Analysis of Video Feature Learning in Two-Stream CNNs on the Example of Zebrafish Swim Bout Classification
This source code accompanies the paper "Analysis of Video Feature Learning in Two-Stream CNNs on the Example of Zebrafish Swim Bout Classification" (Breier and Onken, 2020). The work demonstrates the utility of a recent AI explainability technique by visualizing the learned features of a CNN trained on binary classification of zebrafish movements. Beside this readme, the Appendix of the paper gives important further explanations.
The files in the folder "cnn" were used for training our CNNs:
- The main function for training is in file
main.py. experiment_builder.pyperforms the actual forward and backward passes.data_providers.pyimplements Pytorch's Dataset module.- Our two-stream architecture is implemented in
model_architectures.py. - Arguments are read by
arg_extractor.py.
The files in the folder "svm" are derived from the study by Semmelhack et al. (2014) (source code here):
- The main function for training our SVM is in file
main.py. - It depends on
svm.py,tailmetrics.py,framemetrics.py, andpeakdetector.py. - We put the final output from the console into
output.txt. - The points on the tail were fitted with
tailfit.py.
The folder "scripts" contains all other important python scripts, including analyses with iNNvestigate, heatmap generation, and creation of other figures:
preprocess.pywas used to compute the npz-file of 1,214 centered, cropped and normalized videos from the original raw avi-files.shuffle.pyto randomly shuffle the npz-file.augment.pyto receive hdf5-files in a highly parallelized way, applying flipping, cropping, and subsampling.create_pretrained_file.pyto extract PyTorch weights from the matlab-file imagenet-vgg-m-2048.matanalyze.pyto load the trained PyTorch-weights and analyze all samples with Deep