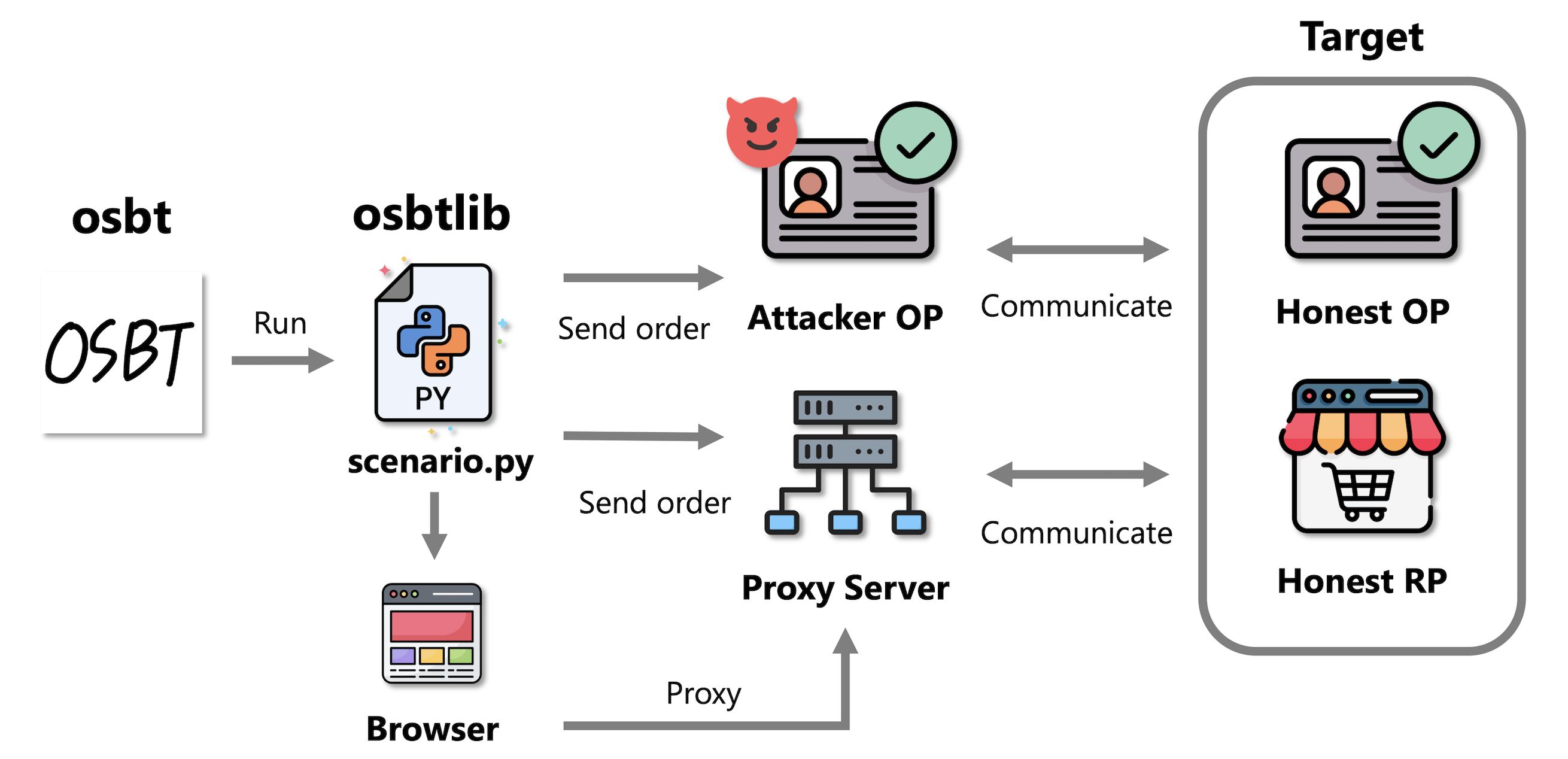
OIDC Scenario Based Tester (OSBT) is a testing tool designed to allow the flexible creation of OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect test scenarios using Python.
OSBT serves to execute more complex and realistic test scenarios against libraries and applications based on OAuth2.0 and OpenID Connect. Testers can construct and execute test scenarios by programming operations such as browser automation, manipulation of proxy servers, and actions of a malicious OpenID provider using the scenario description library provided by OSBT. It also supports integration into CI using GitHub Actions, which can be used for continuous automated security assessment of library applications, and reports showing test results are automatically posted to Issues.
