PROJECT NOT UNDER ACTIVE MANAGEMENT
This project will no longer be maintained by Intel.
Intel has ceased development and contributions including, but not limited to, maintenance, bug fixes, new releases, or updates, to this project.
Intel no longer accepts patches to this project.
If you have an ongoing need to use this project, are interested in independently developing it, or would like to maintain patches for the open source software community, please create your own fork of this project.
Contact: webadmin@linux.intel.com
In this reference kit, we demonstrate one way in which we can use Artificial Intelligence (AI) to design a Product Recommendation System for an e-commerce business.
Check out more workflow examples in the Developer Catalog.
When a new customer without any previous purchase history visits the e-commerce website for the first time and a business without any user-item purchase history, a product recommendation system will recommend the products based on the textual clustering analysis on the text given in the product description. Once, the customer makes a purchase, the product recommendation system updates and recommends other products based on the purchase history and ratings provided by other users on the website. Considering the journey of a new customer from the time the customer lands on the e-commerce website for the first time to when it makes repeat purchases, this reference kit can help e-commerce businesses to bring targeted products to customers using textual clustering analysis on the text given in the product description.
This reference kit solution extends to demonstrate the advantages of using the Intel® oneAPI AI Analytics Toolkit on the task of building a product recommendation system from product descriptions via cluster analysis. The savings gained from using Intel® technologies can lead an analyst to more efficiently explore and understand customer archetypes, leading to better and more precise targeted solutions.
Learn to use Intel's XPU hardware and Intel optimized software for a clustering algorithm with Scikit-learn, Intel® Extension for Scikit-learn and Intel® Distribution for Python*.
Intel® Extension for Scikit-learn uses the Intel® oneAPI Data Analytics Library (oneDAL) to achieve its acceleration. This library enables all the latest vector instructions, such as the Intel® Advanced Vector Extensions (Intel AVX-512). It also uses cache-friendly data blocking, fast BLAS operations with the Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library (oneMKL), and scalable multithreading with the Intel® oneAPI Threading Building Blocks (oneTBB).
The experiment aimed to build a Product Recommendation System for the customers, in a scenario of a business without any user-item purchase history using an unsupervised learning algorithm. The goal is to train a clustering model (textual clustering analysis given in the product description). The algorithm used for clustering is k-means which allows creating product clustering and provides product recommendations from that cluster. We also focus on the below critical factors:
- Faster model development
- Performance efficient model inference and deployment mechanism.
The customer recommendation system has been built to recommend products based on textual clustering analysis of the text given in the product description. k-means clustering is an unsupervised learning algorithm, which groups the unlabeled dataset into different clusters. k-means aptly fits the Product Recommendation system in this specific case where we don't have prior user history and the only data available is the product description. For the unsupervised clustering model, the product description dataset, which is text-based, has been converted to a sparse matrix using a Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) Vectorizer. In this stage, the feature of text type has been changed to numerical type for further analysis and prediction.
The following Intel® packages are being used for this project:
-
Intel® Distribution for Python* The Intel® Distribution for Python* provides:
- Scalable performance using all available CPU cores on laptops, desktops, and powerful servers
- Support for the latest CPU instructions
- Near-native performance through acceleration of core numerical and machine learning packages with libraries like the Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library (oneMKL) and Intel® oneAPI Data Analytics Library
- Productivity tools for compiling Python code into optimized instructions
- Essential Python bindings for easing integration of Intel® native tools with your Python* project
-
Intel® Extension for Scikit-learn* With Intel® Extension for Scikit-learn you can accelerate your Scikit-learn applications and still have full conformance with all Scikit-learn APIs and algorithms. This is a free software AI accelerator that brings over 10-100X acceleration across a variety of applications. And you do not even need to change the existing code!
The reference kit implementation is a reference solution to the described use case that includes:
- A reference End to End (E2E) architecture to arrive at an AI solution with k-means from Scikit-learn
- An Optimized reference E2E architecture enabled with Intel® Extension for Scikit-learn* available as part of Intel® oneAPI AI toolkit optimizations
There are workflow-specific hardware and software setup requirements depending on how the workflow is run. Bare metal development system and jupyter notebooks have the same system requirements.