Taylor Decomposition, or another technique available in the iNNvestigate library.heatmap.pyand the other heatmap scripts to overlay spatial and temporal inputs with relevance heatmaps, either for single samples or averaged.cut_agarose.pywas used to remove experimental artifacts from the videosevaluate_probs.ipynb,get_temporal_stats.ipynb,get_training_curve.ipynb, andpreprocess_get_figure.ipynbare the jupyter notebook we used to create some of the figures of the relevance analysis and of preprocessing.
The best CNN weights we obtained can be found here (after removing artifacts in the data), so you could try running analyses without training the CNN again.
All scripts use Python 3. They require the following modules with versions: NumPy 1.16.4, Matplotlib 3.1.1, h5py 2.9.0, tqdm 4.32.2, OpenCV 4.1.0.25, scikit-learn 0.21.2, PyTorch 1.1.0, TensorFlow 1.14.0, Keras 2.2.4, iNNvestigate 1.0.8
File paths inside scripts have to be adapted to the local setup. We marked them as TODOs.
In many scripts we used a debug-flag which can be switched on to receive more informative output.
Some further explanations to the setup:
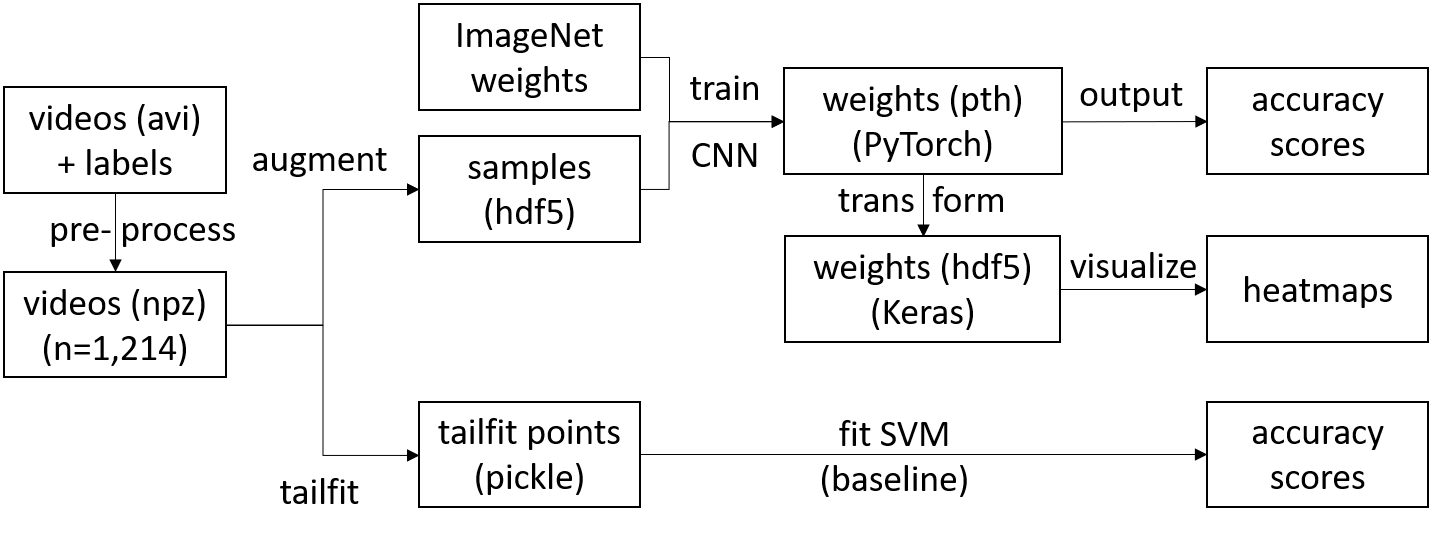 Project pipeline: The pipeline starts with videos in avi format and ends with CNN and SVM accuracy scores, as well as one heatmap per (augmented) sample
Project pipeline: The pipeline starts with videos in avi format and ends with CNN and SVM accuracy scores, as well as one heatmap per (augmented) sample
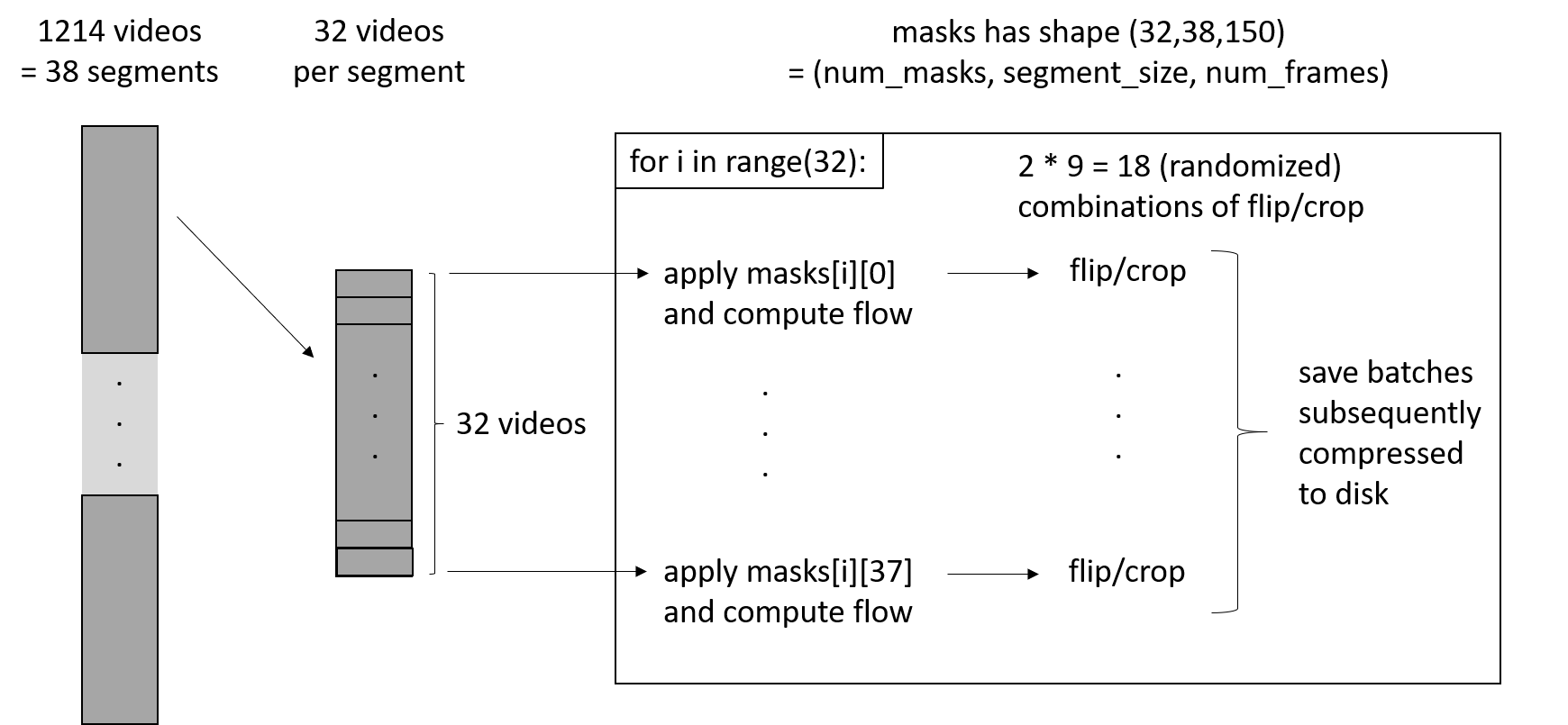 Augmentation procedure: The augmentation procedure includes flow-computation/subsampling, flipping, and cropping
Augmentation procedure: The augmentation procedure includes flow-computation/subsampling, flipping, and cropping
The files in the cnn-folder are originally based on code from the course MLP 2018/2019 at The University of Edinburgh.