- A comparison of demonstrations for the detection of the following vulnerabilities through manual testing and OSBT.
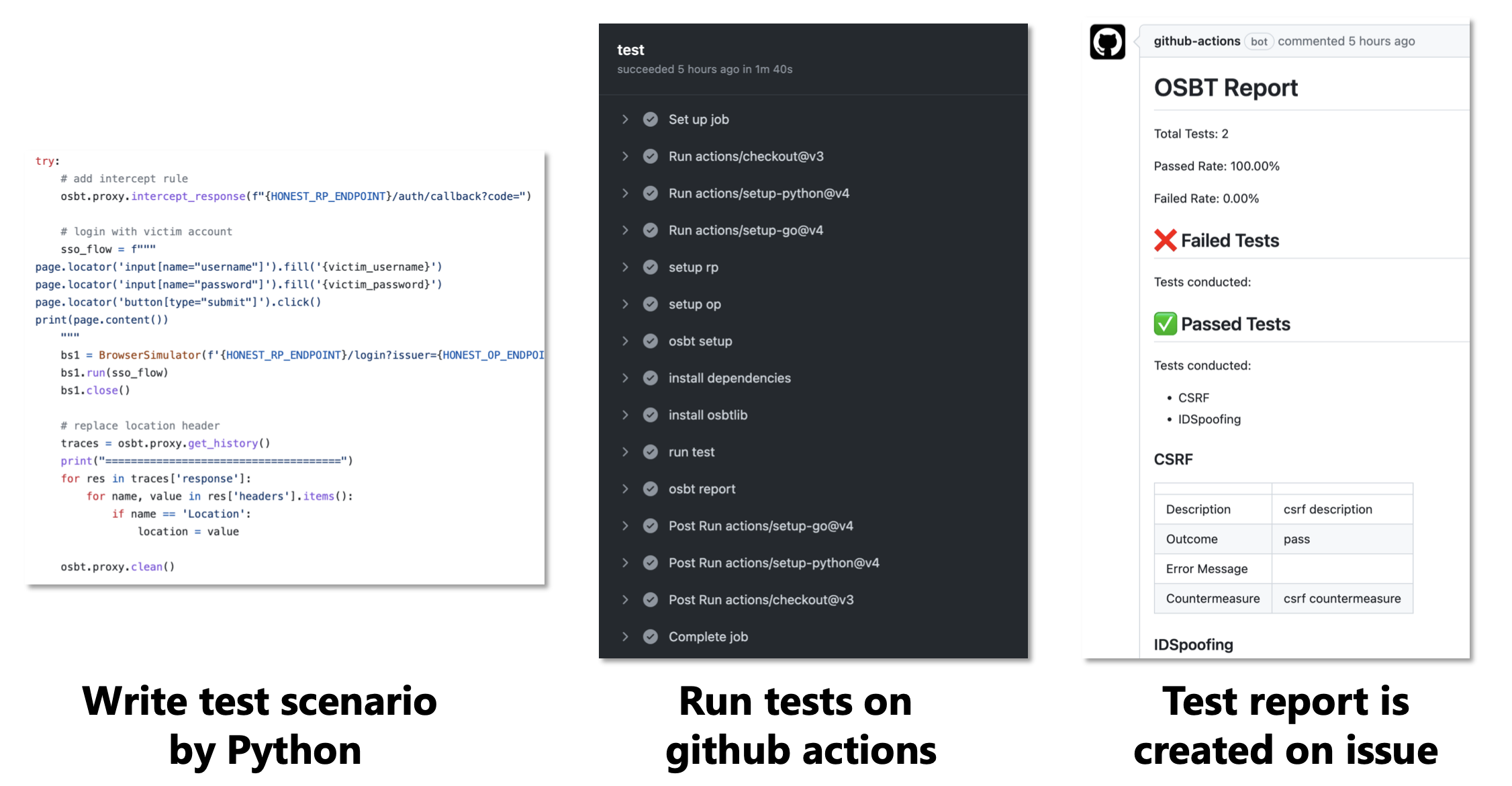
- Demonstrations for using OSBT on GitHub Actions.
- Easy to customize: test by scripting scenarios in Python.
- Free manipulation of HTTP traces: interact with mitmproxy extension to freely manipulate HTTP traces.
- More realistic scenario: testing with malicious OpenID Provider(OP).
- Useful CLI tool: Automatic report generation from test execution results.
Download the binary from the Releases page, or compile it from the source.
$ curl -Lo osbt https://github.com/oidc-scenario-based-tester/osbt/releases/download/v0.0.2/osbt_0.0.2_linux_amd64
$ sudo mv osbt /usr/local/bin/
$ sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/osbt
Download the binary from the Releases page, or compile it from the source.
