连接平台的连接器下包含触发事件和执行动作,分别用来触发数据流和操作或接收数据流。连接平台目前最常用的是固定出入参的接口或数据事件的创建编辑功能。但是,当遇到出入参是随着系统配置变化的时候,执行动作和触发事件通过固定出入参无法适配。
当系统配置发生变化时,执行动作和触发事件也会随着配置变化而变化(例如:MySQL调整了表,表的名字、字段会发生变化,因此操作某个表的执行动作或触发事件的字段也应该会变化),这种情况,需要通过使用集成网关来将系统深度集成到连接平台。
- 集成元素
通过网关进行集成,提供给钉钉连接平台进行调用的一类概念的简称。我们可以将接口API、数据表、搭建出的表单等作为集成元素。
- 类目
是对集成元素进行分类的一类概念的简称。一般说来数据表的集成,是先通过数据表是存放在数据库下的,因此归类上将数据表分类到数据库下 我们使用类目配置项,来进行筛选,在类目都被确定后,可以根据类目的配置选择出集成元素的列表。
- 额外属性
钉钉连接平台对注册的触发器或执行动作都提供额外属性配置(key-value形式),通过这些配置,开发者可以根据不同配置来控制集成元素被调用时的不同行为
本项目是一个集成型连接器开发的实践样例,它提供了将MySQL数据库表集成到连接平台进行各种操作(增、删、改、查、搜索)的连接能力。
效果预览:
- 调试:
todo
- 实际使用:
todo
- 阿里云ECS或其它支持Java应用部署的环境 —— 用于部署应用。
- 阿里云RDS或自建MySQL服务 —— 用于将MySQL集成到连接平台。
- 公网IP —— 用于将应用提供的接口暴露到公网,供钉钉连接平台调用。
- Java 1.8+
- spring-boot系列
- spring-boot-starter-jdbc 数据库操作
- spring-boot-starter-web HTTP框架
- druid-spring-boot-starter 数据库连接池
- mysql-connector-java MySQL数据库驱动
代码实现设计
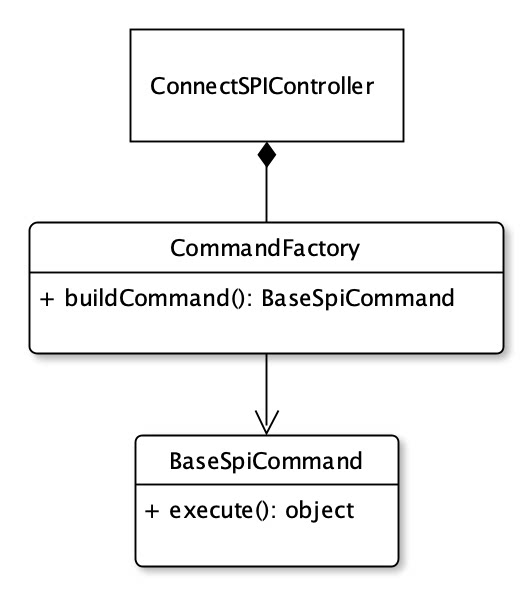
实现比较简单,我们通过controller接收来自钉钉连接平台的SPI指令,通过CommandFactory得到可执行的SPI命令实例,将命令执行后的结果返回即可
我们需要构建一个对外暴露的HTTP接口,用于接收连接平台调用SPI的指令请求
- 指令是以HTTP POST的方法,通过Body传入的,Body的内容格式为Json,是一个对象格式
- SPI只会调用一个HTTP路径
/**
* 说明:接收指令
*
* @author donghuai.zjj
* @date 2022/12/05
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/connect/v1/spi")
public class ConnectSpiController {
private final CommandFactory commandFactory;
@Autowired
public ConnectSpiController(CommandFactory commandFactory) {
this.commandFactory = commandFactory;
}
/**
* SPI指令接收接口
*
* @param requestBody 指令的请求体
* @return 指令的执行结果
*/
@PostMapping
public SpiResult<?> onCommand(@RequestBody JSONObject requestBody) {
BaseSpiCommand<?> spiCommand = commandFactory.buildCommand(requestBody);
return spiCommand.execute();
}
}我们通过一个指令工厂,将不同的SPI调用指令请求转换为可执行的指令。
PS: 配置完成后,我们可以先启动应用,将应用暴露到公网上
注意:这两个参数是普通执行动作和触发事件才会使用到的,如果纯粹使用集成网关集成,这两个值虽然要求必填但不会用到,我这里随便填了两个值。
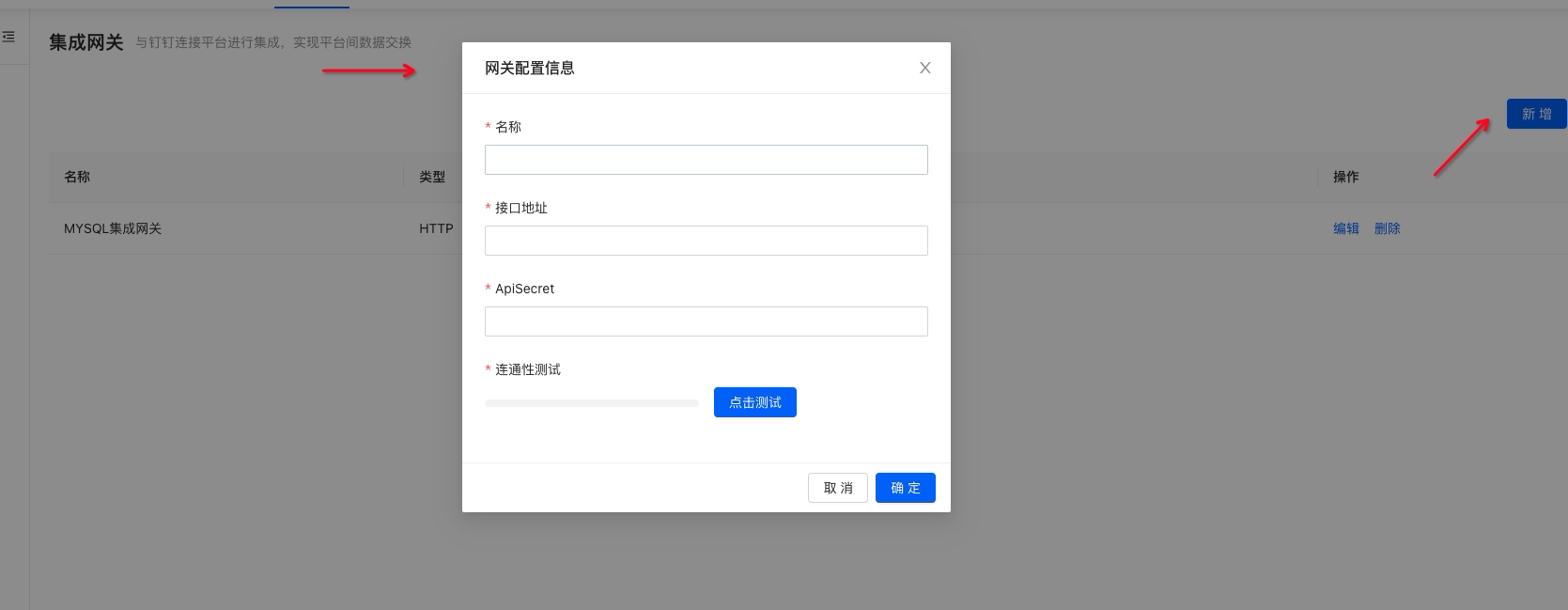
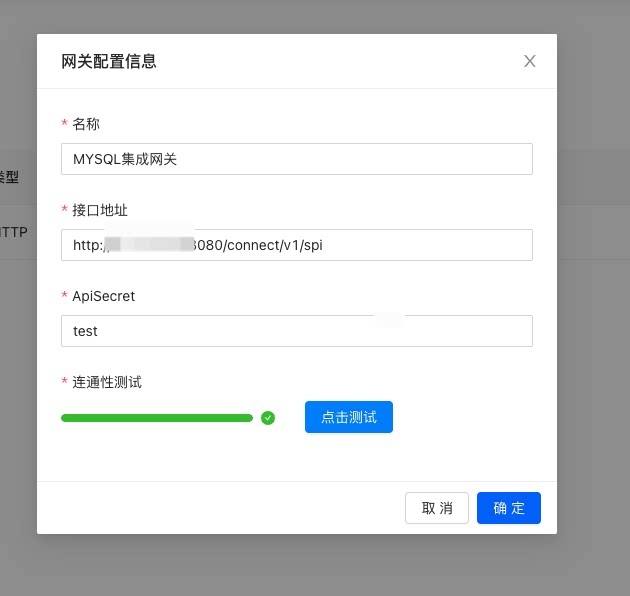
- 第二步:将暴露的SPI接收的接口作为集成网关注册进去
PS: ApiSecret是网关通信使用使用的加密验签密钥,用来保障请求发起是由钉钉连接平台发起的。
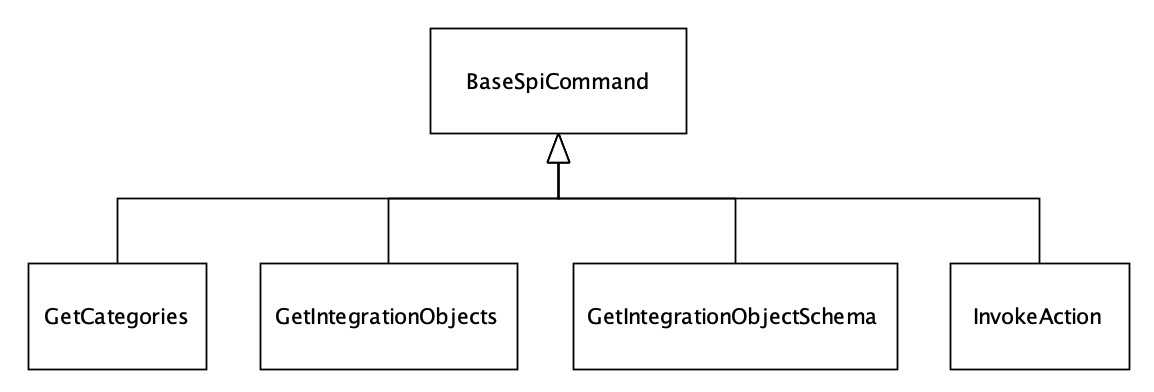
