Ambari service for easily installing and managing NiFi on HDP cluster and viewing metrics.
Features:
- By default, downloads the current GA version - HDF 1.1.2.0 package (nifi 0.5.1) - but also gives option to build the latest Nifi from source instead
- Exposes nifi.properties, bootstrap.conf, logback.xml in Ambari UI (so you can configure port, memory, log dir etc)
- Sets up initial flow.xml.gz that sets up Ambari reporting task to send Ambari metrics
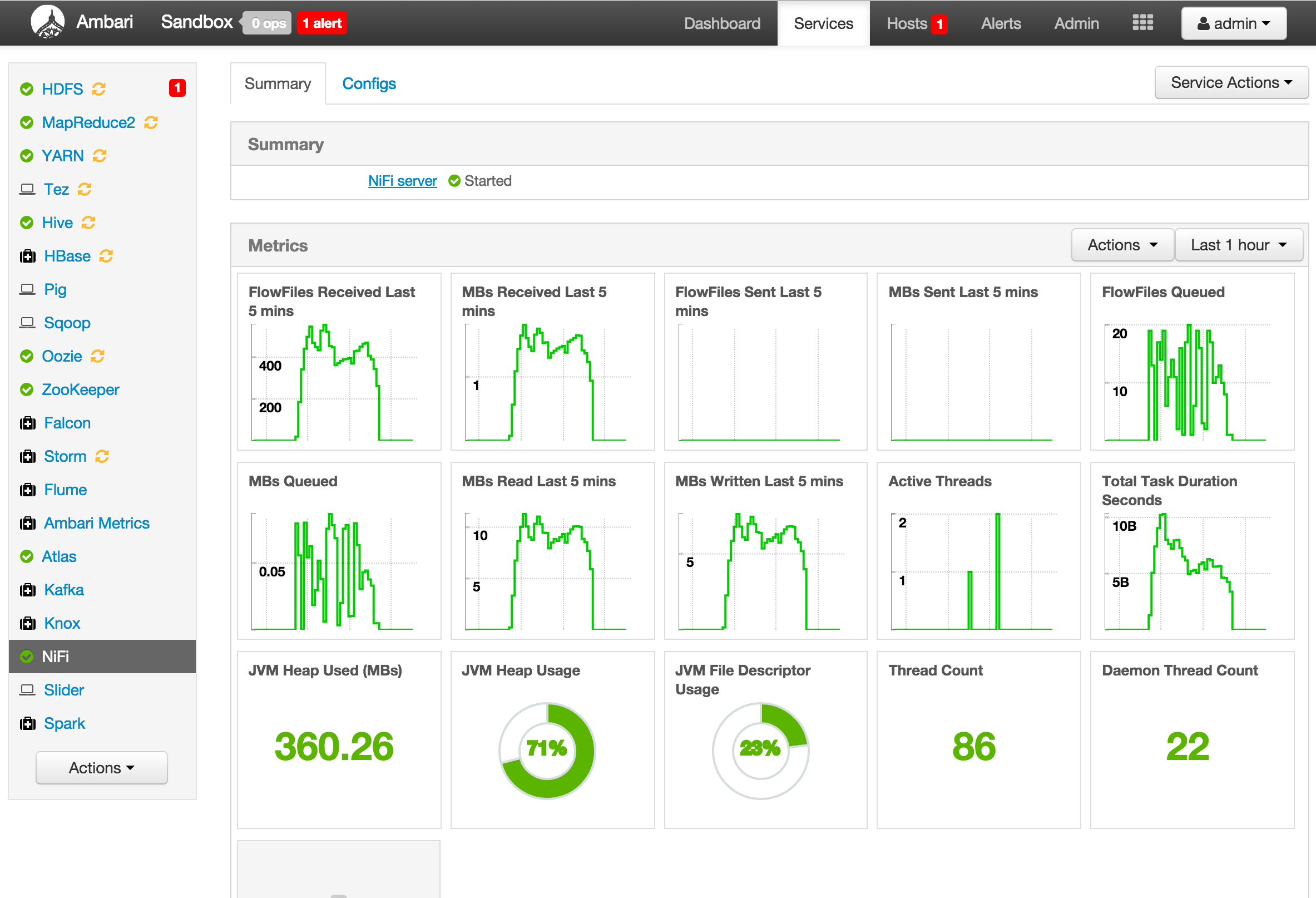
- Includes metrics widgets from here
Limitations:
- This is not an officially supported service and is not meant to be deployed in production systems. It is only meant for testing demo/purposes
- It does not support Ambari/HDP upgrade process and will cause upgrade problems if not removed prior to upgrade
- Not tested on secured clusters
Authors:
- Ali Bajwa: Nifi Install/start/stop via Ambari
- Bryan Bende: Ambari metrics integration
- Download HDP 2.4 sandbox VM image (Hortonworks_sanbox_with_hdp_2_4_vmware.ova) from Hortonworks website
- Import Hortonworks_sanbox_with_hdp_2_4_vmware.ova into VMWare and set the VM memory size to 8GB
- Now start the VM
- After it boots up, find the IP address of the VM and add an entry into your machines hosts file. For example:
192.168.191.241 sandbox.hortonworks.com sandbox
-
Note that you will need to replace the above with the IP for your own VM
-
Connect to the VM via SSH (password hadoop)
ssh root@sandbox.hortonworks.com
-
(Optional) To see Nifi metrics in Ambari, login to Ambari (admin/admin) and start Ambari Metrics service http://sandbox.hortonworks.com:8080
-
To download the NiFi service folder, run below
VERSION=`hdp-select status hadoop-client | sed 's/hadoop-client - \([0-9]\.[0-9]\).*/\1/'`
rm -rf /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/stacks/HDP/$VERSION/services/NIFI
sudo git clone https://github.com/abajwa-hw/ambari-nifi-service.git /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/stacks/HDP/$VERSION/services/NIFI
- Restart Ambari
#sandbox
service ambari restart
#non sandbox
sudo service ambari-server restart
- Then you can click on 'Add Service' from the 'Actions' dropdown menu in the bottom left of the Ambari dashboard:
On bottom left -> Actions -> Add service -> check NiFi server -> Next -> Next -> Change any config you like (e.g. install dir, port, setup_prebuilt or values in nifi.properties) -> Next -> Deploy
-
By default:
- Port is set to 9090
- Max JVM memory size is 512mb
- Run schedule for Nifi's Ambari reporting task is 1 min
