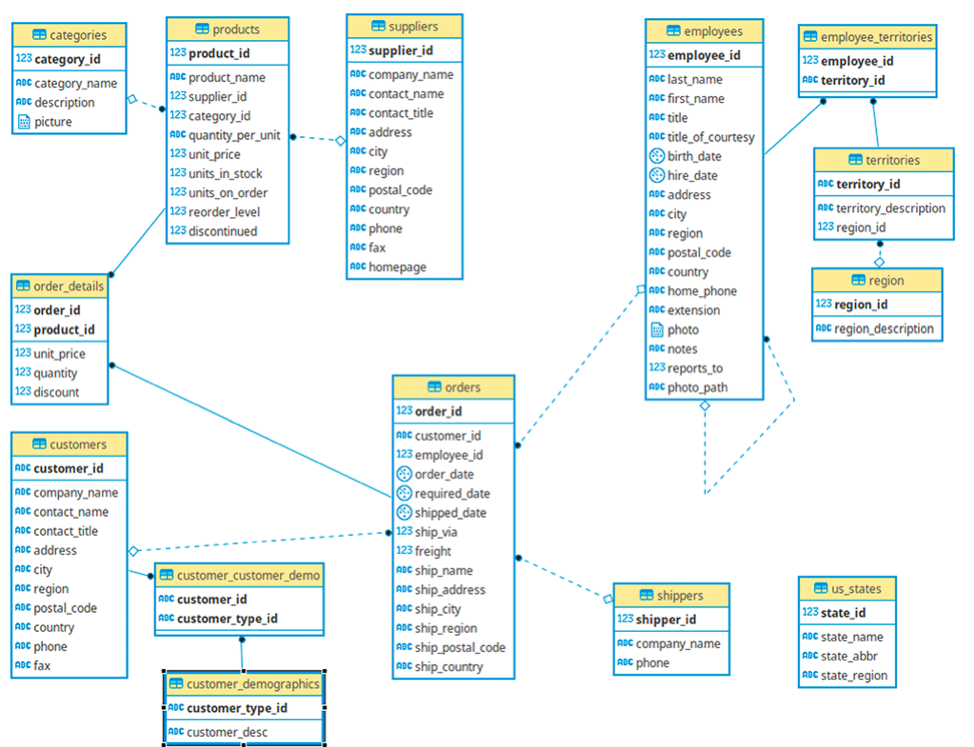
This repository contains several SQL views created to analyze data from the Northwind database, which simulates a real-world ERP system. The analyses provide valuable insights into revenue, customer spending, and product performance. Below are the SQL views and their explanations.
This project showcases the power of SQL in performing advanced data analysis and deriving valuable business insights. By creating reusable SQL views, we can efficiently analyze revenue trends, customer spending patterns, and product performance.
The Northwind database is a comprehensive dataset that mirrors the structure and functionality of an ERP system.
It includes data related to orders, products, customers, and suppliers, providing a rich foundation for performing various business analyses.
In this project, I have created multiple SQL views to streamline and enhance future analyses. SQL views are crucial because they:
- Provide a simplified interface for complex queries.
- Improve query performance by pre-processing complex joins and aggregations.
By utilizing SQL views, businesses can:
- Analyze revenue trends and identify key drivers of growth.
- Monitor customer spending patterns and optimize marketing strategies.
- Generate actionable insights to drive data-driven decision-making.
Calculates the total revenue for the year 1997.
CREATE VIEW total_revenue_1997 AS
SELECT
SUM(od.unit_price * od.quantity * (1 - discount)) AS total_revenue_1997
FROM
orders AS o
JOIN
order_details AS od
ON
o.order_id = od.order_id
WHERE
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM o.order_date) = 1997;Calculates the monthly revenue and year-to-date (YTD) revenue, along with the monthly difference and percentage change.
CREATE VIEW cumulative_revenue AS
WITH MonthlyRevenue AS (
SELECT
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date) AS year,
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM order_date) AS month,
SUM(od.unit_price * od.quantity * (1 - od.discount)) AS Monthly_Revenue
FROM
orders AS o
INNER JOIN
order_details AS od ON o.order_id = od.order_id
GROUP BY
year,
month
),
CumulativeRevenue AS (
SELECT
year,
month,
Monthly_Revenue,
SUM(Monthly_Revenue) OVER (PARTITION BY year ORDER BY month) AS Revenue_YTD
FROM
MonthlyRevenue
)
SELECT
year,
month,
Monthly_Revenue,
Monthly_Revenue - LAG(Monthly_Revenue) OVER (PARTITION BY year ORDER BY month) AS Monthly_Difference,
Revenue_YTD,
(Monthly_Revenue - LAG(Monthly_Revenue) OVER (PARTITION BY year ORDER BY month)) / LAG(Monthly_Revenue) OVER (PARTITION BY year ORDER BY month) * 100 AS Monthly_Change_Percentage
FROM
CumulativeRevenue
ORDER BY
year, month;Monthly Revenue Calculation:
- Extracts the year and month from the order date.