SPI的指令分为类目查询、集成元素查询、集成元素出入参详情获取、执行动作调用集成元素四个,分别可以由不同的触发事件和执行动作发起。
/**
* 说明:指令工场
*
* @author donghuai.zjj
* @date 2022/12/05
*/
@Component
public class CommandFactory implements InitializingBean {
/**
* 指令名与指令实体类的对应MAP配置
*/
private Map<String, Class<? extends BaseSpiCommand<?>>> commandMap = Collections.emptyMap();
/**
* 注入Spring Bean到指令中的处理器
*/
private final AutowireCapableBeanFactory autowireCapableBeanFactory;
public CommandFactory(@Autowired AutowireCapableBeanFactory autowireCapableBeanFactory) {
this.autowireCapableBeanFactory = autowireCapableBeanFactory;
}
/**
* 将接口入参转换为实际要执行的SPI指令
*
* @param requestBody 入参
* @return 可执行SPI指令
*/
public BaseSpiCommand<?> buildCommand(JSONObject requestBody) {
String commandName = requestBody.getString("requestBody");
// 获取指令实例
Class<? extends BaseSpiCommand<?>> commandType = Optional.ofNullable(commandMap.get(commandName))
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("unknown requestBody[" + commandName + "], onlySupport" + JSON.toJSONString(commandMap.keySet())));
// JSON转换为指令数据
BaseSpiCommand<?> spiCommand = requestBody.toJavaObject(commandType);
// 注入依赖
autowireCapableBeanFactory.autowireBean(spiCommand);
return spiCommand;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// 包扫描加载各类SPI指令实现
Reflections reflections = new Reflections(new ConfigurationBuilder()
.forPackages("com.dingtalk.open.example")
.addScanners(Scanners.SubTypes));
//noinspection rawtypes
Set<Class<? extends BaseSpiCommand>> commandClasses = reflections.getSubTypesOf(BaseSpiCommand.class);
Map<String, Class<? extends BaseSpiCommand<?>>> commandMap = new HashMap<>(commandClasses.size());
//noinspection rawtypes
for (Class<? extends BaseSpiCommand> commandClass : commandClasses) {
// 获取指名名对应的指令类,并注册路由关系MAP
String commandName = Optional.ofNullable(commandClass.getAnnotation(SpiCommand.class))
.map(SpiCommand::value)
.orElseGet(commandClass::getSimpleName);
if (commandMap.containsKey(commandName) && !commandMap.get(commandName).equals(commandClass)) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(String.format("duplicated command registered, commandName=%s, commandClasses=%s",