-
Note: On the latest sandbox there is a bug where when user gets to the 'Customize Services' page of the 'Add service wizard', it prompts for:
- On Ranger tab: "Ranger Admin user's password for Ambari"
- Type
rangeradmin
- Type
- On Oozie tab: it complains about a security related property
- Delete the property
- On Ranger tab: "Ranger Admin user's password for Ambari"
-
On successful deployment you will see the NiFi service as part of Ambari stack and will be able to start/stop the service from here:
-
You can see the parameters you configured under 'Configs' tab
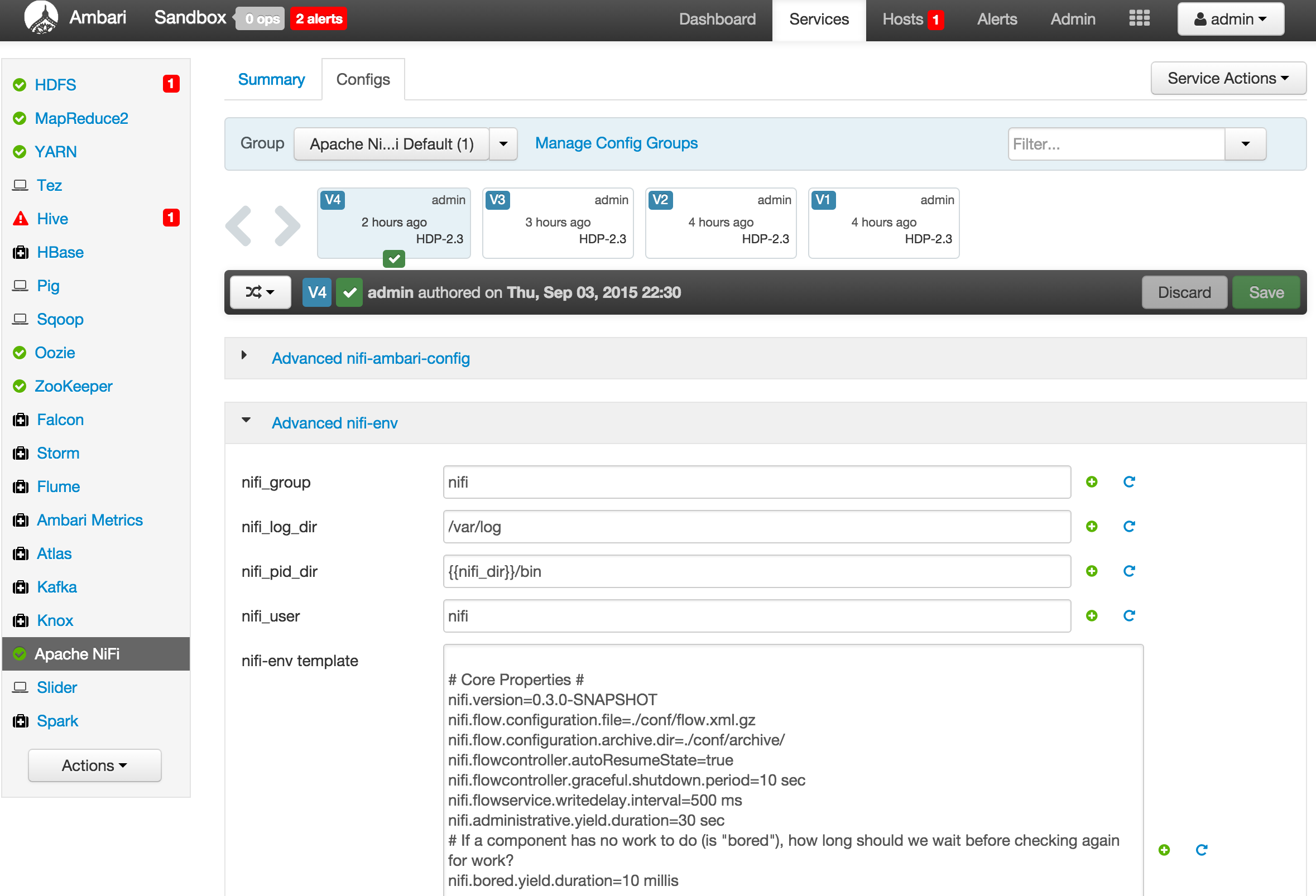
-
One benefit to wrapping the component in Ambari service is that you can now monitor/manage this service remotely via REST API
export SERVICE=NIFI
export PASSWORD=admin
export AMBARI_HOST=localhost
export CLUSTER=Sandbox
#get service status
curl -u admin:$PASSWORD -i -H 'X-Requested-By: ambari' -X GET http://$AMBARI_HOST:8080/api/v1/clusters/$CLUSTER/services/$SERVICE
#start service
curl -u admin:$PASSWORD -i -H 'X-Requested-By: ambari' -X PUT -d '{"RequestInfo": {"context" :"Start $SERVICE via REST"}, "Body": {"ServiceInfo": {"state": "STARTED"}}}' http://$AMBARI_HOST:8080/api/v1/clusters/$CLUSTER/services/$SERVICE
#stop service
curl -u admin:$PASSWORD -i -H 'X-Requested-By: ambari' -X PUT -d '{"RequestInfo": {"context" :"Stop $SERVICE via REST"}, "Body": {"ServiceInfo": {"state": "INSTALLED"}}}' http://$AMBARI_HOST:8080/api/v1/clusters/$CLUSTER/services/$SERVICE
- ...and also install via Blueprint. See example here on how to deploy custom services via Blueprints
-
Bring up 4 VMs imaged with RHEL/CentOS 6.x (e.g. node1-4 in this case)
-
On non-ambari nodes, install ambari-agents and point them to ambari node (e.g. node1 in this case)
export ambari_server=node1
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/seanorama/ambari-bootstrap/master/ambari-bootstrap.sh | sudo -E sh
- On Ambari node, install ambari-server
export install_ambari_server=true
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/seanorama/ambari-bootstrap/master/ambari-bootstrap.sh | sudo -E sh
yum install -y git
sudo git clone https://github.com/abajwa-hw/ambari-nifi-service.git /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/stacks/HDP/2.4/services/NIFI
- Restart Ambari
service ambari-server restart
service ambari-agent restart
- Confirm 4 agents were registered and agent remained up
curl -u admin:admin -H X-Requested-By:ambari http://localhost:8080/api/v1/hosts
service ambari-agent status
