{
"Records": [
{
"s3": {
"object": {
"key": "HappyFace.jpg",
...
},
"bucket": {
"name": "sourcebucket",
...
},
...
},
...
}
]
}
Keeping this in mind, please write the code. Here are the guidelines for that:
- First of all, make sure you have your Node.js and NPM utilities installed. If not, follow these instructions
- Open a Node.js project from
exercise1directory of this repo (masterbranch) and runnpm install - Open index.js and write down the code of the app
- There are only 2 api calls to S3 which will be required:
- To help you with the task, we have set up a suite of unit tests, so you need to make them green
- To run your tests, open your terminal,
cdto theexercise1directory and runnpm test - Don't use any additional libraries or create any additional files - you just don't need them for that simple exercise! KISS!
- Don't move
new AWS.S3();outside of handler function - that will brake tests
If you managed to get your tests all green, go ahead and upload the code of index.js into your lambda function:
- In AWS Console, go to
Lambdaservice, then open your functionfoundation-labs-lambda-<your_name> - Click on the block with your function name:

- Scroll down to
Function codeblock and paste there contents of yourindex.js - Click Save in right top corner
Once all steps are completed, we can see how our indexer works:
- In AWS Console, go to S3, then to your bucket
- Upload any file to our bucket
- Check if
index.lstis created in the root of the bucket and contains uploaded file name
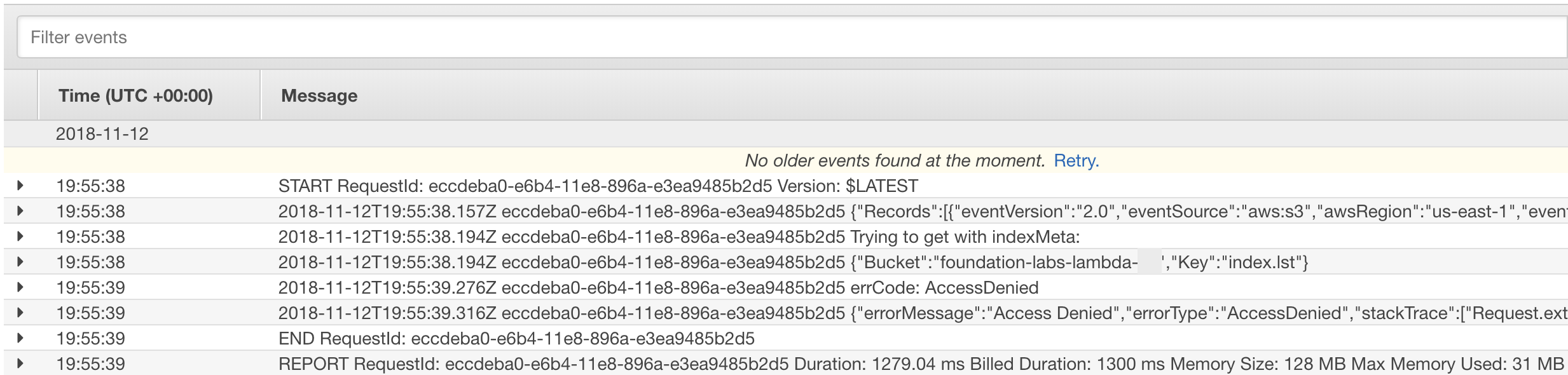
If you don't see index.lst created, you will need to troubleshoot your lambda by going to CloudWatch logs. For the purpose of this exercise we'll see anyway how logs look like there:
- On your lambda function main screen, click on
Monitoringtab, then click onView logs in CloudWatch - It should navigate you to the
Cloudwatch->Logssection and display a list of log streams for your lambda. AWS Navigation path should display something likeCloudWatch > Log Groups > Streams for /aws/lambda/foundation-labs... - Click on the stream with the latest
Last Event Time - Here you can see related logs and execution errors if any
If everything is done properly and debugged, your indexer application should work!
The approach to developing lambda functions described above is straightforward and a bit tedious. There are however frameworks in the market that streamlines creation of the serverless applications. Serverless framework is one of them. It allows to define all steps we did manually in this exercise (and much more) as a code, in simple and easy to understand form. We recommend have a look on quick REST API tutorial in their blog