commandName, JSON.toJSONString(Arrays.asList(
commandMap.get(commandName).getName(),
commandClass.getName()
))));
}
//noinspection unchecked,CastCanBeRemovedNarrowingVariableType
commandMap.put(commandName, (Class<? extends BaseSpiCommand<?>>) commandClass);
}
this.commandMap = commandMap;
}
}
- 可以根据SPI调用的请求体中的command字段,得到指令的类型
- SPI指令由不同执行动作或触发事件发起,请求体中会包含几个字段标识是哪个执行动作或触发事件发起的指令
- corpId 指令发起的组织
- dingtalkIntegrationType 发起指令的是执行动作还是触发事件
- dingtalkIntegrationId 发起指令的执行动作或触发事件的唯一标识
- userId 指令发起的操作人(除了调用执行动作都会有该字段)
- props 指令发起执行动作或触发事件的属性配置
由于不同的执行动作,其执行的出入参根据其使用场景可能会有所不同,所以我们要区分执行动作的行为
- 可以通过硬编码关联执行动作的ID来绑定指令的行为
- 可以通过props配置,根据其中的配置项来绑定指令的行为
这里我们通过方式2来绑定指令的行为,MySQL我们要实现的执行动作的行为包括了:
- 插入数据到指定库下的指定表,对应action定义为insert
- 更新指定库下指定表的一条数据,对应action定义为update
- 插入或者更新已存在的指定库下指定表的一条数据,对应action定义为upsert
- 根据主键获取指定库下指定表的一条数据,对应action定义为select
- 搜索指定库下指定表的一批数据最多100条,对应action定义为selectList
- 根据主键删除指定库下指定表的一条数据,对应action定义为delete
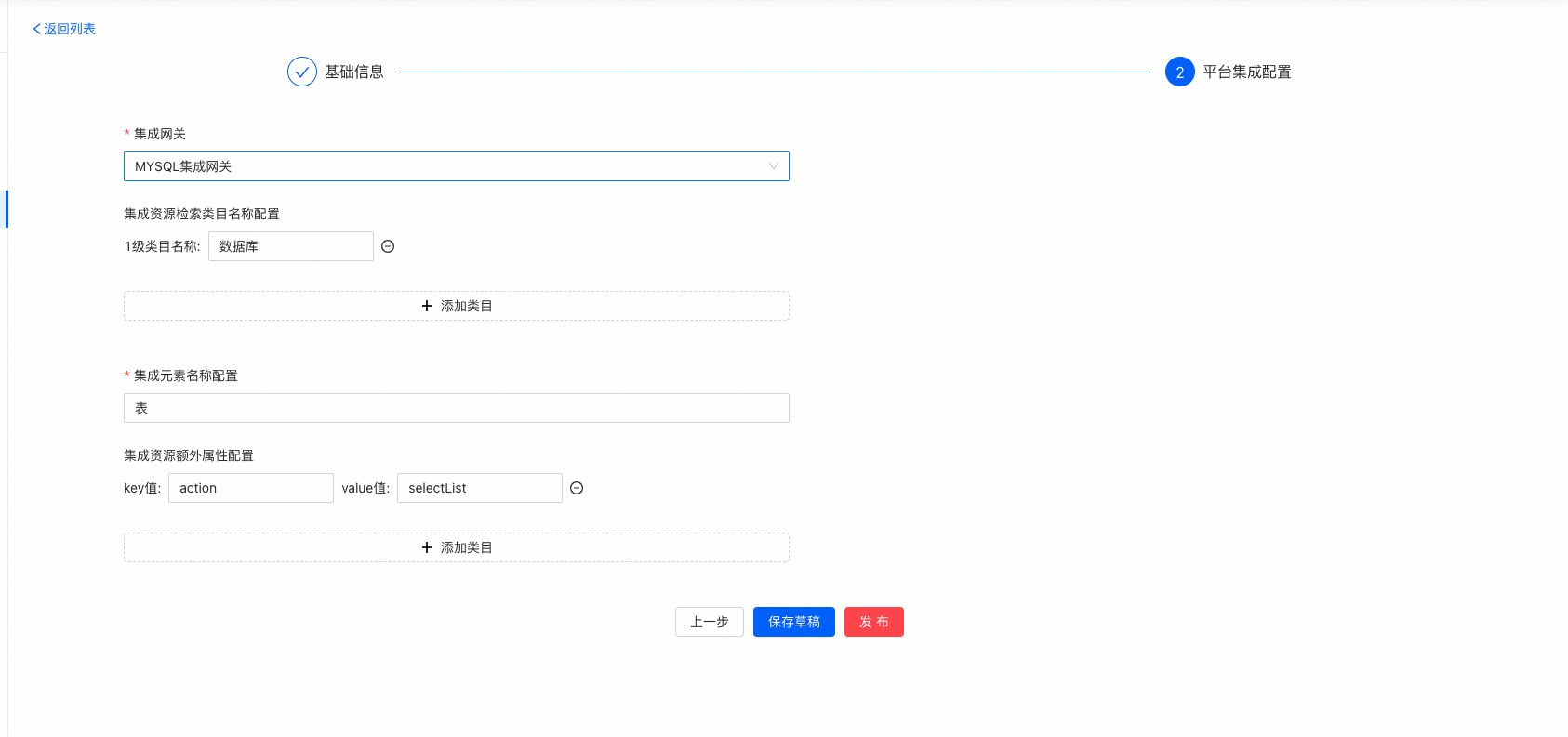
在使用集成类型执行动作时,需要选择到具体操作哪张表,但是确定一个表,需要先知道有哪些数据库,再根据数据库存得到有哪些表,最终选择到表后进行操作。因此对于这个场景MySQL库表集成,数据库就是MySQL表的一个集成类目。而数据表则是MySQL表的集成元素。
@SpiCommand("getCategories")
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)
public class GetCategories extends BaseSpiCommand<GetCategoriesResponse> {
public static final int SELECT_DATABASE_LIST = 0;
/**
* 当前级联查询的值
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private List<Category> categories;
/**
* 关键字
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private String keywords;
/**
* 当前级联的级别
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private Integer currentLevel;
/**
* 集成的类型
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private String dingtalkIntegrationType;
/**
* 集成钉钉的连接标识
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private String dingtalkIntegrationId;
/**
* 操作人
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private String userId;
@Resource