- (Optional) - You can generate BP and cluster file using Ambari recommendations API using these steps. For more details, on the bootstrap scripts see bootstrap script git
yum install -y python-argparse
git clone https://github.com/seanorama/ambari-bootstrap.git
#Select the services to be deployed
#option A: for only NIFI
#export ambari_services="NIFI"
#option B: for minimal services
#export ambari_services="HDFS MAPREDUCE2 YARN ZOOKEEPER HIVE NIFI"
#option C: for most services
#export ambari_services="ACCUMULO FALCON FLUME HBASE HDFS HIVE KAFKA KNOX MAHOUT OOZIE PIG SLIDER SPARK SQOOP MAPREDUCE2 STORM TEZ YARN ZOOKEEPER NIFI"
bash ./ambari-bootstrap/deploy/deploy-recommended-cluster.bash
- You can monitor the progress of the deployment via Ambari (e.g. http://node1:8080).
-
The NiFi webUI login page should come up at the below link: http://sandbox.hortonworks.com:9090/nifi
- On VirtualBox you will need to manually forward port 9090 before you can do this. This is not required on VMWare
-
You can also open it from within Ambari via iFrame view
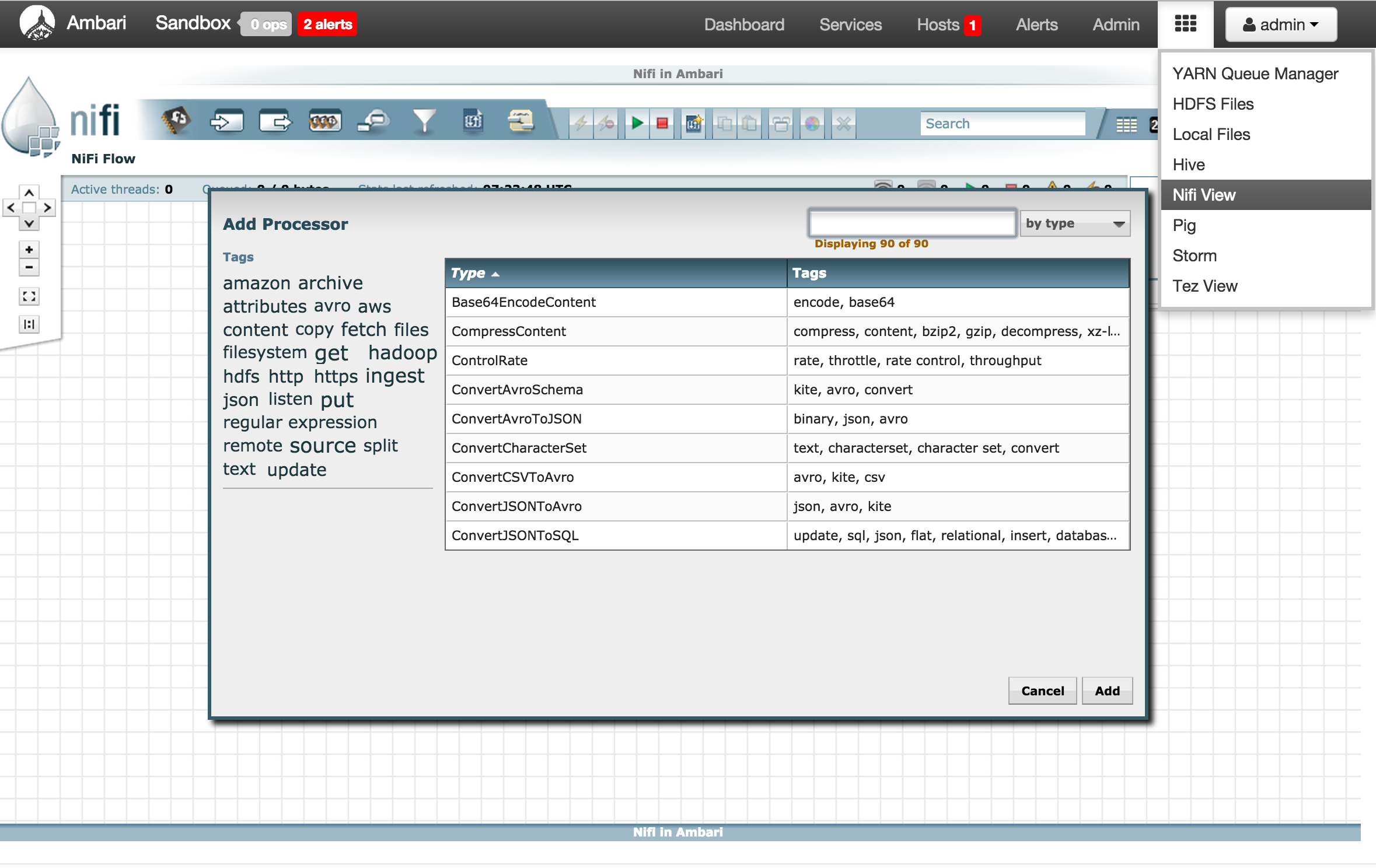
- Sample steps to automate this (requires maven):
git clone https://github.com/abajwa-hw/iframe-view.git sed -i "s/IFRAME_VIEW/NIFI_VIEW/g" iframe-view/src/main/resources/view.xml sed -i "s/iFrame View/Nifi View/g" iframe-view/src/main/resources/view.xml sed -i "s#sandbox.hortonworks.com:6080#sandbox.hortonworks.com:9090/nifi/#g" iframe-view/src/main/resources/index.html sed -i "s/iframe-view/nifi-view/g" iframe-view/pom.xml sed -i "s/Ambari iFrame View/Nifi View/g" iframe-view/pom.xml mv iframe-view nifi-view cd nifi-view mvn clean package cp target/*.jar /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/views ambari-server restart
- Install Nifi via Ambari service on sandbox by running below and running 'Add service' wizard
VERSION=`hdp-select status hadoop-client | sed 's/hadoop-client - \([0-9]\.[0-9]\).*/\1/'`
sudo git clone https://github.com/abajwa-hw/ambari-nifi-service.git /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/stacks/HDP/$VERSION/services/NIFI
#sandbox
service ambari restart
#non sandbox
service ambari-server restart
- Drag processors (first icon on upper left) to Nifi canvas and make below configurations:
- ListenUDP: pull data from port 9091 info flow files
- Set
Port=9091
- Set
- ExtactText: extract text from flow file
- MergeContent: merge multiple text into one
- Set
Min num entries=5 - Set
Max Bin Age=5s - Terminate all relationships except for 'Merged'