| Recommended Hardware |
|---|
| CPU: Intel® 2nd Gen Xeon® Platinum 8280 CPU @ 2.70GHz or higher |
| RAM: 187 GB |
| Recommended Free Disk Space: 20 GB or more |
- Operating system: Ubuntu* 22.04 LTS
The following diagram describes the E2E workflow:
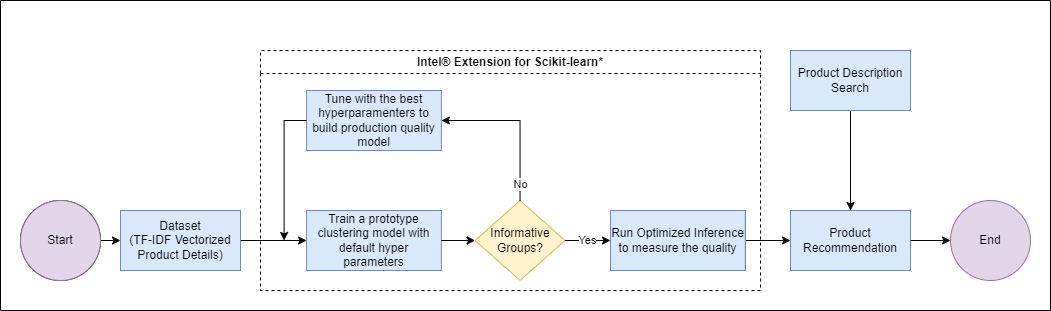
- A list of product recommendations is provided as input.
- A clustering model us trained.
- Hyperparameters are tunned.
- Optimized inference is run to measure quality.
- A product recommendation is delivered as output.
In a realistic pipeline, this training process would follow the above Use Case E2E flow diagram, adding a human in the loop to determine the quality of the clustering solution from each of the saved models/predictions in the saved_models directory, or better, while tuning the model. The quality of a clustering solution is highly dependent on the human analyst and they have the ability to not only tune hyper-parameters, but also modify the features being used to find better solutions.
As mentioned above, this Product recommendation system uses k-means from the Scikit-learn library to train an AI model and generate cluster labels for the passed-in data. This process is captured within the run_benchmarks.py script. This script reads and preprocess the data, and performs training, predictions and hyperparameter tuning analysis on k-means, while also reporting on the execution time for all the mentioned steps (we will use this information later when we are optimizing the implementation for Intel® architecture). Furthermore, this script can also save each of the intermediate models/cluster labels for an in-depth analysis of the quality of fit.
Expected Input-Output:
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
| Product Name | List of product recommendations which is falling under the predicted cluster |
| Example Input | Example Output |
|---|---|
| water | shower,water,faucet,valve,handle,easy,brass,drain,pressure,design |
Hyperparameters tuning is optional and can be enabled (detailed info will be provided later).
The following variables could be adapted by the user and will be used during the E2E workflow.
export WORKSPACE=$PWD/product-recommendationsDefine DATA_DIR and OUTPUT_DIR as follows:
export DATA_DIR=$WORKSPACE/data
export OUTPUT_DIR=$WORKSPACE/outputClone the Product Recommendation repository:
mkdir -p $WORKSPACE && cd $WORKSPACEgit clone https://github.com/oneapi-src/product-recommendations.git $WORKSPACE-
Download the appropriate Miniconda Installer for linux.
wget -q https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
-
In your terminal window, run.
bash Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
-
Delete downloaded file.
rm Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
To learn more about conda installation, see the Conda Linux installation instructions.
The $WORKSPACE/env/intel_env.yml file contains all dependencies to create the intel environment necessary for running the workflow.
Execute next command to create and activate the product_recommendation_intel conda environment.
conda install -n base conda-libmamba-solver
conda config --set solver libmamba
conda env create -f env/intel_env.yml -y
conda activate product_recommendation_intelEnvironment setup is required only once. This step does not cleanup the existing environment with the same name hence we need to make sure there is no conda environment with the same name.
During this setup, product_recommendation_intel conda environment will be created with the dependencies listed in the YAML configuration.
| YAML file | Environment Name | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
env/intel_env.yml |
product_recommendation_intel |
Python=3.10.x with Intel® Extension for Scikit-learn* |
A Kaggle* account is necessary to use the Kaggle* CLI. Instructions can be found at Kaggle* api website.
Within this process, an API Token File will be created and as consequence, a json file named kaggle.json will be downloaded. That json file should be stored in a .kaggle folder that should be created by the user (usually in the home folder).
If you are behind a proxy, the kaggle.json file can be modified to add it. An example is shown as follows:
{"username":"your_user","key":"your_key","proxy":"your_proxy"}...where your_user and your_key were previously generated by Kaggle*. You should replace your_proxy with you proxy ip address.