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
@Override
public SpiResult<GetCategoriesResponse> execute() {
int level = CollectionUtils.size(categories);
if (level == SELECT_DATABASE_LIST) {
// 第一级是查数据库列表
return selectDatabaseList();
}
SpiResult<GetCategoriesResponse> result = new SpiResult<>();
result.setSuccess(false);
return result;
}
private SpiResult<GetCategoriesResponse> selectDatabaseList() {
List<String> databaseNames = namedParameterJdbcTemplate.queryForList(
"SELECT SCHEMA_NAME FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.SCHEMATA",
Collections.emptyMap(), String.class);
List<Category> records = databaseNames.stream().map(databaseName -> {
Category category = new Category();
category.setName(databaseName);
category.setValue(databaseName);
return category;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
GetCategoriesResponse response = new GetCategoriesResponse();
response.setRecords(records);
response.setLevel(CollectionUtils.size(categories) + 1);
return SpiResult.success(response);
}
}在类目选项确定(选择数据库)后,我们需要根据选项返回集成元素(MySQL表)列表供交互界面进行选择。
@SpiCommand("getIntegrationObjects")
public class GetIntegrationObjects extends BaseSpiCommand<GetIntegrationObjectsResponse> {
public static final int SELECT_TABLE_LIST_IN_DATABASE = 1;
/**
* 当前级联查询的值
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private List<Category> categories;
/**
* 关键字
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private String keywords;
/**
* 当前级联的级别
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private Integer currentLevel;
/**
* 集成的类型
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private String dingtalkIntegrationType;
/**
* 集成钉钉的连接标识
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private String dingtalkIntegrationId;
/**
* 操作人
*/
@Getter
@Setter
private String userId;
@Resource
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
@Override
public SpiResult<GetIntegrationObjectsResponse> execute() {
int level = CollectionUtils.size(categories);
if (level == SELECT_TABLE_LIST_IN_DATABASE) {// 第二级是查询表列表