- Set
- PutHDFS: write merged content into HDFS files into /tmp/logs
- Set
Directory=/tmp/logs - Set
Hadoop Config resources=/etc/hadoop/conf/core-site.xml - Auto terminate all relationships (Succcess and Failure)
- Set
- ListenUDP: pull data from port 9091 info flow files
- Alternatively, you can import this template for the above flow
- Start the flow by clicking the Play icon
- Push name node log to port 9091 in UDP format using netcat:
tail -f /var/log/hadoop/hdfs/hadoop-hdfs-namenode-sandbox.hortonworks.com.log | nc -4u localhost 9091
- After few seconds data should start flowing into
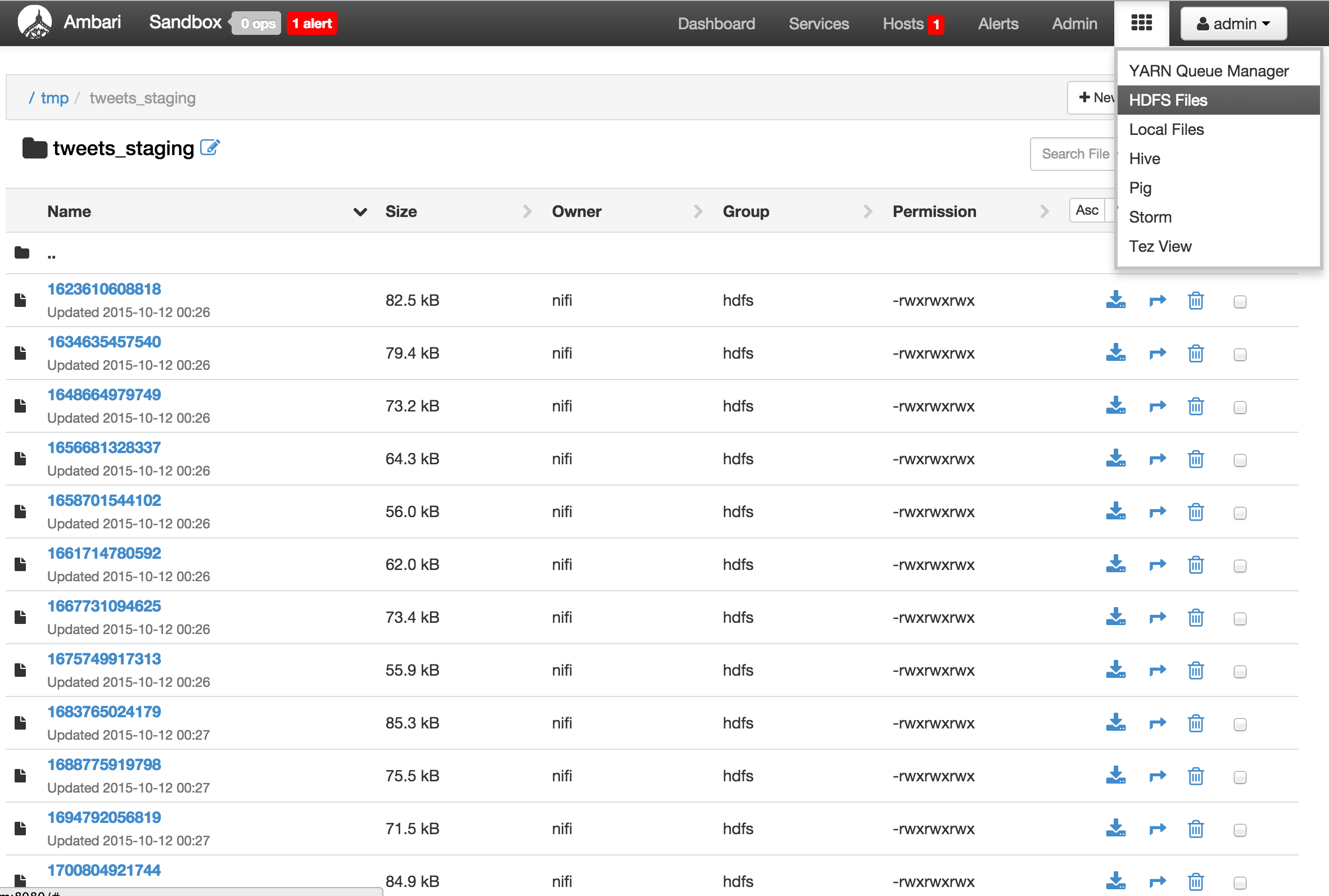
/tmp/logsdir in HDFS.- Open Files view: http://sandbox.hortonworks.com:8080/#/main/views/FILES/1.0.0/Files

- Open Files view: http://sandbox.hortonworks.com:8080/#/main/views/FILES/1.0.0/Files
- Install Nifi via Ambari service on sandbox by running below and running 'Add service' wizard
VERSION=`hdp-select status hadoop-client | sed 's/hadoop-client - \([0-9]\.[0-9]\).*/\1/'`
sudo git clone https://github.com/abajwa-hw/ambari-nifi-service.git /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/stacks/HDP/$VERSION/services/NIFI
#sandbox
service ambari restart
#non sandbox
service ambari-server restart
-
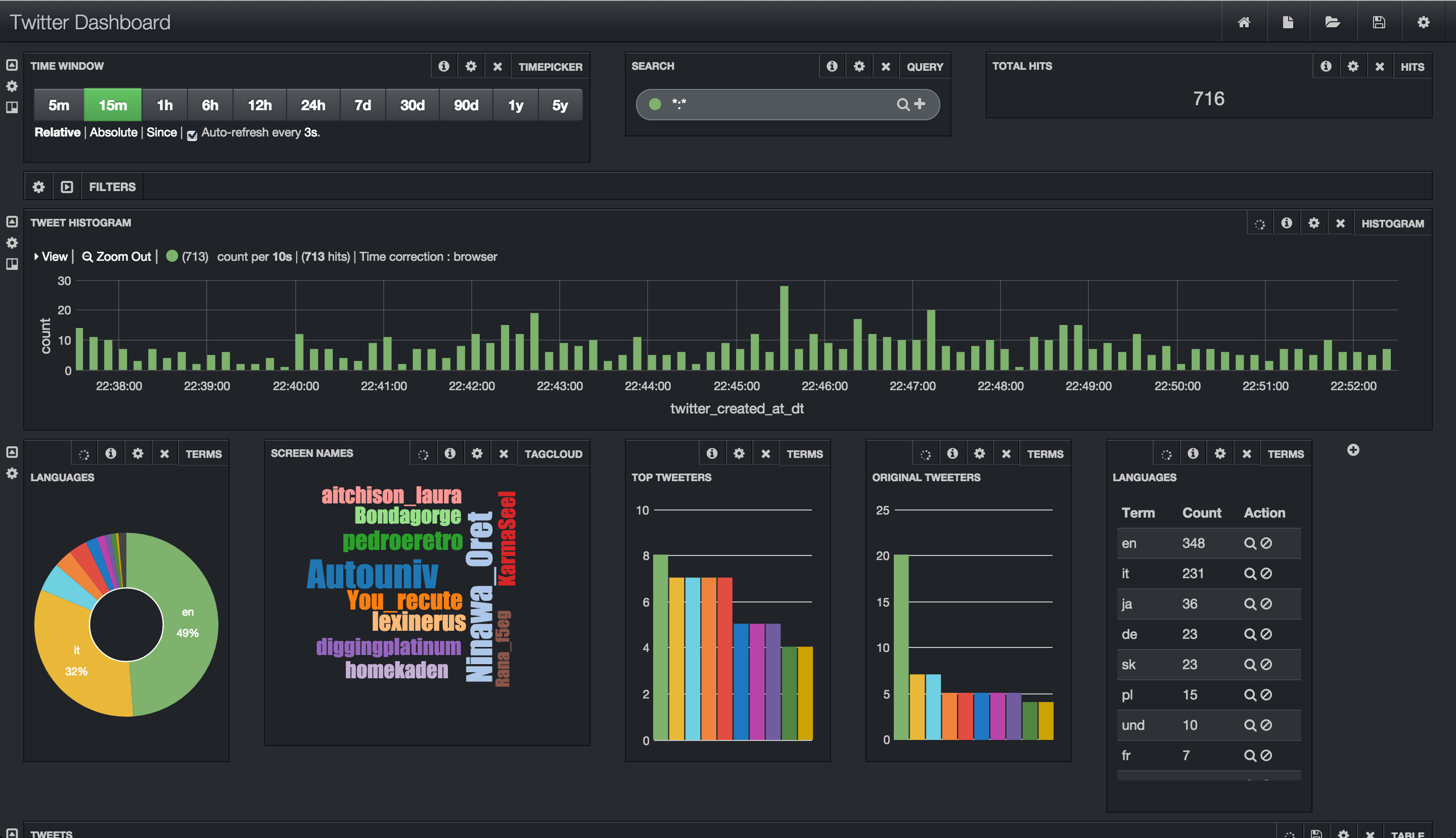
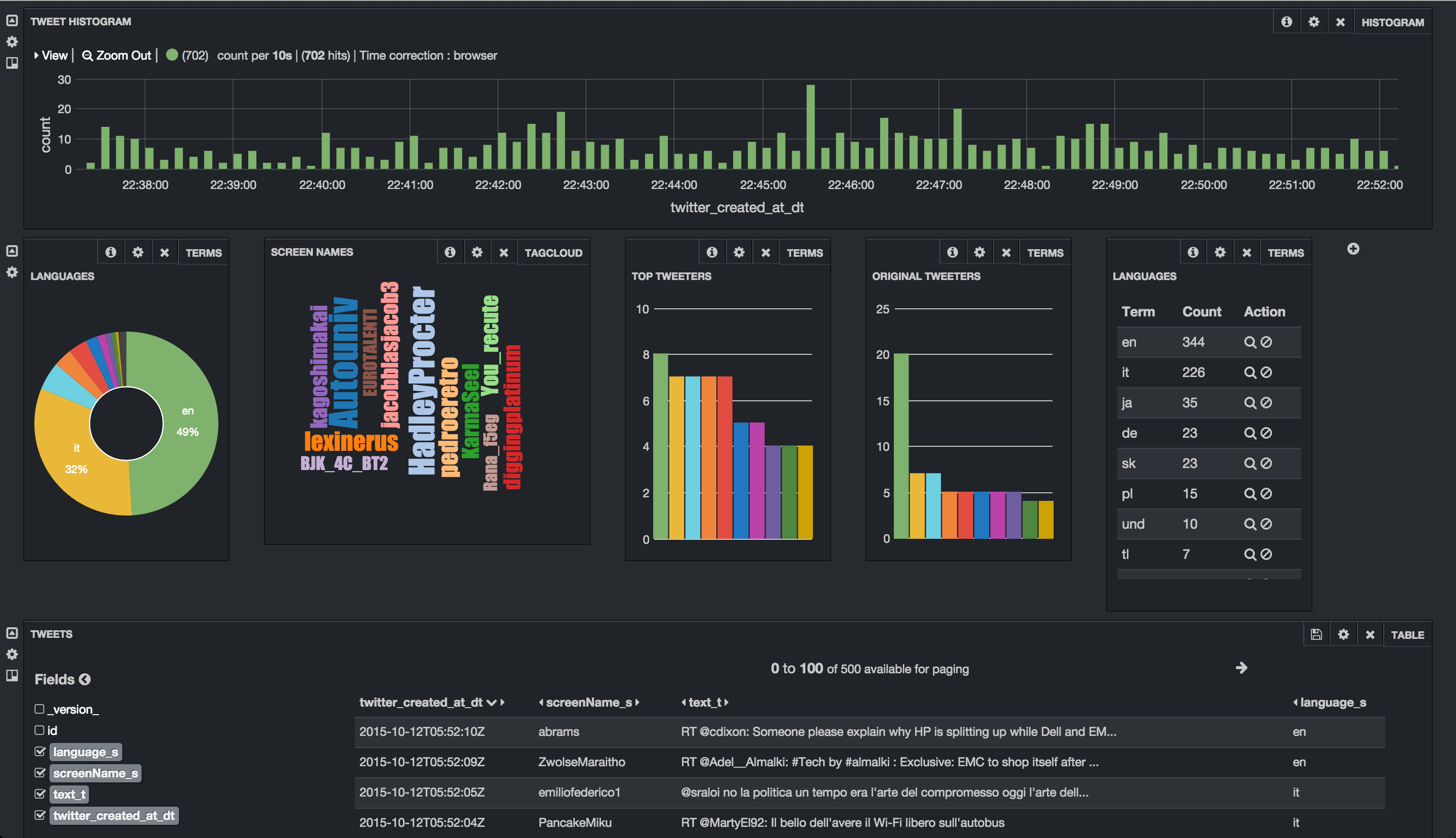
Import simple flow to read Tweets into HDFS/Solr and visualize using Banana dashboard
-
HDP sandbox comes LW HDP search. Follow the steps below to use it to setup Banana, start SolrCloud and create a collection
- If running on an Ambari installed HDP 2.4 cluster (instead of sandbox), run the below to install HDPsearch first. These are not needed on sandbox.
yum install -y lucidworks-hdpsearch sudo -u hdfs hadoop fs -mkdir /user/solr sudo -u hdfs hadoop fs -chown solr /user/solr- Ensure no log files owned by root
chown -R solr:solr /opt/lucidworks-hdpsearch/solr #current sandbox version has files owned by root here which causes problems- Run remaining setup steps as solr user
su solr- Setup the Banana dashboard by copying default.json to dashboard dir
cd /opt/lucidworks-hdpsearch/solr/server/solr-webapp/webapp/banana/app/dashboards/ mv default.json default.json.orig wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abajwa-hw/ambari-nifi-service/master/demofiles/default.json- Edit solrconfig.xml by adding
<str>EEE MMM d HH:mm:ss Z yyyy</str>underParseDateFieldUpdateProcessorFactoryso it looks like below. This is done to allow Solr to recognize the timestamp format of tweets.
