A gamified chat application where users interact with a chatbot. Users send messages with dynamic pricing, contribute to a centralized pot, and have a randomized chance to win the pot. This project is designed with a modular architecture, employing FastAPI for the backend, Streamlit for the frontend, and a relational database for persistence.
- Authentication: Users can register and log in using JWT-based authentication.
- Dynamic Pricing: The cost of sending messages increases incrementally based on the user's message count.
- Pot System: Contributions are added to a centralized pot with a randomized chance of winning.
- Streamlit UI: A user-friendly frontend for interacting with the system.
- Database Schema: Relational database design with tables for users and the pot.
- Gamified interactions for entertainment or education.
- Demonstrates a modular approach to designing interactive web applications.
- Provides a template for building backend-driven applications with dynamic logic.
The root directory contains essential configuration files, documentation, and scripts for running and deploying the project.
.
├── Procfile # Specifies commands for deployment platforms (e.g., Heroku).
├── README.md # Project documentation with an overview, usage, and architecture details.
├── alembic.ini # Alembic configuration file for managing database migrations.
├── docker-compose.yaml # Docker Compose file for containerizing the application.
├── requirements.txt # Python dependencies for the project.
├── main.py # Entry point for the FastAPI backend.
The app/ directory contains the core backend logic for the application.
├── app
│ ├── __init__.py # Makes `app` a package.
│ ├── config.py # Configuration settings (e.g., database URL, secret keys).
│ ├── core # Core utilities and helper modules.
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── auth.py # Authentication logic, including password hashing and JWT handling.
│ ├── db # Database-related code.
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── crud.py # CRUD operations for database interactions.
│ │ ├── database.py # SQLAlchemy engine and session management.
│ │ └── models.py # SQLAlchemy models defining database schema.
│ ├── routers # API route handlers.
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── currency.py # Endpoints for managing user currency.
│ │ ├── messaging.py # Endpoints for message sending with dynamic pricing.
│ │ ├── pot.py # Endpoints for pot management (contributions and resets).
│ │ └── user.py # Endpoints for user registration, login, and profile.
│ └── schemas # Pydantic schemas for request and response validation.
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── user.py # User-related schemas (e.g., login, registration).
The frontend/ directory contains the Streamlit-based user interface for interacting with the application.
├── frontend
│ └── app.py # Streamlit UI for user registration, login, balance, pot, and messaging.
The tests/ folder contains unit and integration tests for various application components.
├── tests
│ ├── __init__.py # Makes `tests` a package.
│ ├── test_currency_endpoints.py # Tests for currency management endpoints.
│ ├── test_messaging_endpoints.py # Tests for messaging service endpoints.
│ ├── test_pot_endpoints.py # Tests for pot management endpoints.
│ ├── test_user_endpoints.py # Tests for user registration and login endpoints.
- Procfile: Deployment instructions, often used for platforms like Heroku.
- docker-compose.yaml: Defines services, networks, and volumes for running the application in containers.
- FastAPI: High-performance Python framework for building APIs.
- SQLAlchemy: ORM for database interactions.
- Alembic: Database migration tool.
- Cockroach DB: Relational database for data persistence.
- Streamlit: Simple and interactive UI framework for Python.
- PlantUML: For generating architecture diagrams.
- Pytest: For testing API endpoints and database operations.
- JWT: For authentication and authorization.
- Railway: For deploying the application to the cloud.
- Vercel: For hosting the Streamlit frontend.