return selectTableList();
}
SpiResult<GetIntegrationObjectsResponse> result = new SpiResult<>();
result.setSuccess(false);
return result;
}
private SpiResult<GetIntegrationObjectsResponse> selectTableList() {
String databaseName = ListUtils.emptyIfNull(categories).stream().findFirst()
.map(Category::getValue)
.orElse(null);
List<String> tableNames = namedParameterJdbcTemplate.queryForList(
"SELECT TABLE_NAME FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = :database",
Collections.singletonMap("database", databaseName), String.class);
List<Category> records = tableNames.stream().map(tableName -> {
Category category = new Category();
category.setName(tableName);
category.setValue("mysql://" + getCorpId() + "/" + databaseName + "?table=" + tableName);
return category;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
GetIntegrationObjectsResponse response = new GetIntegrationObjectsResponse();
response.setRecords(records);
response.setLevel(CollectionUtils.size(categories) + 1);
return SpiResult.success(response);
}
}SPI指令中会返回交互中选择的数据库信息,我们需要返回数据库下对应的表的列表。
每个张表作为集成元素,我们都需要给它定义一个唯一标识,这里我们使用URI风格的标识,将组织、数据库、表的信息组合进去,格式为 mysql://{组织}/{数据库}?table={表},这个唯一标识在每次处理集成元素相关的SPI时都会传入,我们需要将这个标识重新解析出来得到其中组合信息。
不同执行动作的行为对应的出参入参信息是不同的
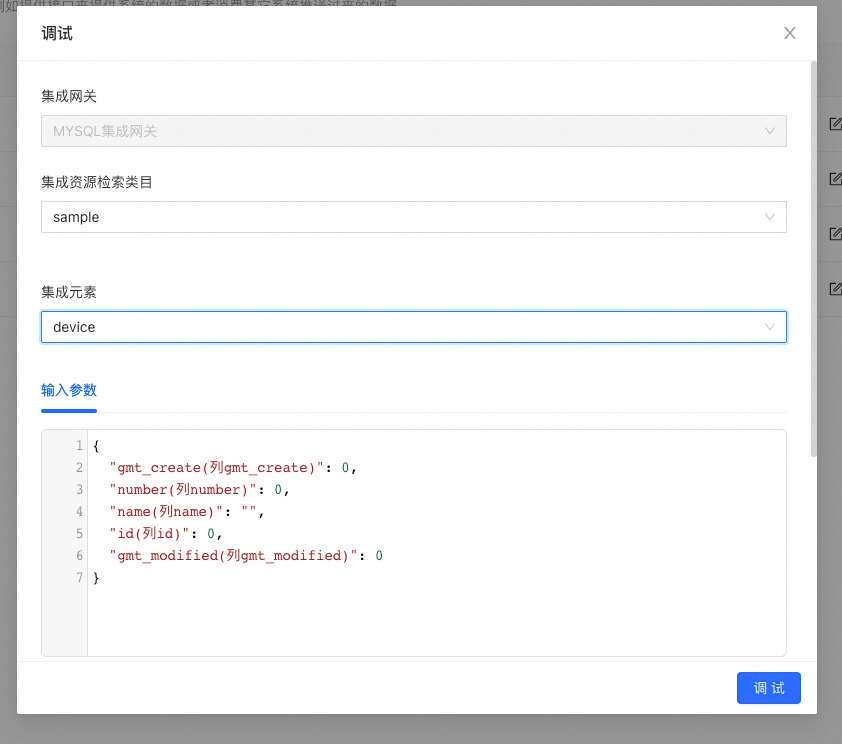
- insert\upsert将表数据结构作为入参结构,出参为写入记录数
- update将表数据非主键部分作为数据结构,将主键部分作为条件结构,入参结构由数据结构和条件结构组成,出参为更新记录数
- delete将主键部分作为入参结构
- select将主键部分作为入参结构
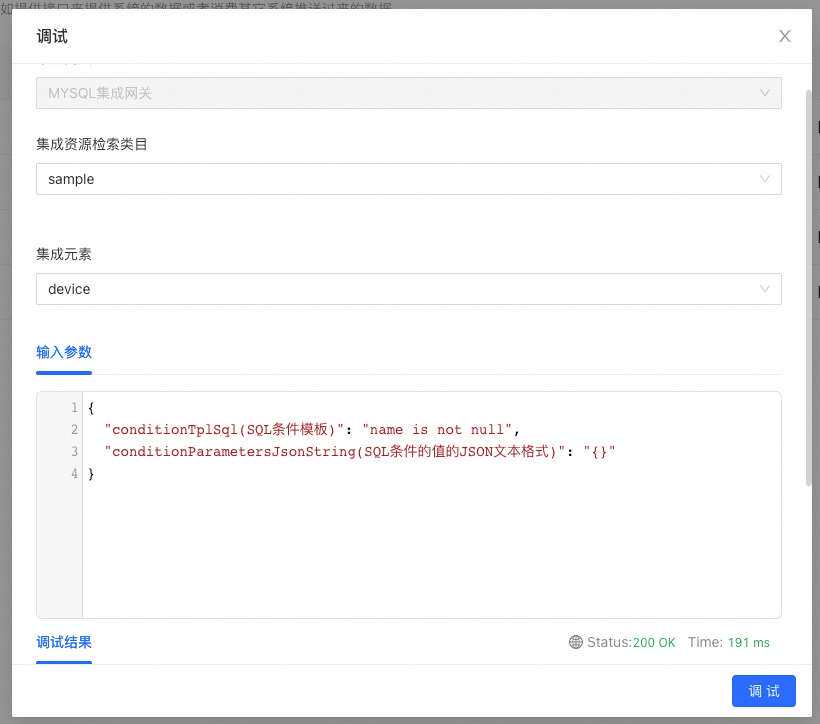
- selectList定义入参结构由条件SQL模板与入参JsonString为数据结构
具体实现可以参考本项目代码
@SpiCommand("getIntegrationObjectSchema")
public class GetIntegrationObjectSchema extends BaseSpiCommand<GetIntegrationObjectSchemaResponse> {
public static final String PROP_VALUE_ACTION = "action";
public static final String PROP_VALUE_TRIGGER = "trigger";
/**
* 当前请求Schema的连接器操作类型(触发器/执行动作)
*/
@Setter
@Getter
private String dingtalkIntegrationType;
/**
* 将MYSQL中的数据表作为集成元素时,表示MYSQL表的唯一标识, 格式为 mysql://{corpId}/{database}?table={tableName}
*/
@Setter
@Getter
private String integrationObject;
