This page is a one-minute-read info about the brightest features of the system. The complete overview can be found on Wiki
Please note that this repository is hosting the releases of CS-Script (v4.0.0 and higher). The previous content of this repository and wiki (.NET Framework edition of CS-Script) has been moved to the new repository: https://github.com/oleg-shilo/cs-script.net-framework
Note .NET SDK is required to have all features. However, the core features can utilized even with .NET Runtime only. See details.
CS-Script is a CLR-based scripting system that uses ECMA-compliant C# as a programming language.
CS-Script is one of the most mature C# scripting solutions. It became publicly available in 2004, just two years after the first release of .NET. It was the first comprehensive scripting platform for .NET
CS-Script supports both hosted and standalone (CLI) execution models. This makes it possible to use the script engine as a pure C# alternative for PowerShell. As well as extending .NET applications with C# scripts executed at runtime by the hosted script engine.
CS-Script allows seamlessly switching underlying compiling technology without affecting the code base. Currently supported compilers are dotnet.exe and csc.exe.
CS-Script also offers comprehensive integration with the most common development tools:
- Visual Studio (built-in feature via
-vsCLI argument) - VSCode
- Sublime Text 3
- Legacy .NET Framework plugins that are yet to be ported to .NET 5:
It can be run on Win and Linux. Class library for hosting the script engine is compiled for ".NET Standard" so it can be hosted by any managed application.
Over the long history of CS-Script it has been downloaded through Notepad++ x86 plugin manager alone over 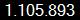