vi /opt/lucidworks-hdpsearch/solr/server/solr/configsets/data_driven_schema_configs/conf/solrconfig.xml<processor class="solr.ParseDateFieldUpdateProcessorFactory"> <arr name="format"> <str>EEE MMM d HH:mm:ss Z yyyy</str>- Start Solr in cloud mode and create a collection called tweets
export JAVA_HOME=<JAVA_HOME used by Ambari> /opt/lucidworks-hdpsearch/solr/bin/solr start -c -z localhost:2181 /opt/lucidworks-hdpsearch/solr/bin/solr create -c tweets \ -d data_driven_schema_configs \ -s 1 \ -rf 1- Exit to run remaining steps as root
exit- Ensure the time on your sandbox is accurate or you will get errors using the GetTwitter processor. To fix the time, run the below:
yum install -y ntp service ntpd stop ntpdate pool.ntp.org service ntpd start -
-
Now open Nifi webui and run the remaining steps there:
-
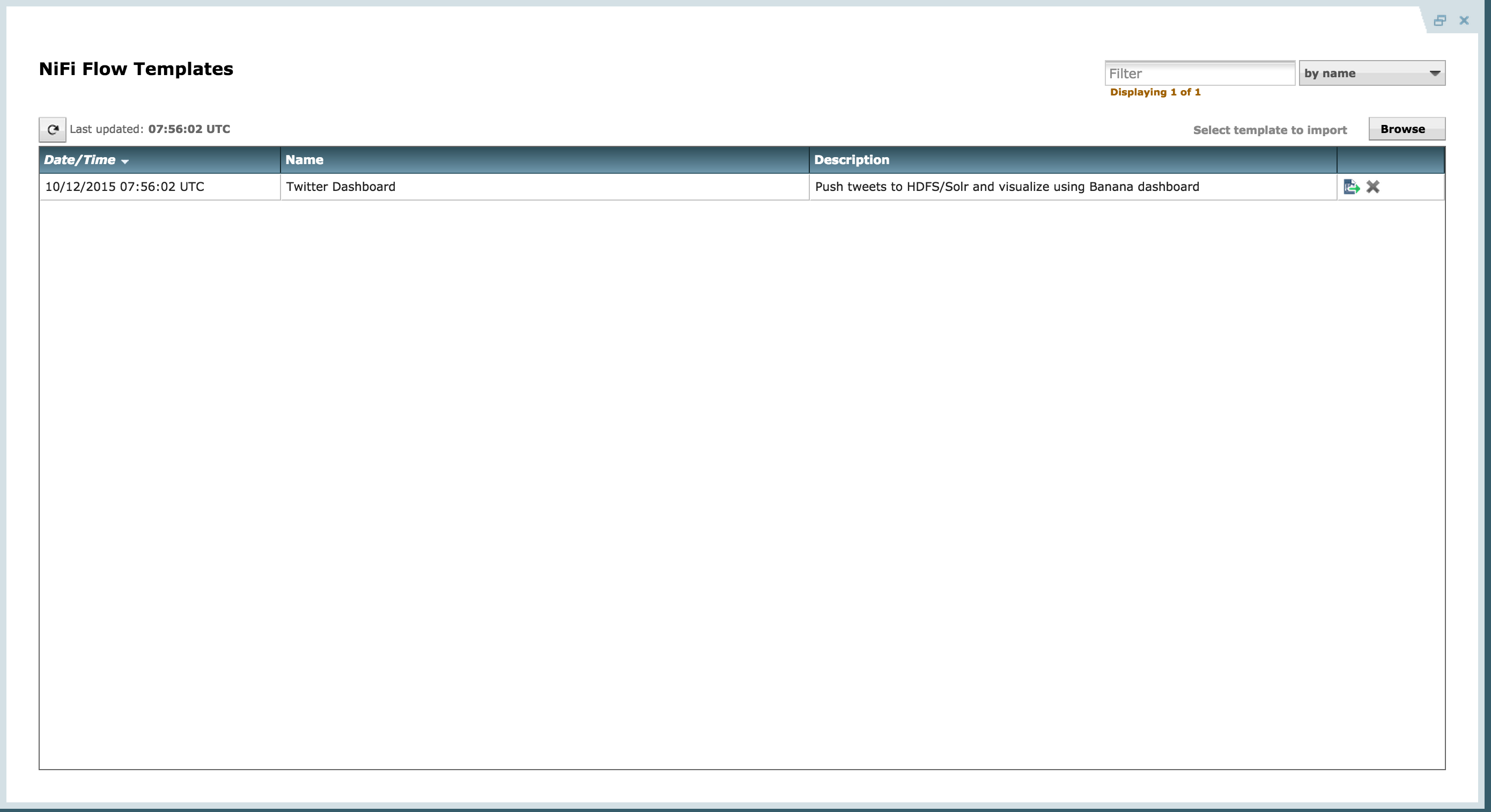
Download prebuilt Twitter_Dashboard.xml template to your laptop from here
-
Import flow template info Nifi:
-
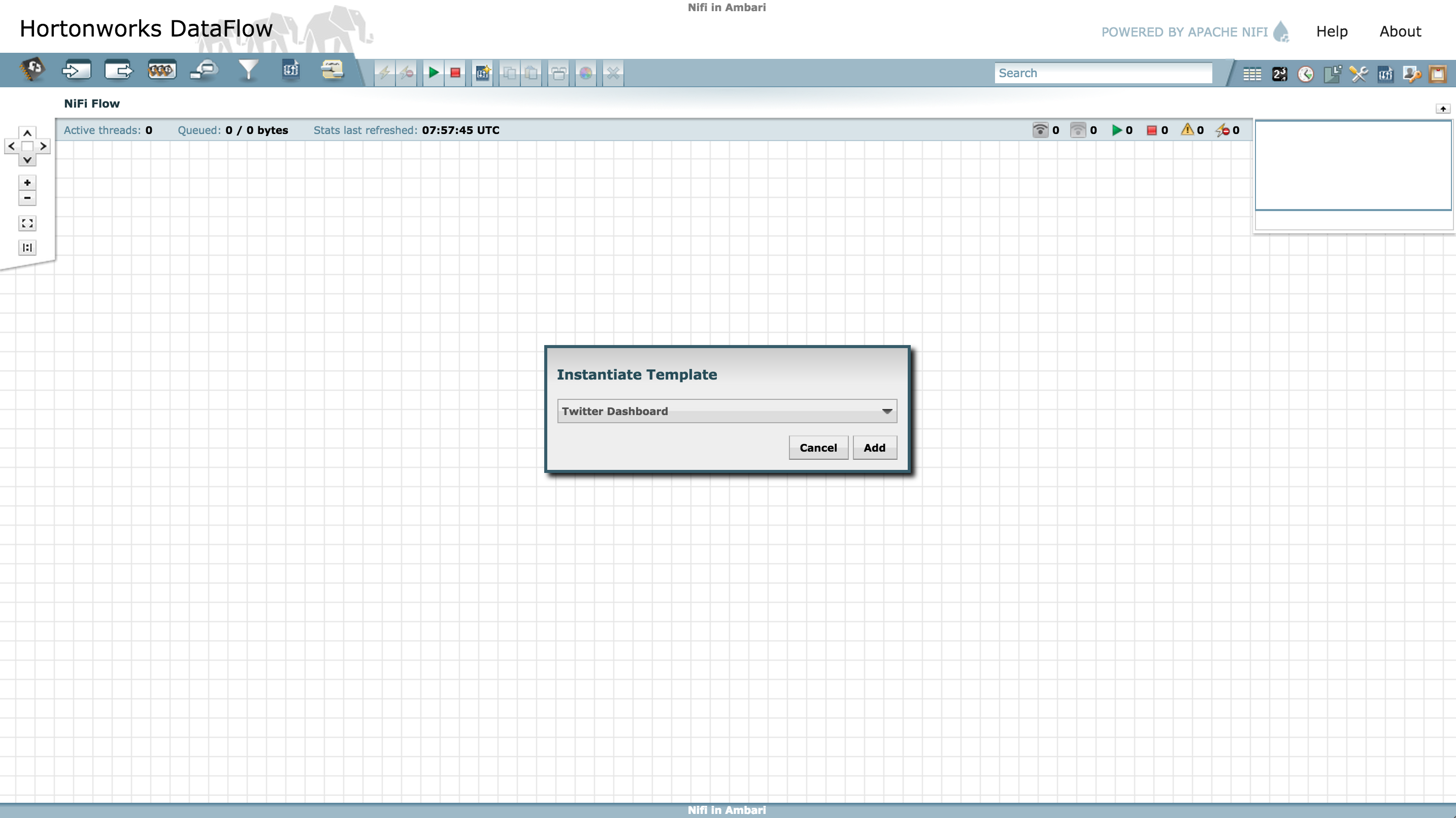
Instantiate the Twitter dashboard template:
-
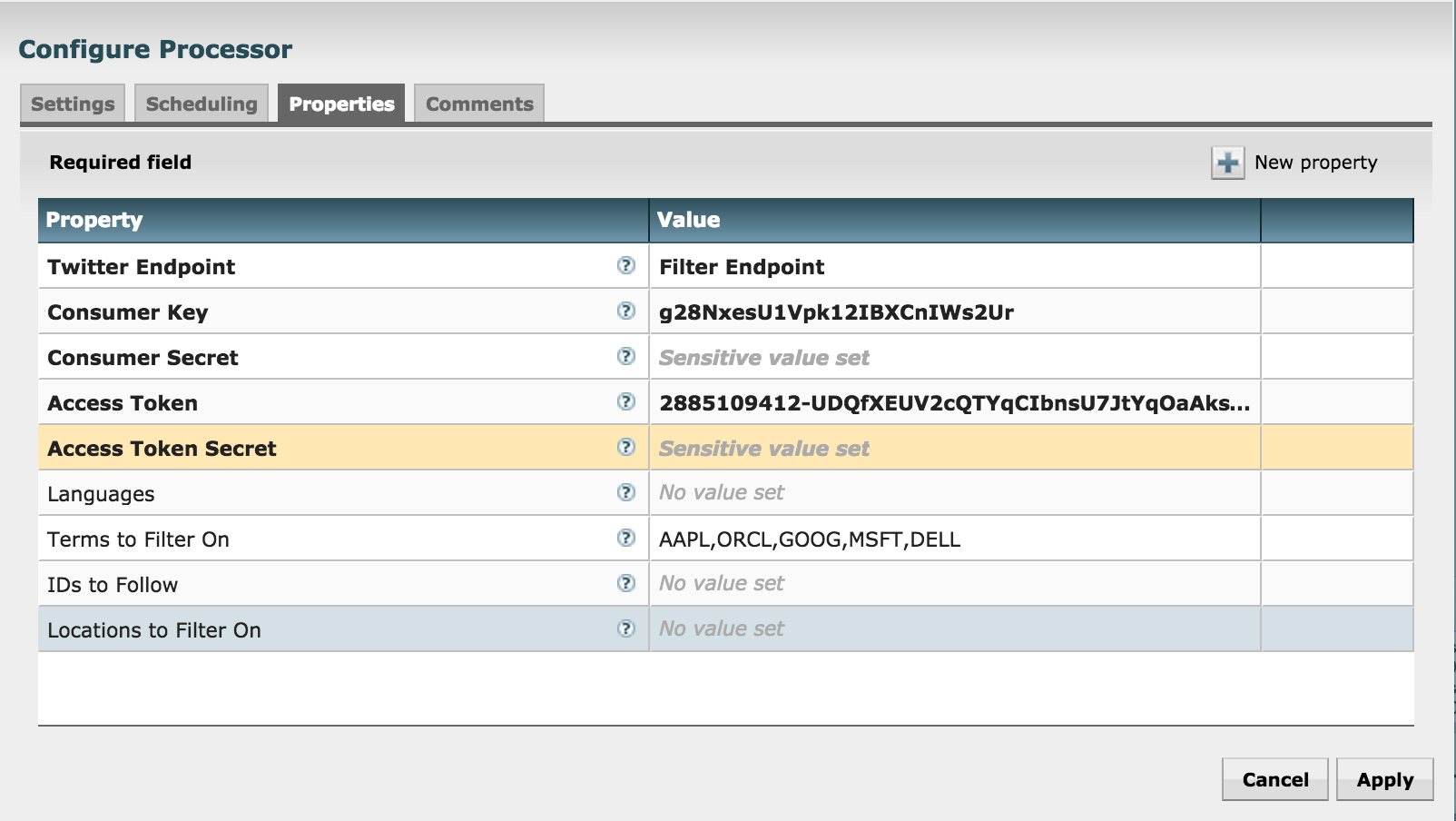
Configure GetTwitter processor
-
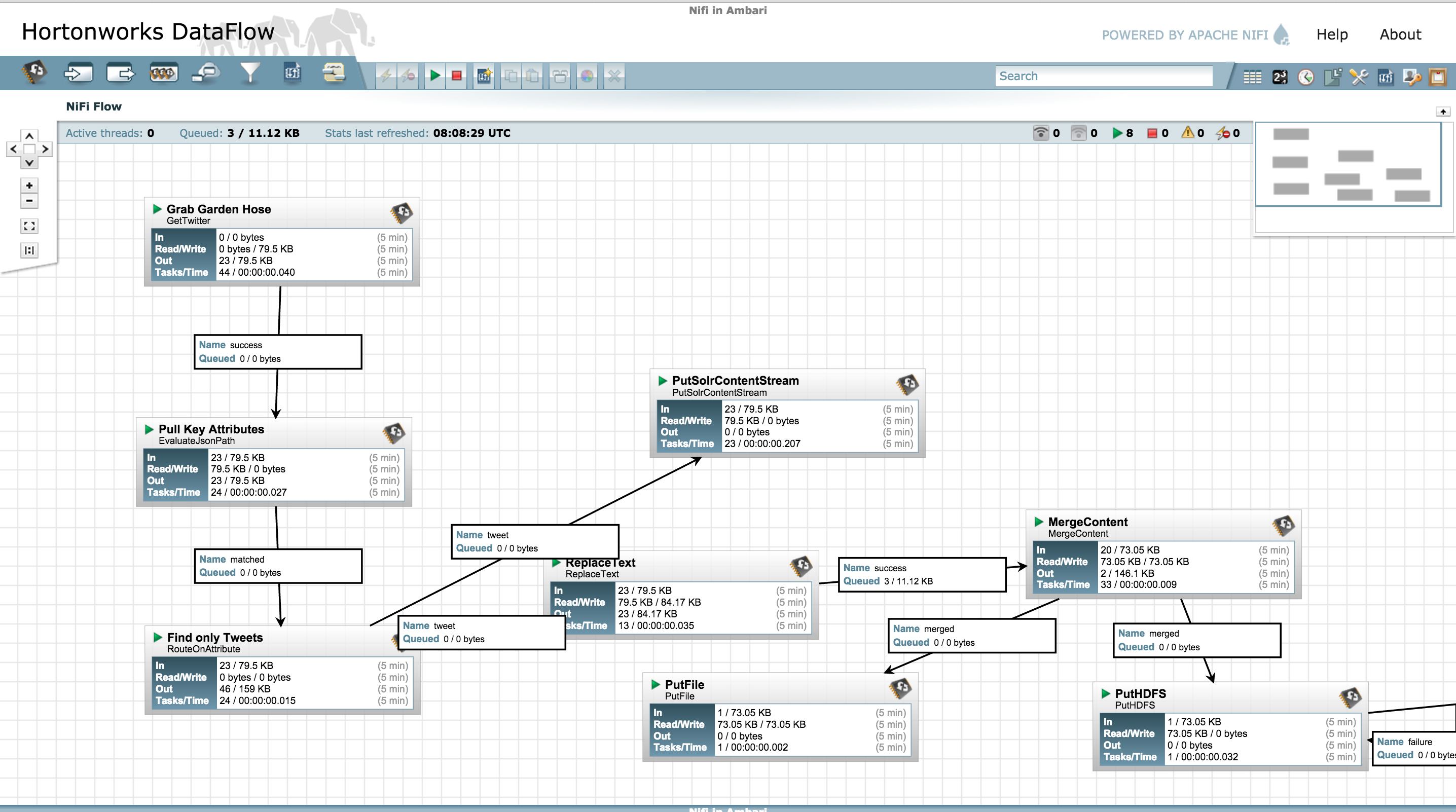
Review the other processors and modify properties as needed:
- EvaluateJsonPath: Pulls out attributes of tweets
- RouteonAttribute: Ensures only tweets with non-empty messages are processed
- PutSolrContentStream: Writes the selected attributes to Solr. In this case, assuming Solr is running in cloud mode with a collection 'tweets'
- ReplaceText: Formats each tweet as pipe (|) delimited line entry e.g. tweet_id|unixtime|humantime|user_handle|message|full_tweet
- MergeContent: Merges tweets into a single file (either 20 tweets or 120s, whichever comes first)
- PutFile: writes tweets to local disk under /tmp/tweets/
- PutHDFS: writes tweets to HDFS under /tmp/tweets_staging
-
If setup correctly, the top left hand of each processor on the canvas will show a red square (indicating the flow is stopped)
-
Click the Start button (green triangle near top of screen) to start the flow
-
Create Hive table to be able to run queries on the tweets
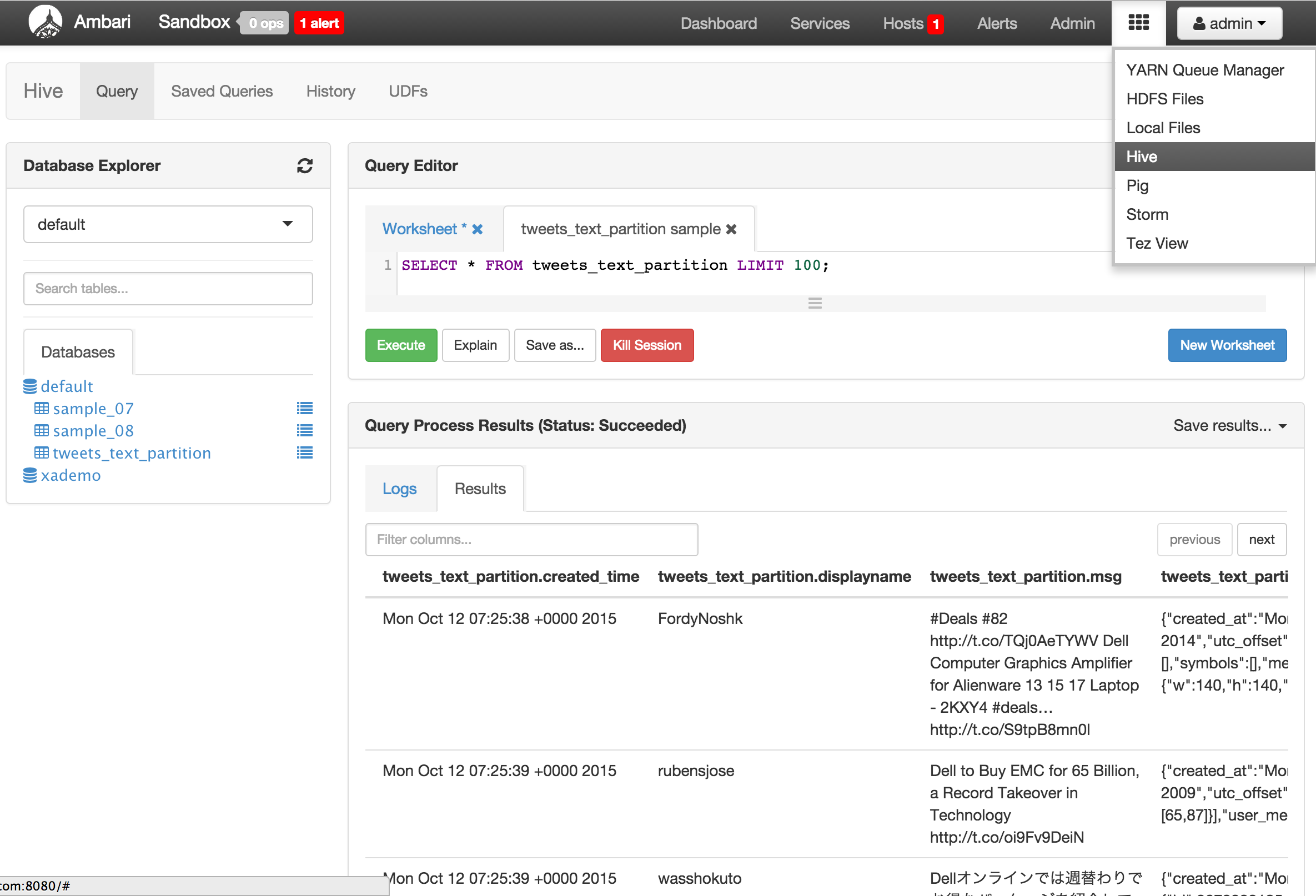