- Calculates the monthly revenue using:
SUM(od.unit_price * od.quantity * (1-od.discount)).Cumulative Revenue Calculation:
- Uses the SUM function as a window function to calculate the cumulative revenue (YTD) within each year, ordered by month.
Final Output:
- Displays the monthly revenue, monthly difference, YTD revenue, and the percentage change in monthly revenue.
Importance:
- Monthly Revenue: Helps in understanding the revenue generated each month.
- YTD Revenue: Provides a running total of revenue throughout the year, giving insight into overall performance.
- Monthly Change Percentage: Shows the growth or decline in revenue month-over-month, crucial for trend analysis.
This analysis provides valuable insights into business performance and helps in making informed decisions.
Calculates the total revenue per customer.
CREATE VIEW total_revenue_per_customer AS
SELECT
DISTINCT company_name,
SUM(unit_price * quantity * (1 - discount)) OVER (PARTITION BY company_name) AS total_spent
FROM
customers
JOIN
orders ON orders.customer_id = customers.customer_id
JOIN
order_details ON orders.order_id = order_details.order_id
ORDER BY
total_spent DESC;
Groups customers into 5 segments based on their total spending.
CREATE VIEW total_revenue_per_customer_group AS
SELECT
company_name,
SUM(unit_price * quantity * (1 - discount)) AS total_spend,
NTILE(5) OVER (ORDER BY SUM(unit_price * quantity * (1 - discount)) DESC) AS ranking
FROM
customers
JOIN
orders ON orders.customer_id = customers.customer_id
JOIN
order_details ON orders.order_id = order_details.order_id
GROUP BY
company_name
ORDER BY
total_spend DESC;
Identifies the top 60% of customers by total spending, who are potential targets for marketing campaigns.
CREATE VIEW marketing_clients AS
WITH marketing_clients AS (
SELECT
company_name,
SUM(unit_price * quantity * (1 - discount)) AS total_spend,
NTILE(5) OVER (ORDER BY SUM(unit_price * quantity * (1 - discount)) DESC) AS ranking
FROM
customers
JOIN
orders ON orders.customer_id = customers.customer_id
JOIN
order_details ON orders.order_id = order_details.order_id
GROUP BY
company_name
ORDER BY
total_spend DESC
)
SELECT * FROM marketing_clients
WHERE ranking >= 3;Lists the top 10 products by total quantity sold.
CREATE VIEW top_10_products AS
SELECT
products.product_name,
SUM(order_details.quantity) AS total
FROM
products
INNER JOIN
order_details ON order_details.product_id = products.product_id
GROUP BY
products.product_name
ORDER BY
total DESC
LIMIT 10;Identifies UK customers who have spent more than $1000.
CREATE VIEW uk_clients_who_pay_more_then_1000 AS
SELECT
customers.company_name,
SUM(order_details.unit_price * order_details.quantity * (1.0 - order_details.discount)) AS total_spend
FROM
customers
INNER JOIN
orders ON customers.customer_id = orders.customer_id
INNER JOIN
order_details ON orders.order_id = order_details.order_id
WHERE
UPPER(customers.country) = 'UK'
GROUP BY
customers.company_name
HAVING
SUM(order_details.unit_price * order_details.quantity * (1.0 - order_details.discount)) > 1000;After the analysis, I used Docker to store the database, ensuring a portable, consistent, and isolated environment that can be easily shared and scaled. Docker enhances the development process by allowing seamless replication of the database setup across different systems.
- Install and configure PostgreSQL and pgadmin
- Import the provided
nortwhind.sqlfile to populate your database
-
You need to install Docker and Docker Compose
-
Initialize Docker Compose Run the command below using git bash inside the folder to upload the services:
docker-compose upWait for the configuration messages, such as:
Creating network "northwind_psql_db" with driver "bridge" Creating volume "northwind_psql_db" with default driver Creating volume "northwind_psql_pgadmin" with default driver Creating pgadmin ... done Creating db ... done
-
Conectar o PgAdmin Access PgAdmin via the URL: http://locpostgrealhost:5050, with the password
postgres.
Set up a new server in PgAdmin:
* **General tab**:
* Name: db
* **Connection tab**:
* Host name: db
* Username: postgres
* Password: natan
Then select the “northwind” database".
-
Stopping Docker Compose Stop the started server by the command
docker-compose upusing Ctrl-C and remove the containers with:docker-compose down -
Files and Persistence Your changes to the Postgres databases will be persisted on the Docker volume
postgresql_dataand can be recovered by restarting Docker Compose withdocker-compose up. To delete the data from the database, run:docker-compose down -v