To setup the data for benchmarking under these requirements, run the following set of commands:
Please see this data set's applicable license for terms and conditions. Intel Corporation does not own the rights to this data set and does not confer any rights to it.
mkdir -p $DATA_DIR
cd $DATA_DIR
kaggle datasets download -d PromptCloudHQ/flipkart-products
unzip flipkart-products.zip -d flipkart-products-ecommerceThe train-test split is 70:30.
You can execute the references pipelines using the following environments:
Follow these instructions to set up and run this workflow on your own development system.
With recommended hardware, it should take about 5 minutes from downloading data to get the final recommendations.
Our examples use the
condapackage and environment on your local computer. If you don't already havecondainstalled, go to Set up conda or see the Conda Linux installation instructions.
Create a folder called saved_models inside OUTPUT_DIR to save the trained models before the training script is run:
mkdir -p $OUTPUT_DIR/saved_modelsThe script run_benchmarks.py takes the following arguments:
usage: run_benchmarks.py [-h][-d DATASET][-l LOGFILE][-t TUNNING][-mp MODELPATH]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-d DATASETSIZE, --dataset DATASETSIZE
Size of the dataset
-l LOGFILE, --logfile LOGFILE
Log file to output benchmarking results to
-t TUNNING, --tunning TUNING
Hyper parameter tuning (0/1)
-mp MODELPATH --modelpath MODELPATH
Model path for inferenceAs an example of using this, we can run the following command to train and save k-means models.
python $WORKSPACE/src/run_benchmarks.py -d 1000We are training with 1k data size here. Similarly, one can try with 5k, 10k, 15k & 20k.
Output Should be similar to this:
Intel(R) Extension for Scikit-learn* enabled (https://github.com/intel/scikit-learn-intelex)
DEBUG:root:(100000, 2)
DEBUG:root:(100000, 10)
INFO:root:Data preparation time:9.813132762908936
Top terms per cluster:
Cluster 0:
cabinet
vanity
finish
storage
design
easy
faucet
hardware
wood
sink
INFO:root:Kmeans_training_time_without_Hyperparametertunning:0.16348862648010254
Saving model..........
Running Cluster Analysis/Predictions: To run the batch and real time inference run the following command:
python $WORKSPACE/src/run_benchmarks.py -d 1000 -mp $OUTPUT_DIR/saved_models/prod_rec.joblibHere we have tried inference with the trained model for batch size of 1k. Similarly one can try with other sizes like 1.5k & 2k.
Inference output:
Recommendations for : cutting tool
Cluster 0:
cm
diwan
cotton
inch
cover
sheet
details
diamond
features
40
INFO:root:time taken for realtime recommendation:0.00015091896057128906
See more information at Expected Output
Hyperparameter tuning: Loop Based Hyperparameter Tuning is used to apply fit method to train and optimize by applying different parameter values in loops to get the best Sihoutte score and thereby a better performing model.
Parameters Considered:
| Parameter | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
n_clusters |
Number of clusters | 5, 10, 15, 20 |
max_iter |
Max iteration value | 400, 450, 500, 550 |
To run Hyperparameter tuning with Intel® Distribution for Python* and Intel® technologies, we would run (after creating the appropriate environment as above):
python $WORKSPACE/src/run_benchmarks.py -d 1000 -t 1We are training with 1k data size here. Similarly, one can try with 5k, 10k, 15k & 20k also.
Follow these steps to restore your $WORKSPACE directory to an initial step. Please note that all downloaded dataset files, conda environment, and logs created by workflow will be deleted. Before executing next steps back up your important files.
rm -rf $OUTPUT_DIR
conda deactivate
conda remove --name product_recommendation_intel --all -yIf you want to remove all the repository, execute the following command:
rm -rf $WORKSPACEYou can directly access the Jupyter Notebook shared in this repo here.
- Follow the instructions described on Get Started to set required environment variables.
To launch Jupyter Notebook, execute the next commands:
-
Execute Set Up Conda and Set Up Environment steps.
-
Activate Intel environment.
conda activate product_recommendation_intel
-
Install the IPython Kernel Package.
conda install -c conda-forge ipykernel -y
-
Create a virtual environment and Install Jupyter Notebook.
conda create -n jupyter_server -c intel nb_conda_kernels notebook -y
-
Activate Jupyter Server environment.
conda activate jupyter_server
-
Change to working directory.
cd $WORKSPACE
-
Execute Jupyter command.
jupyter notebook
Above command prints some information about the notebook server in your terminal, including the URL of the web application (by default, http://localhost:8888), for example:
To access the notebook, open this file in a browser:
file:///path/to/jupyter/notebook/server/open.html
Or copy and paste one of these URLs:
http://localhost:8888/?token=*****************************************
or
http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=*****************************************
Copy and paste one of the URLs into a web browser to open the Jupyter Notebook Dashboard.