@Resource
private Map<String, ActionSchemaProvider> beanNameActionSchemaProviderMap;
@Resource
private MysqlDatabaseHelper mysqlDatabaseHelper;
@Override
public SpiResult<GetIntegrationObjectSchemaResponse> execute() {
// 这里根据在开放平台连接器配置中的额外属性,来定义不同属性的执行动作/触发器的数据结构
Map<String, String> props = getProps();
URI uri = URI.create(integrationObject);
UriComponentsBuilder uriComponentsBuilder = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUri(uri);
UriComponents uriComponents = uriComponentsBuilder.build();
String databaseName = uriComponents.getPathSegments().stream().findFirst().orElse(null);
String tableName = uriComponents.getQueryParams().getFirst("table");
// 当集请求Schema的操作类型为执行动作时
if (PROP_VALUE_ACTION.equals(dingtalkIntegrationType)) {
String action = MapUtils.getString(props, PROP_VALUE_ACTION);
String beanName = StringUtils.join(action, "SchemaProvider");
ActionSchemaProvider actionSchemaProvider = beanNameActionSchemaProviderMap.get(beanName);
if (actionSchemaProvider == null) {
return SpiResult.fail("不支持的操作类型");
}
try {
return SpiResult.success(actionSchemaProvider.getSchema(getCorpId(), databaseName, tableName));
} catch (SpiRuntimeException e) {
return SpiResult.fail(e.getErrorCode(), e.getErrorMsg());
}
} else if (PROP_VALUE_TRIGGER.equals(dingtalkIntegrationType)) {
// 无论增删改查,都是使用一个事件出参模型,即数据完整实例
try {
return getTriggerSchema(getCorpId(), databaseName, tableName);
} catch (SpiRuntimeException e) {
return SpiResult.fail(e.getErrorCode(), e.getErrorMsg());
}
}
return SpiResult.fail("不支持的操作类型");
}
private SpiResult<GetIntegrationObjectSchemaResponse> getTriggerSchema(String corpId, String databaseName, String tableName) throws SpiRuntimeException {
Table tableInfo = Optional.ofNullable(mysqlDatabaseHelper.getTableInfo(databaseName, tableName))
.orElseThrow(() -> new SpiRuntimeException("integration_object_not_exists", "数据表不存在"));
GetIntegrationObjectSchemaResponse schemaResponse = new GetIntegrationObjectSchemaResponse();
schemaResponse.setIntegrationObject("mysql://" + corpId + "/" + databaseName + "?table=" + tableName);
schemaResponse.setOutputSchema(tableInfo.toJsonSchema());
schemaResponse.setName(tableName);
return SpiResult.success(schemaResponse);
}
}我们通过策略模式,构建不同执行动作的出入参数据 例如当执行动作的自定义属性项action为insert时,会通过调用名称为insertActionSchemaProvider的Bean得到插入数据表所需要的出入参信息
@SpiCommand("invokeAction")
public class InvokeAction extends BaseSpiCommand<InvokeActionResponse> {
/**
* 当前请求Schema的连接器操作类型(触发器/执行动作)
*/
@Setter
@Getter
private String dingtalkIntegrationType;
/**
* 将MYSQL中的数据表作为集成元素时,表示MYSQL表的唯一标识, 格式为 mysql://{corpId}/{database}?table={tableName}
*/
@Setter
@Getter
private String integrationObject;
@Setter
@Getter
private Map<String, Object> input;
@Resource
private Map<String, ActionExecutor> beanNameActionExecutorMap;
@Override
public SpiResult<InvokeActionResponse> execute() {
// 这里根据在开放平台连接器配置中的额外属性,来定义不同属性的执行动作/触发器的数据结构
Map<String, String> props = getProps();
URI uri = URI.create(integrationObject);
UriComponentsBuilder uriComponentsBuilder = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUri(uri);
UriComponents uriComponents = uriComponentsBuilder.build();
String databaseName = uriComponents.getPathSegments().stream().findFirst().orElse(null);
String tableName = uriComponents.getQueryParams().getFirst("table");
// 当集请求Schema的操作类型为执行动作时
if ("action".equals(dingtalkIntegrationType)) {
String action = MapUtils.getString(props, "action");
String beanName = StringUtils.join(action, "ActionExecutor");
ActionExecutor actionExecutor = beanNameActionExecutorMap.get(beanName);
if (actionExecutor == null) {
return SpiResult.fail("不支持的操作类型");
}
try {
Object result = actionExecutor.execute(getCorpId(), databaseName, tableName, new JSONObject(input));
InvokeActionResponse response = new InvokeActionResponse();
response.setData(result);
response.setIntegrationObject(uri.toString());
return SpiResult.success(response);
} catch (SpiRuntimeException e) {
return SpiResult.fail(e.getErrorCode(), e.getErrorMsg());
}
}
return SpiResult.fail("不支持的操作类型");
}
}同样通过策略模式,执行不同的表操作.
例如当执行动作的自定义属性项action为insert时,会通过调用名称为insertActionExecutor的Bean完成插入数据到指定表的操作。
这里需要注意的是,执行动作的入参是按照上一步的入参模型返回的,因此执行操作后,要按照上一步给出的出参模型返回结果。
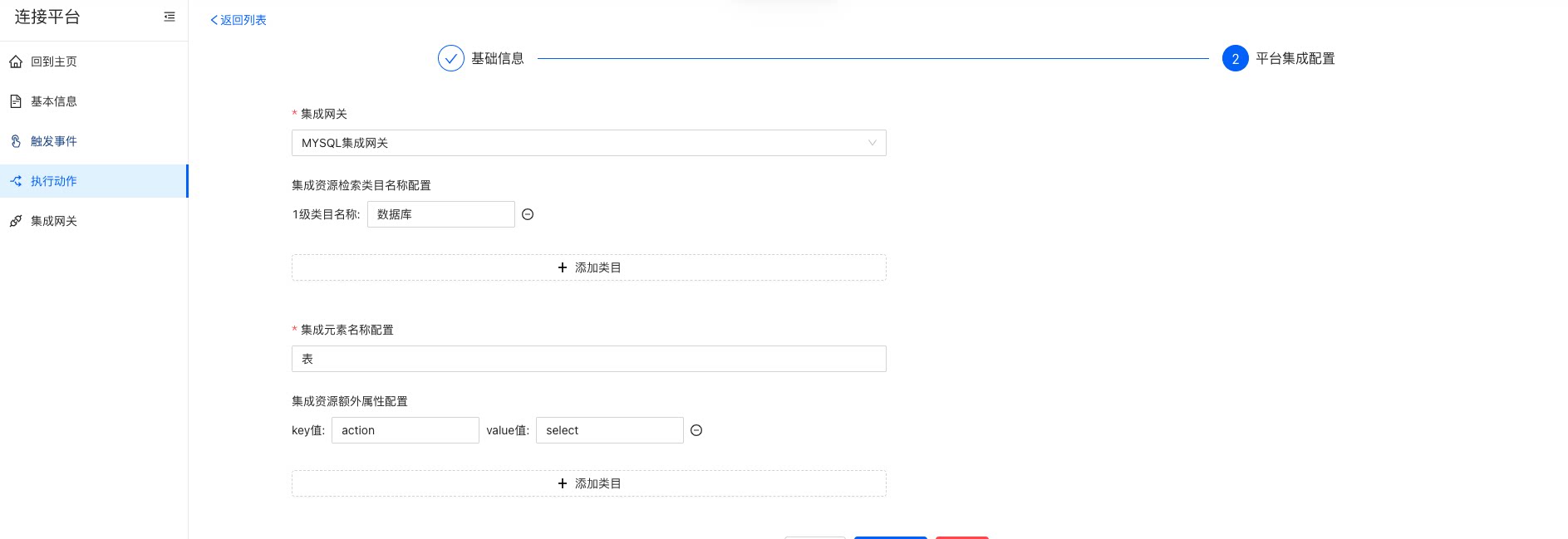
- 第一步:新建执行动作
- 第二步:配置类目、集成元素
因为选择到MySQL的表,需要先确定表在哪个数据库中,因此将数据库作为类目进行配置。 因为我们集成的是MySQL的数据表,因此我们的集成元素的名称就是表。 - 第三步:配置自定义属性
因为我们是通过自定义属性action来定义执行动作调用集成元素的行为的,我们这里配置一个查询行为,配置action对应的值为select。
顺序
- 启动数据库(如果是云数据库可以不用)
- 启动应用并将接口发布到外网
- 使用连接平台调试
java -jar mysql-connector.jar --spring.datasource.url={你的数据库链接地址} --spring.datasource.username={你的数据库用户名} --spring.datasource.password={你的数据库密码}