sudo -u hdfs hadoop fs -chmod -R 777 /tmp/tweets_staging hive> create table if not exists tweets_text_partition( tweet_id bigint, created_unixtime bigint, created_time string, displayname string, msg string, fulltext string ) row format delimited fields terminated by "|" location "/tmp/tweets_staging"; -
-
Other Nifi features
-
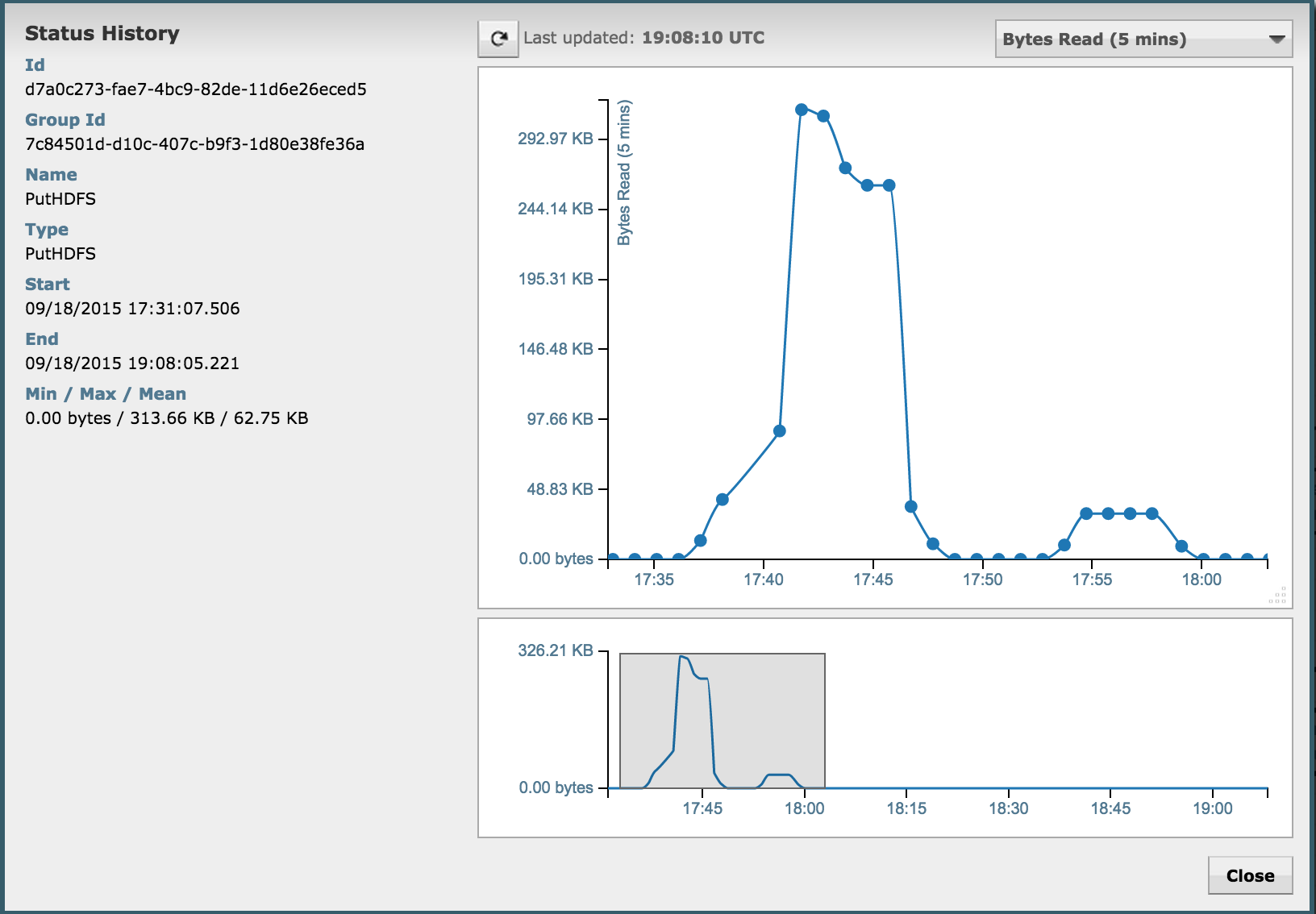
Flow statistics/graphs:
-
Data provenance in Nifi:
- In Nifi home screen, click Provenance icon (5th icon from top right corner) to open Provenance page:

- Click Show lineage icon (2nd icon from right) on any row

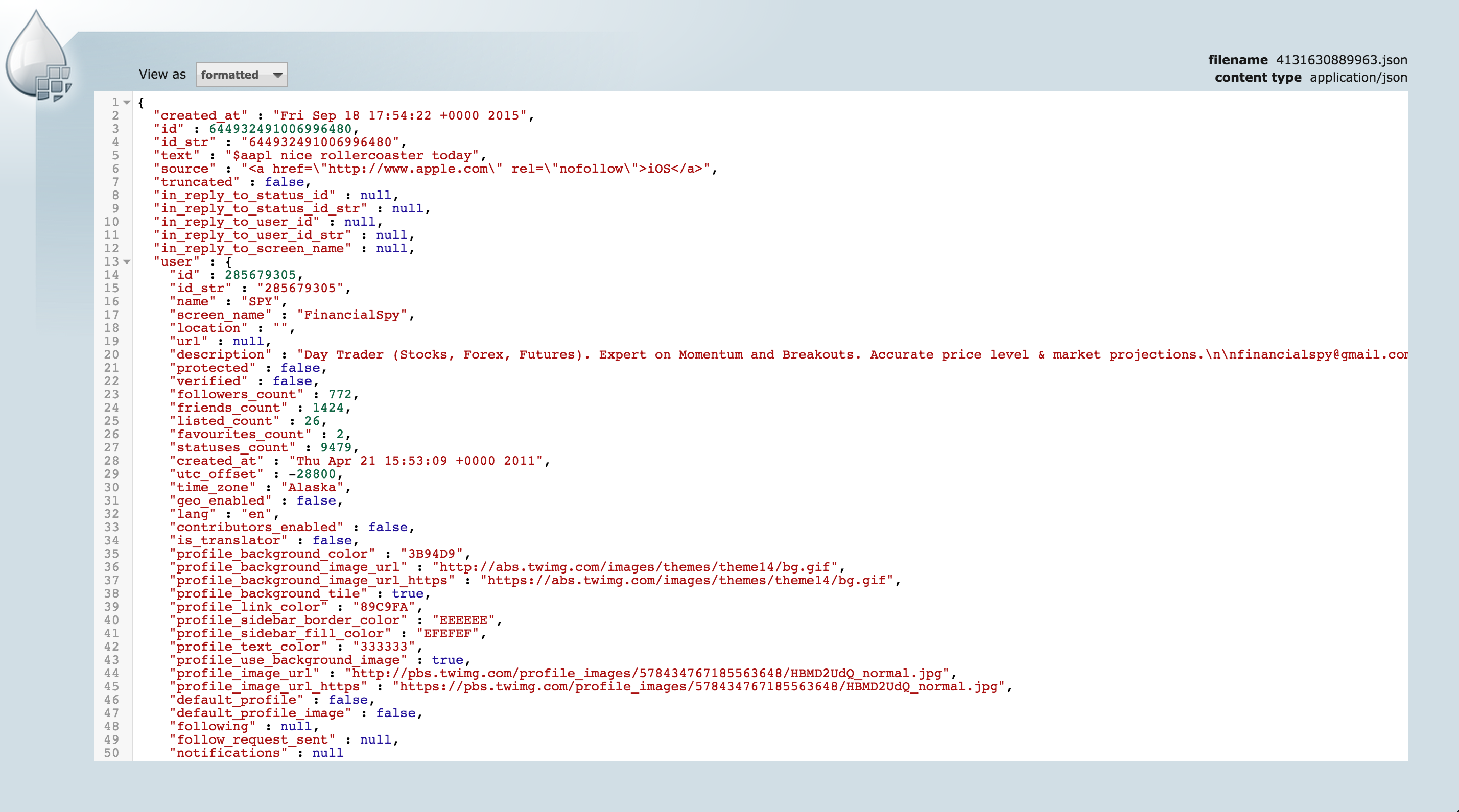
- Right click Send > View details > Content
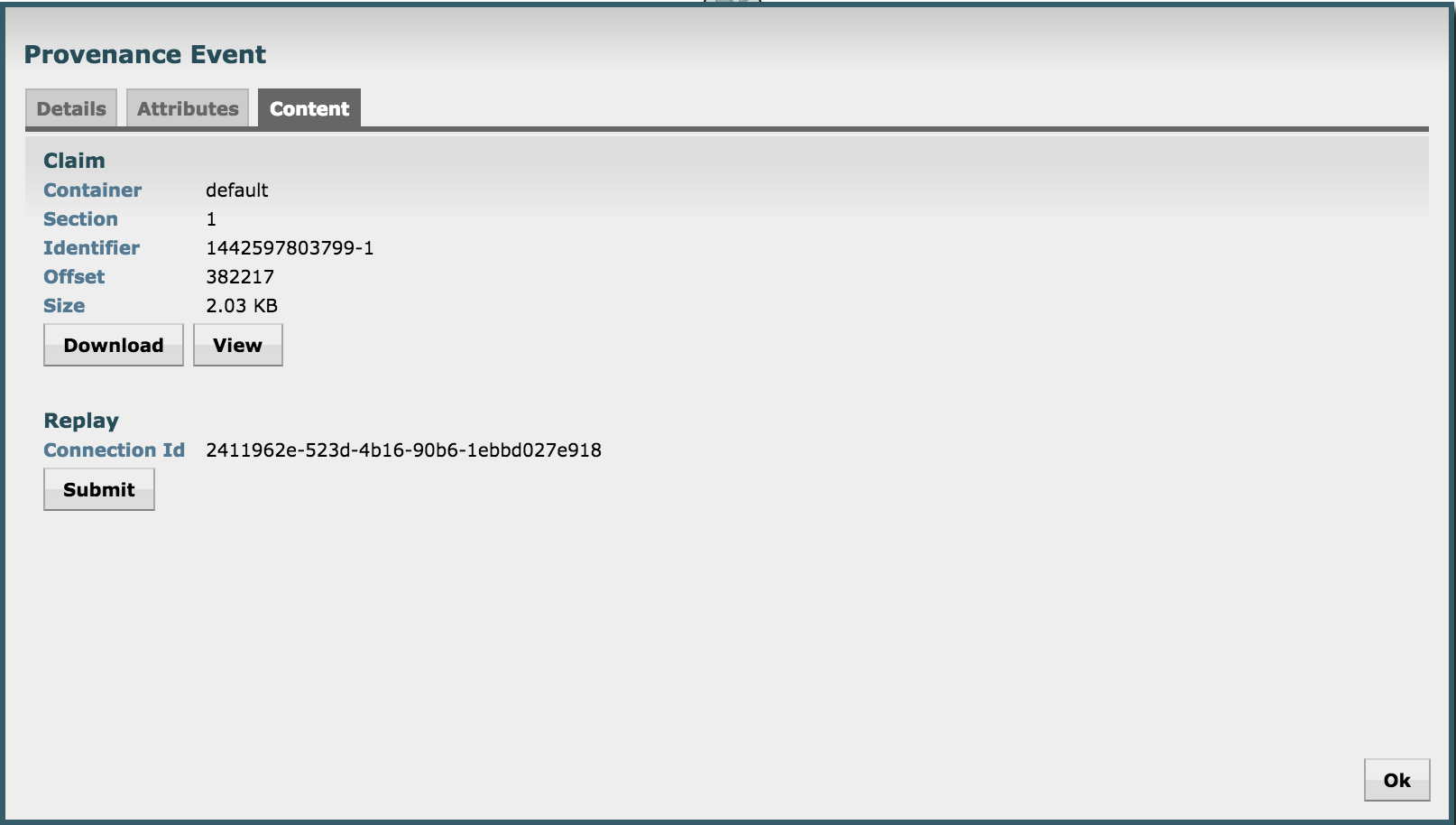
- From here you can view the tweet itself by
- You can also replay the event by
- Replay > Submit
- Close the provenance window using x icon on the inner window
- Notice the event was replayed

- Re-open the the provenance window on the row you you had originally selected

- Notice that by viewing and replaying the tweet, you changed the provenance graph of this event: Send and replay events were added to the lineage graph
- Right click on the Send event near the bottom of the flow and select Details

- Notice that the details of request to view the tweet are captured here (who requested it, at what time etc)