Once in Jupyter, click on product_recommendation.ipynb to get an interactive demo of the workflow.
Clean Bare Metal and Jupyter environments executing the following commands:
conda deactivate
conda remove --name jupyter_server --all -y
conda remove --name product_recommendation_intel --all -y
rm -rf $OUTPUT_DIRIf you want to remove all the repository, execute the following command:
rm -rf $WORKSPACEA successful execution of python $WORKSPACE/src/run_benchmarks.py -d 1000 should return similar results as shown below:
import the intel sklearnex
DEBUG:root:Loading intel libraries..
Intel(R) Extension for Scikit-learn* enabled (https://github.com/intel/scikit-learn-intelex)
20000
1000
DEBUG:root:(1000, 15)
DEBUG:root:(419, 15)
DEBUG:root:(419, 10)
INFO:root:Data preparation time:0.3751637935638428
Top terms per cluster:
Cluster 0:
jewellery
nishtaa
zirconia
cubic
ring
silver
kiara
rhodium
sterling
clutch
Cluster 1:
cm
diwan
sheet
cover
inch
cotton
40
cushion
embroidered
length
Cluster 2:
cm
details
cotton
diwan
inch
women
fabric
cover
printed
material
Cluster 3:
mug
ceramic
akup
mugs
coffee
mm
300
ml
quality
safe
Cluster 4:
shorts
gym
cycling
solid
details
swim
mynte
women
fabric
dry
Cluster 5:
kurta
details
straight
women
neck
sleeve
printed
fabric
round
pattern
Cluster 6:
ring
diamond
gold
18
free
cash
shipping
com
genuine
flipkart
Cluster 7:
kiara
rhodium
zirconia
cubic
silver
sterling
jewellery
ring
guarantee
cash
Cluster 8:
pieces
wearyourshine
expert
expressive
pc
newest
keepsakes
curation
jeweller
today
Cluster 9:
clutch
synthetic
dressberry
gold
nishtaa
black
code
chain
strap
secured
Cluster 10:
diamond
ring
like
solitaire
solitana
connoisseur
marvel
flaunt
piece
designer
Cluster 11:
usb
warranty
cable
charger
furst
battery
adapter
covered
white
service
INFO:root:Kmeans_training_time_without_Hyperparametertunning:0.07413744926452637
Saving model..........
A successful execution of python $WORKSPACE/src/run_benchmarks.py -d 1000 -mp $OUTPUT_DIR/saved_models/prod_rec.joblib should return similar results as shown below:
import the intel sklearnex
DEBUG:root:Loading intel libraries..
Intel(R) Extension for Scikit-learn* enabled (https://github.com/intel/scikit-learn-intelex)
20000
1000
DEBUG:root:(1000, 15)
DEBUG:root:(419, 15)
DEBUG:root:(419, 10)
INFO:root:Data preparation time:0.3825080394744873
warm up in progress........
Time Analysis for Batch Inference
dataset size (419, 10)
INFO:root:Time of Batch time recomendation:0.0003077983856201172
INFO:root:Time of Batch time recomendation:0.0001919269561767578
INFO:root:Time of Batch time recomendation:0.00016689300537109375
INFO:root:Time of Batch time recomendation:0.0001590251922607422
INFO:root:Time of Batch time recomendation:0.00015783309936523438
INFO:root:Time of Batch time recomendation:0.00018978118896484375
INFO:root:Time of Batch time recomendation:0.0001747608184814453
INFO:root:Time of Batch time recomendation:0.0001678466796875
INFO:root:Time of Batch time recomendation:0.0001628398895263672
INFO:root:Time of Batch time recomendation:0.00015783309936523438
INFO:root:Average Time of Batch time recomendation:0.00018365383148193358
INFO:root:time taken for realtime recommendation:0.00016880035400390625
Recommendations for : cutting tool
Cluster 2:
cm
details
cotton
diwan
inch
women
cover
fabric
printed
sheet
INFO:root:time taken for realtime recommendation:0.0001862049102783203
Recommendations for : spray paint
Cluster 2:
cm
details
cotton
diwan
inch
women
cover
fabric
printed
sheet
INFO:root:time taken for realtime recommendation:0.0001609325408935547
Recommendations for : steel drill
Cluster 2:
cm
details
cotton
diwan
inch
women
cover
fabric
printed
sheet
INFO:root:time taken for realtime recommendation:0.00016260147094726562
Recommendations for : water
Cluster 2:
cm
details
cotton
diwan
inch
women
cover
fabric
printed
sheet
INFO:root:time taken for realtime recommendation:0.0001647472381591797
Recommendations for : powder
Cluster 2:
cm
details
cotton
diwan
inch
women
cover
fabric
printed
sheet
INFO:root:Average Time of Real time recomendation:0.0001686573028564453
A successful execution of python $WORKSPACE/src/run_benchmarks.py -d 1000 -t 1 should return similar results as shown below:
import the intel sklearnex
DEBUG:root:Loading intel libraries..