$ curl -Lo attacker-op https://github.com/oidc-scenario-based-tester/osbt/releases/download/v0.0.2/attacker-op_0.0.2_linux_amd64
$ sudo mv attacker-op /usr/local/bin/
$ sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/attacker-op
Download the source from the Releases page.
$ curl -Lo proxy-extension.py https://github.com/oidc-scenario-based-tester/osbt/releases/download/v0.0.2/proxy-extension.py
- Create a scenario You need to write a scenario to run a test using this tool.
Please refer to oidc-scenario-based-tester/osbtlib for how to write scenarios.
- Start osbt server
Please check Server.
- Start attacker OP
Please check Attacker OP.
- Start proxy extension
Please check Proxy Extension.
- Run tests
Please check Run.
- Get result
Please check Result.
- Get a report
Please check Report.
You must start the server to collect test results and generate a report.
$ osbt server
By default, the HTTP server runs at port 54454 on localhost.
This server interacts with scenarios, collects test results, and handles result retrieval and report generation.
You must start the attacker OP to run tests that assume a malicious OP.
$ attacker-op
By default, the attacker OP runs at port 9997 on localhost.
Attacker OP behaves as a malicious OP that does not follow the protocol specification. It supports the following behaviors that do not conform to the protocol specification.
- ID Token Replacement for Responses
- Providing malicious endpoints using the Discovery service
- Redirect to Honest OP upon an authentication request
The functionality of attacker OP will be expanded in the future.
You must start the proxy extension to manipulate HTTP traces(request/response) between the browser and RP/OP.
$ mitmdump --ssl-insecure -s proxy-extension.py
By default, mitmproxy runs at port 8080 and the extension server runs at port 5555 on localhost.
This extension supports the following HTTP trace operations.
- Adding or tampering with request headers
- Adding or tampering with request query params
- Adding or tampering with request body params
- Interception of requests and responses based on conditions
- Obtaining request and response histories
The functionality of proxy extension will be expanded in the future.
After the setup is complete, you can run test scenarios.
$ osbt run -f scenario.py -t 30
-f,--filescenario file (required)-d,--dirtest directory to run all tests-r,--recursivesearch directories recursively-t,--timeoutscenario execution timeout (default 30s)
You can get the result by sending a request to the server's /results endpoints after testing.
$ curl http://localhost:54454/results | jq
[
{
"test_name": "IDSpoofing",
"description": "\n- The attacker op modifies the id_token to impersonate the victim <br> - The sub claim of the id_token is modified to the victim's sub claim\n",
"outcome": "Passed",
"err_msg": "",
"countermeasure": "\n- Check the signature of the id_token <br> - Check the iss claim of the id_token <br> - Check the sub claim of the id_token\n"
},
...
You can generate a report by sending a request to the server's /report endpoints after testing.
$ curl http://localhost:54454/report
# Test Results
Tests conducted:
- IDSpoofing
## IDSpoofing
| | |
| --- | --- |
| Description |
- The attacker op modifies the id_token to impersonate the victim <br> - The sub claim of the id_token is modified to the victim's sub claim
|
| Outcome | Passed |
| Error Message | |
| Countermeasure |
- Check the signature of the id_token <br> - Check the iss claim of the id_token <br> - Check the sub claim of the id_token
|
Report generated by OSBT.
You can also use osbt in github actions.
Please refer to the actions.yml in the oidc-scenario-based-tester/actions-demo.
- Put test scenarios in
/testdirectory.
https://github.com/oidc-scenario-based-tester/actions-demo/tree/main/test
- Setup target OP and RP.
- name: setup rp
run: >
CLIENT_ID=web
CLIENT_SECRET=secret
ISSUER=http://localhost:9998/
SCOPES="openid profile"
PORT=9999
go run github.com/oidc-scenario-based-tester/actions-demo/oidc/rp &
shell: bash
- name: setup op
run: |
go run github.com/oidc-scenario-based-tester/actions-demo/oidc/op &
shell: bash- Setup osbt and run tests.
You can use osbt-setup-actions.
- name: osbt setup
uses: oidc-scenario-based-tester/osbt-setup-actions@v0.0.1
with:
version: '0.0.1'
...
- name: run test
run: |
osbt run -d ./test
shell: bash- Create a test report on issue.
You can use osbt-report-actions.
- name: osbt report
uses: oidc-scenario-based-tester/osbt-report-actions@v0.0.1image: Flaticon.com