- Exit the Provenance window but clicking the x icon on the outer window
- In Nifi home screen, click Provenance icon (5th icon from top right corner) to open Provenance page:
-
- To remove the Nifi service:
-
Stop the service via Ambari
-
Unregister the service by running below from Ambari node
-
export SERVICE=NIFI export PASSWORD=admin export AMBARI_HOST=localhost
#detect name of cluster
output=curl -u admin:$PASSWORD -i -H 'X-Requested-By: ambari' http://$AMBARI_HOST:8080/api/v1/clusters
CLUSTER=echo $output | sed -n 's/.*"cluster_name" : "\([^\"]*\)".*/\1/p'
#unregister service from ambari curl -u admin:$PASSWORD -i -H 'X-Requested-By: ambari' -X DELETE http://$AMBARI_HOST:8080/api/v1/clusters/$CLUSTER/services/$SERVICE
#if above errors out, run below first to fully stop the service #curl -u admin:$PASSWORD -i -H 'X-Requested-By: ambari' -X PUT -d '{"RequestInfo": {"context" :"Stop $SERVICE via REST"}, "Body": {"ServiceInfo": {"state": "INSTALLED"}}}' http://$AMBARI_HOST:8080/api/v1/clusters/$CLUSTER/services/$SERVICE ```
- Remove artifacts
rm -rf /opt/nifi* rm /tmp/nifi*.zip