Documentation disclaimer Please be aware that the online Documentation Wiki is intended to provide the most detailed information about the product. It is constantly evolving and sometimes may have be a little out of sync concerning the latest product releases.
Though, the most accurate and concise documentation is embedded in the engine executable and can be accessed via CLI "help" command:
css -helpA copy of the help content can be accessed here
Note, every release comes with a detailed description of how to deploy/integrate CS-Script on/with your environment or application. This covers various package distribution solutions
- .NET Tools
- Chocolatey
- WinGet
- Debian package
- NuGet package
The following section describes a few use cases just to give you an idea about the product:
CLI: Executing script from shell
CS-Script follows many elements of the Python user experience model. Thus a script can reference other scripts, .NET assemblies or even NuGet packages. It also uses Python style caching ensuring that script that was executed at least once is never compiled again unless the script code is changes. This ensures ultimate performance. Thus script execution speed of the consecutive runs matches the excution of fully compiled .NET applications.
Create a simple console script: You can script any type of application that .NET supports (e.g. WinForm, WPF, WEB API) and in two supported syntaxes: C# and VB.
cscs -new script.csThis creates a sample script file with a sample code. Of course you can also create the script file by yourself. This is a top-level class script:
using System;
Console.WriteLine(user());
string user()
=> Environment.UserName;Execute script file directly in cmd-prompt/linux-shell without building an executable assembly:
css .\script.cs
Note, while the script engine CLI executables is cscs.exe (on Win) and cscs (on Linux) you can use css shim that is available in both win and linux distro.