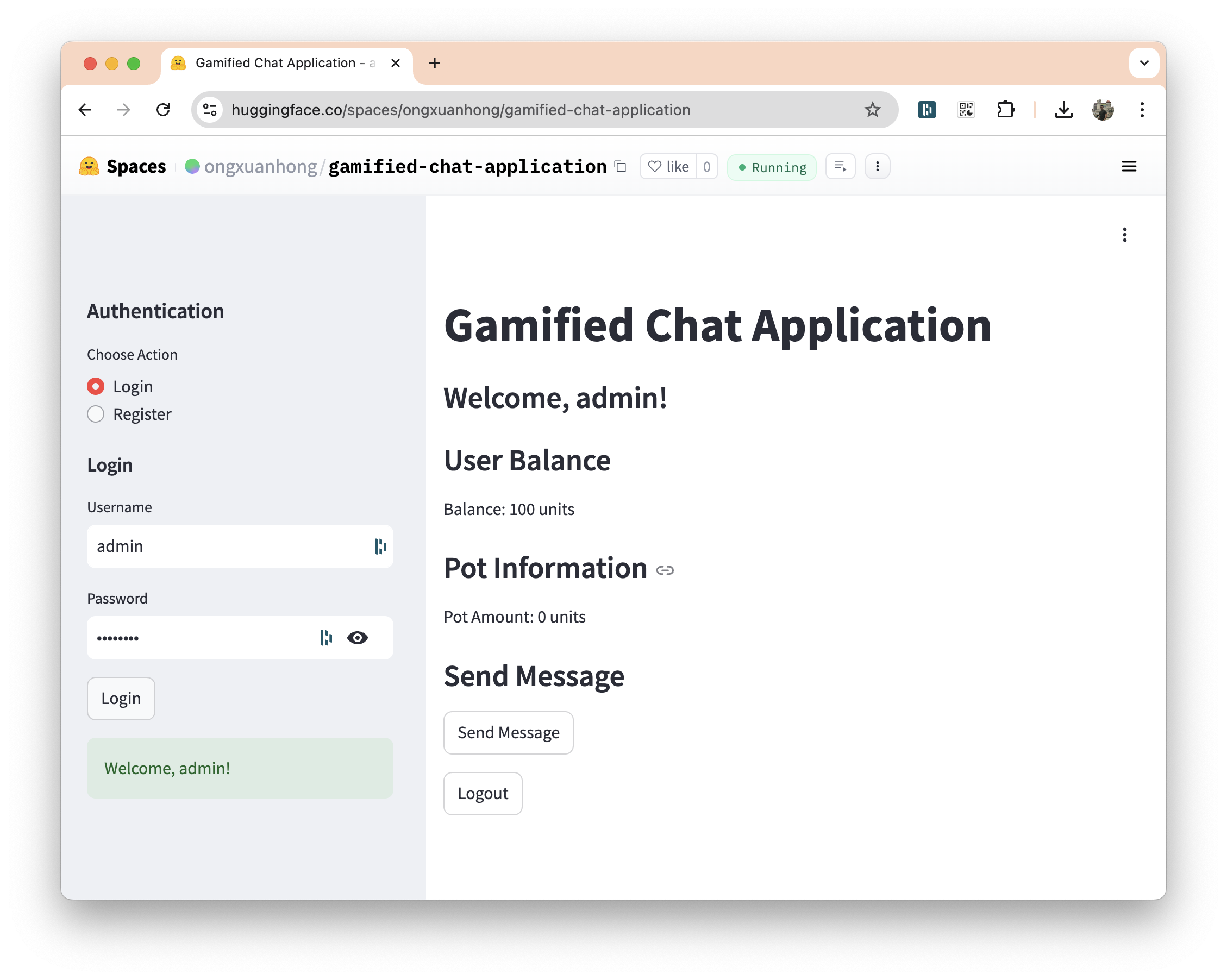
- Register or Login: Navigate to the sidebar and choose between registering a new account or logging in with an existing one.
- View Balance and Pot: Once logged in, view your current balance and the amount in the centralized pot.
- Send a Message: Click "Send Message" to contribute to the pot and see if you win.
- Logout: Click "Logout" to end your session.
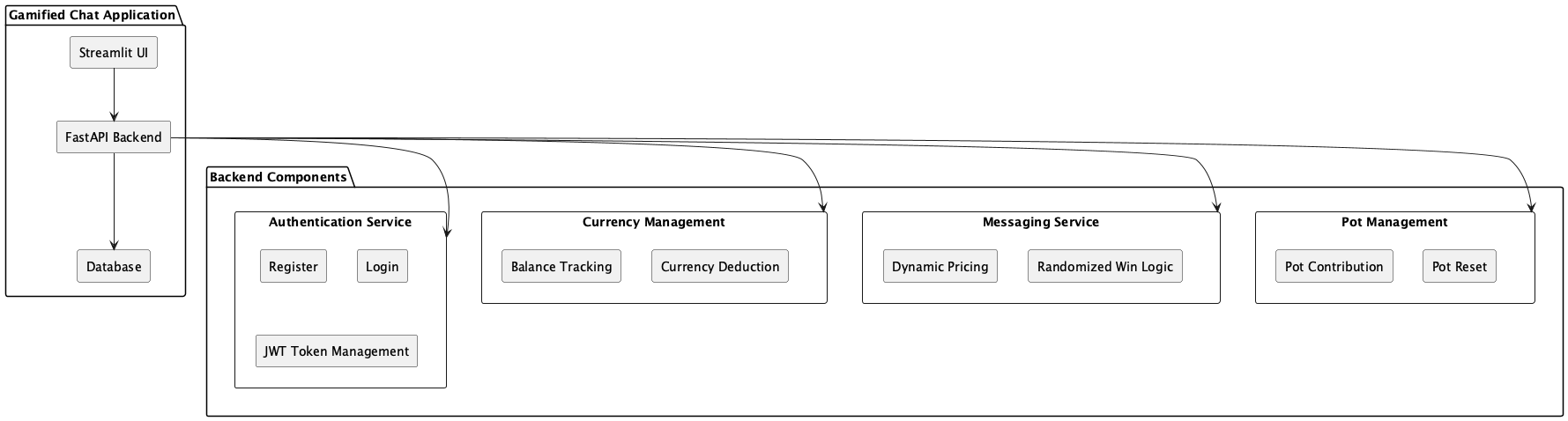
The component diagram showcases the overall structure of the gamified chat application. It highlights the main components:
- Streamlit UI: The frontend user interface where users interact with the system.