Intel(R) Extension for Scikit-learn* enabled (https://github.com/intel/scikit-learn-intelex)
20000
1000
DEBUG:root:(1000, 15)
DEBUG:root:(419, 15)
DEBUG:root:(419, 10)
INFO:root:Data preparation time:0.3815338611602783
No.cluster 5
Max Iter 400
silhoutte score is : 0.3822014176971847
Saving model!!! Best score is ---> 0.3822014176971847
No.cluster 5
Max Iter 450
silhoutte score is : 0.3822014176971847
No.cluster 5
Max Iter 500
silhoutte score is : 0.3822014176971847
No.cluster 5
Max Iter 550
silhoutte score is : 0.3822014176971847
No.cluster 10
Max Iter 400
silhoutte score is : 0.5637014192791263
Saving model!!! Best score is ---> 0.5637014192791263
No.cluster 10
Max Iter 450
silhoutte score is : 0.5637014192791263
No.cluster 10
Max Iter 500
silhoutte score is : 0.5637014192791263
No.cluster 10
Max Iter 550
silhoutte score is : 0.5637014192791263
No.cluster 15
Max Iter 400
silhoutte score is : 0.5072029961921509
No.cluster 15
Max Iter 450
silhoutte score is : 0.5072029961921509
No.cluster 15
Max Iter 500
silhoutte score is : 0.5072029961921509
No.cluster 15
Max Iter 550
silhoutte score is : 0.5072029961921509
No.cluster 20
Max Iter 400
silhoutte score is : 0.5356860601413224
No.cluster 20
Max Iter 450
silhoutte score is : 0.5356860601413224
No.cluster 20
Max Iter 500
silhoutte score is : 0.5356860601413224
No.cluster 20
Max Iter 550
silhoutte score is : 0.5356860601413224
INFO:root:Total fit and predict time taken during Hyperparameter Tuning in sec: 0.736302375793457
Hyperparameter Tuning has been executed successfully!!
Best parameters=====> n_clusters: 10 max_iter : 400
INFO:root:Kmeans_training_time_with the best params:0.0380251407623291
Congratulations! You have successfully completed this workflow.
As clustering analysis is an exploratory task, an analyst will often run on different dataset of different sizes, resulting in different insights that they may use for decisions all from the same raw dataset.
To build a Product Recommendation System, Data Scientist will need to train models for substantial datasets and run inference more frequently. The ability to accelerate training will allow them to train more frequently and achieve better accuracy. Besides training, faster speed in inference will allow them to provide product recommendations in real-time scenarios as well as more frequently. This reference kit implementation provides performance-optimized guide around Product Recommendation System use cases that can be easily scaled across similar use cases.
For more information about or to read about other relevant workflow examples, see these guides and software resources:
- Intel® AI Analytics Toolkit (AI Kit)
- Intel® Distribution for Python*
- Intel® Extension for Scikit-learn*
If you have questions or issues about this use case, want help with troubleshooting, want to report a bug or submit enhancement requests, please submit a GitHub issue.
Please see this data set's applicable license for terms and conditions. Intel®Corporation does not own the rights to this data set and does not confer any rights to it.
*Other names and brands that may be claimed as the property of others. Trademarks.
To the extent that any public or non-Intel datasets or models are referenced by or accessed using tools or code on this site those datasets or models are provided by the third party indicated as the content source. Intel does not create the content and does not warrant its accuracy or quality. By accessing the public content, or using materials trained on or with such content, you agree to the terms associated with that content and that your use complies with the applicable license.
Intel expressly disclaims the accuracy, adequacy, or completeness of any such public content, and is not liable for any errors, omissions, or defects in the content, or for any reliance on the content. Intel is not liable for any liability or damages relating to your use of public content.
Performance varies by use, configuration, and other factors. Learn more on the Performance Index site.
© Intel Corporation. Intel, the Intel logo, and other Intel marks are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries. Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.