CLI: Executing script from IDE
While various IDEs can be used VSCode is arguably the simplest one.
You can either load the existing script into it with css -vscode .\script.cs or create a new script within the IDE if you install the CS-Script extension:
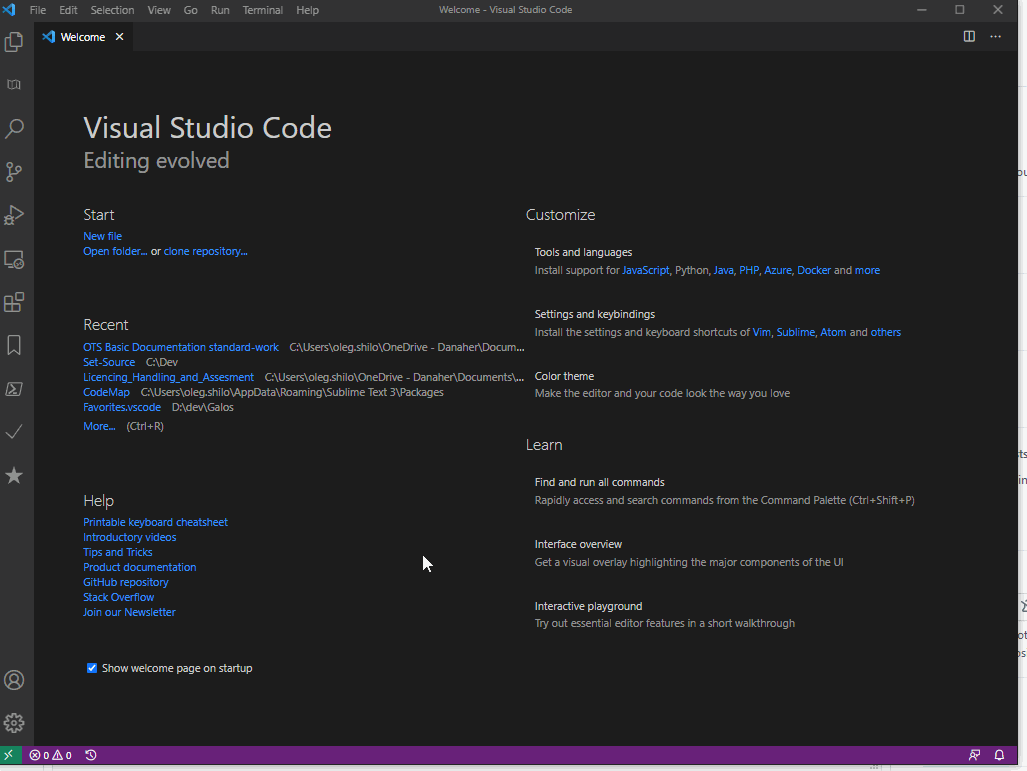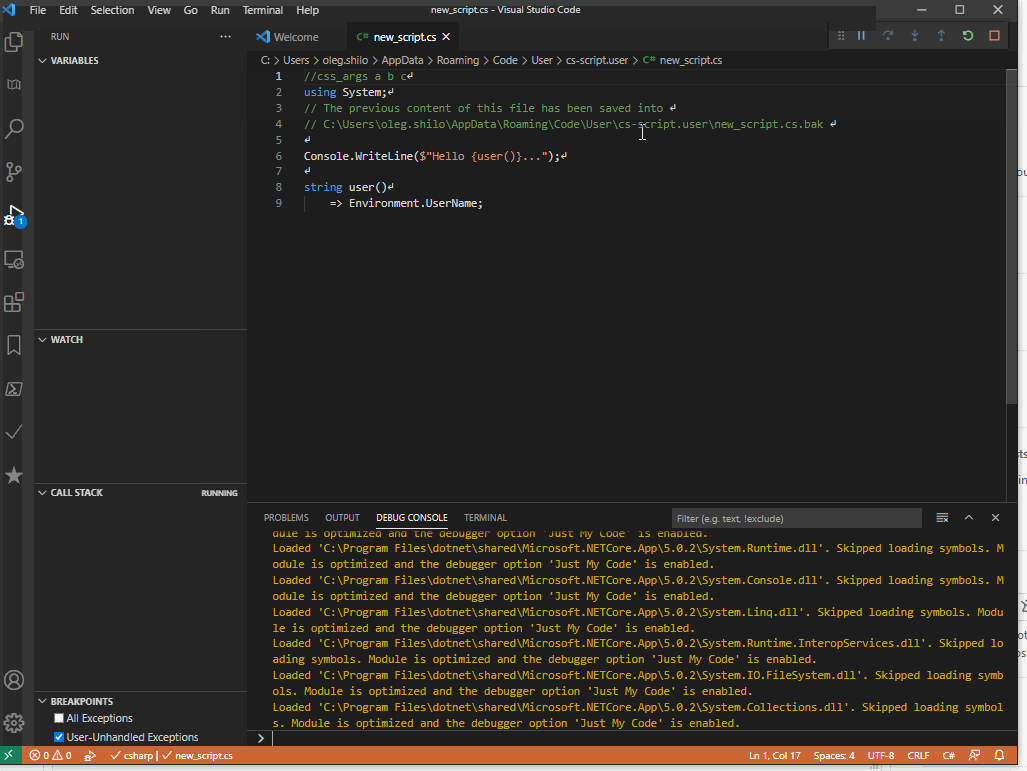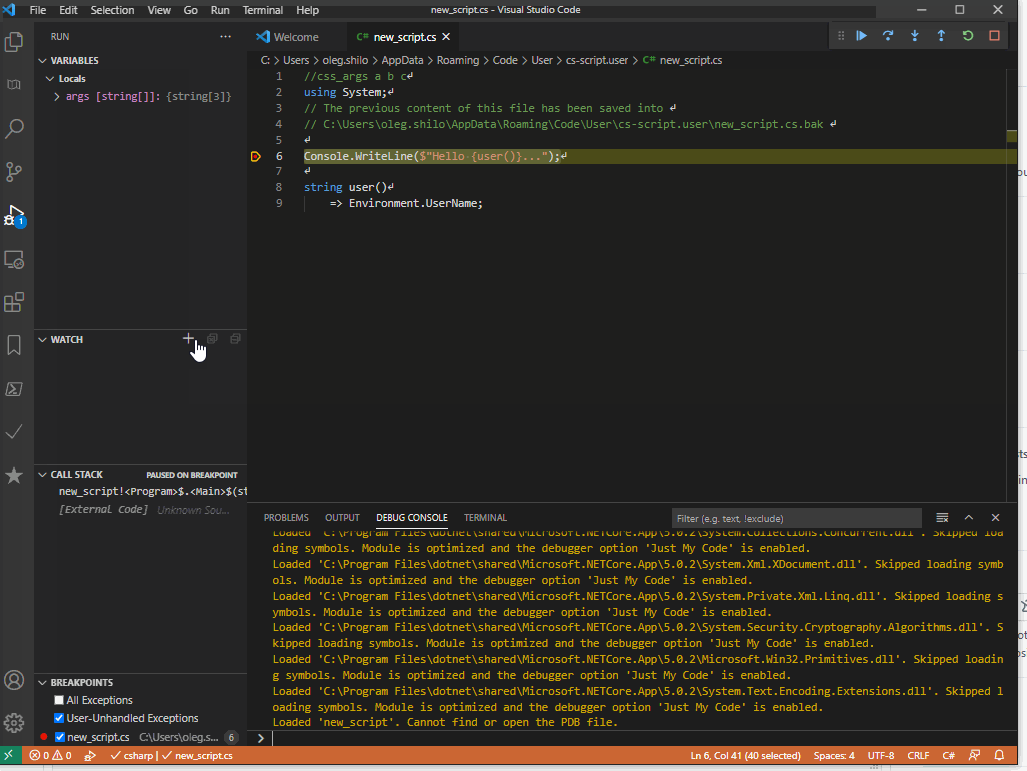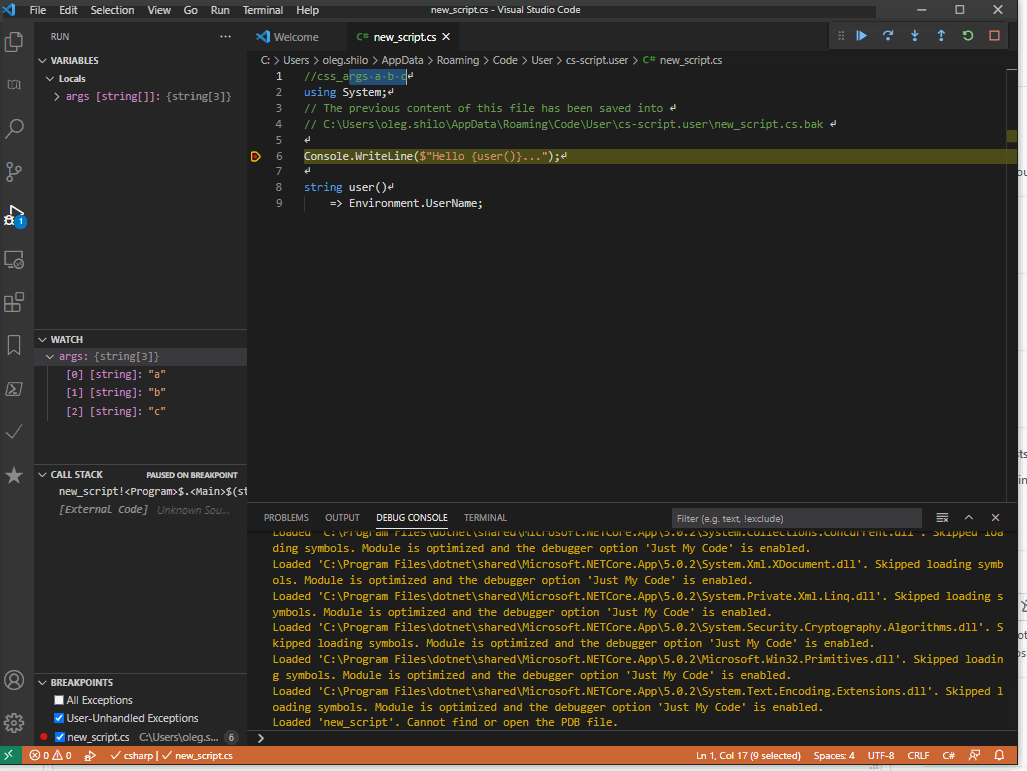
Hosting script engine
You can host the script engine in any .NET application. The class library is distributed as a NuGet package CS-Script.
Install-Package CS-ScriptThe library is built against .NET Standard 2.0 so it can be hosted on any edition of runtime. However the script evaluation is done via .NET 5 tool chain so it needs to be installed on the host PC even if the application is implemented with the older framework (e.g. .NET Framework).
These are just a few samples: The complete content of samples can be found here.
public interface ICalc
{
int Sum(int a, int b);
}
...
// you can but don't have to inherit your script class from ICalc
ICalc calc = CSScript.Evaluator
.LoadCode<ICalc>(@"using System;
public class Script
{
public int Sum(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
}");
int result = calc.Sum(1, 2);dynamic script = CSScript.Evaluator
.LoadMethod(@"int Product(int a, int b)
{
return a * b;
}");
int result = script.Product(3, 2);public interface ICalc
{
int Sum(int a, int b);
int Div(int a, int b);
}
...
ICalc script = CSScript.Evaluator
.LoadMethod<ICalc>(@"public int Sum(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
public int Div(int a, int b)
{
return a/b;
}");
int result = script.Div(15, 3);var log = CSScript.Evaluator
.CreateDelegate(@"void Log(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}");
log("Test message");int sum = CSScript.Evaluator.Eval("6 + 3");