- FastAPI Backend: The backend responsible for handling API requests, business logic, and database interactions.
- Database: The persistent storage for user data and pot information.
- Authentication Service for registration and login.
- Currency Management for tracking user balances and deducting currency.
- Messaging Service for dynamic pricing and randomized win logic.
- Pot Management for handling contributions and resets.
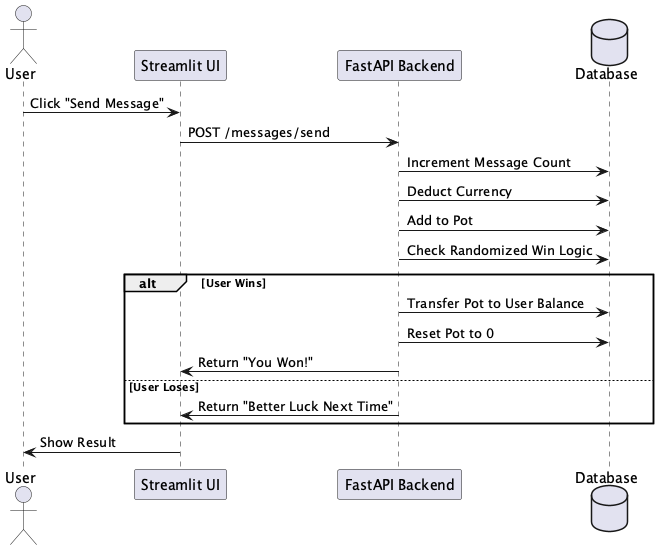
The sequence diagram describes the flow of events when a user sends a message. It visualizes interactions between the user, the Streamlit UI, the FastAPI backend, and the database.
- The user initiates the action by clicking "Send Message."
- The backend processes the message, updates the database, and determines whether the user wins the pot.
- The result is returned to the user via the UI.
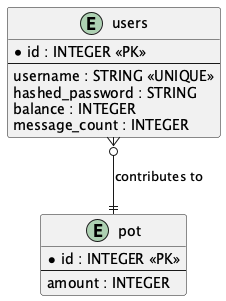
The ERD provides a detailed view of the database schema. It defines the relationships between tables:
- Users Table: Stores user information, such as
id,username,balance, andmessage_count. - Pot Table: Tracks the current amount in the centralized pot.
- The
userstable is related to thepottable via contributions. - Supports operations like balance deduction, pot contributions, and pot resets.
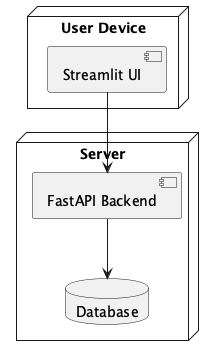
The deployment diagram illustrates the setup of the application in a real-world environment. It shows how the frontend, backend, and database components are deployed and interact.
- The Streamlit UI runs on the user’s device and communicates with the backend.
- The FastAPI Backend is hosted on a server, handling all API requests and connecting to the database.
- The Database is a centralized data store accessible by the backend.
pip install -r requirements.txt
uvicorn uvicorn app.main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000Deployed Railway: https://web-production-65db.up.railway.app/docs Deployed Huggingface: https://huggingface.co/spaces/ongxuanhong/gamified-chat-application
pytest tests/alembic init alembic
alembic init migrations
alembic revision --autogenerate -m "Initial migration"
alembic upgrade head- Install PlantUML locally or use an online PlantUML renderer.
- Save each
.pumlfile provided in thediagramsdirectory. - Generate the diagrams:
- Command-line:
java -jar plantuml-1.2024.8.jar filename.puml
- Online Tool: Copy and paste the code into PlantUML Online Editor.
- Command-line: